Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 5-9 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


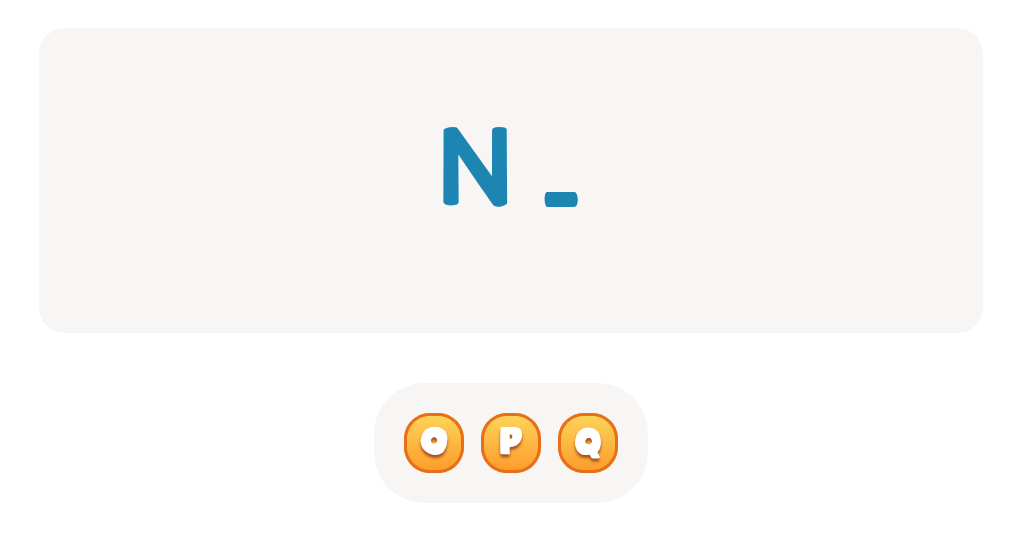
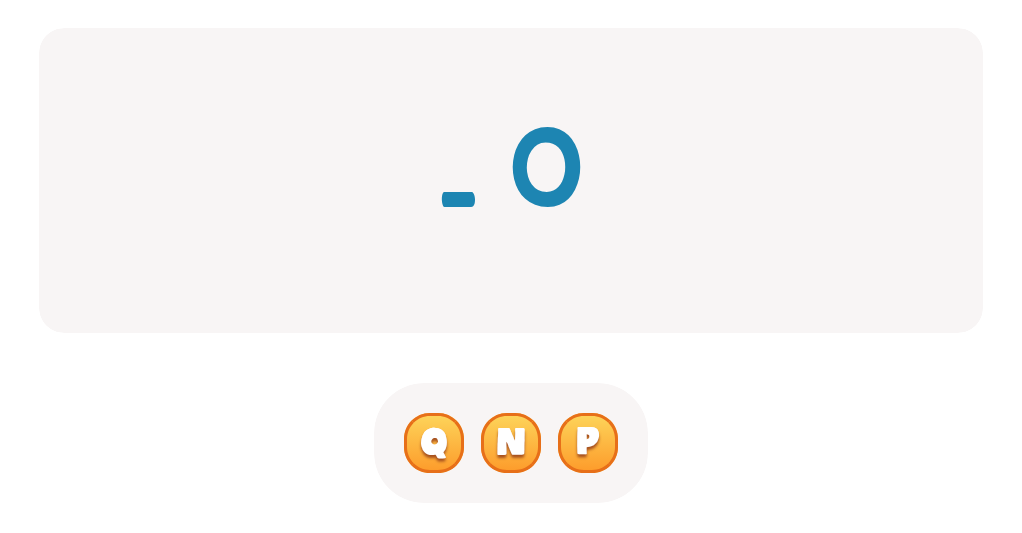
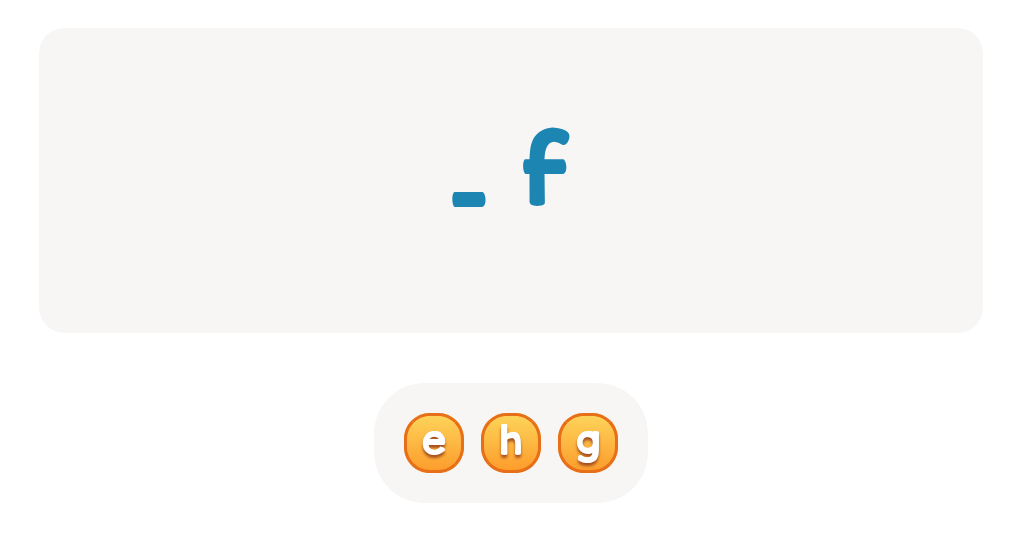
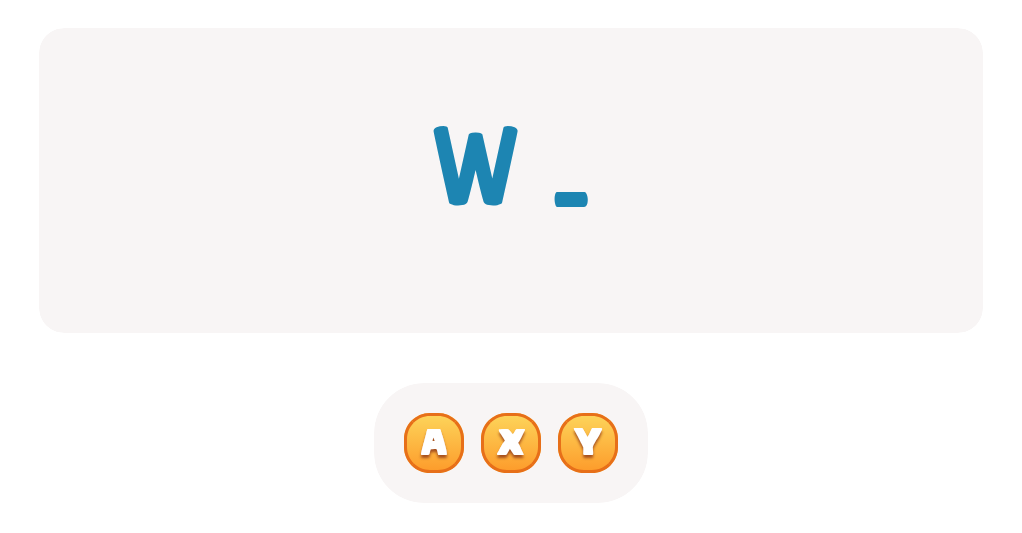
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize handwriting practice of ABC letters for children aged 5-9 as it is fundamentally linked to their early cognitive and motor skill development. During these formative years, writing by hand hones fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination, crucial for daily tasks and academic success. Penmanship practice also aids in orthographic learning, reinforcing the visual recognition and correct formation of letters. This repetitive exercise builds muscle memory, making writing more automatic and fluent.
Furthermore, the process of handwriting fosters improved concentration and memory retention. Research suggests that the act of writing engages more cognitive processes than typing, enhancing learning and comprehension. For young learners, mastering the alphabet is the cornerstone of literacy, making it easier for them to read and spell more efficiently.
The developmental benefits extend beyond academics as well. Handwriting activities can boost a child's confidence and foster a sense of achievement. It also nurtures creativity and self-expression, essential components for emotional growth and social interaction.
Thus, integrating consistent handwriting practice into early education equips children with essential skills that support their overall intellectual and emotional development, setting a solid foundation for future learning and success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students