Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 5-9 - Page 7
149 filtered results
-
From - To
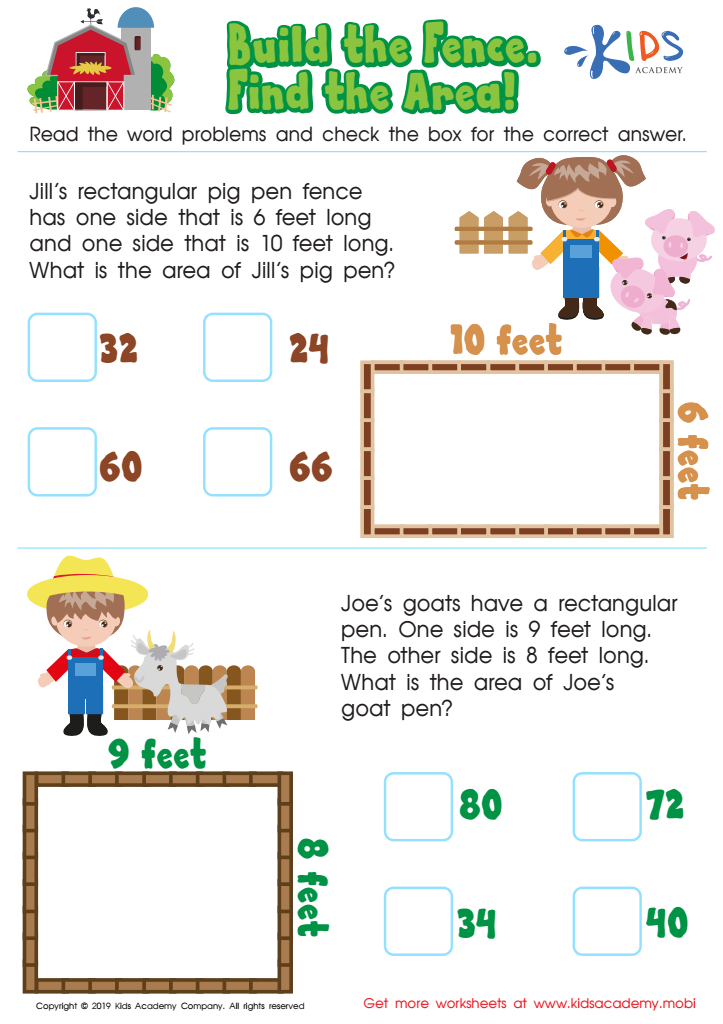

Build the Fence, Find the Area Worksheet
Problem-solving skills are essential for children aged 5-9 as they form the foundation for critical thinking and independent learning. At this age, children are naturally curious and full of questions, making it an ideal time to encourage problem-solving through activities like addition. Engaging in addition not only boosts their math skills but also enhances cognitive abilities such as reasoning, logic, and analytical thinking.
When parents and teachers prioritize problem-solving through addition, they teach children how to approach challenges systematically. This skill is transferable across all subjects and life situations, helping children learn to break down complex problems into manageable parts, consider various solutions, and select the best option.
Moreover, developing these skills at a young age fosters resilience. Children learn that mistakes are part of the learning process and that perseverance leads to success. This mindset is crucial for their overall emotional and social development.
Caregivers and educators can create a supportive environment that encourages exploration and hands-on learning, ultimately empowering children to become confident decision-makers. By nurturing problem-solving skills in addition, parents and teachers equip children with vital tools for academic achievement and life challenges.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students