Handwriting improvement Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-7
4 filtered results
-
From - To
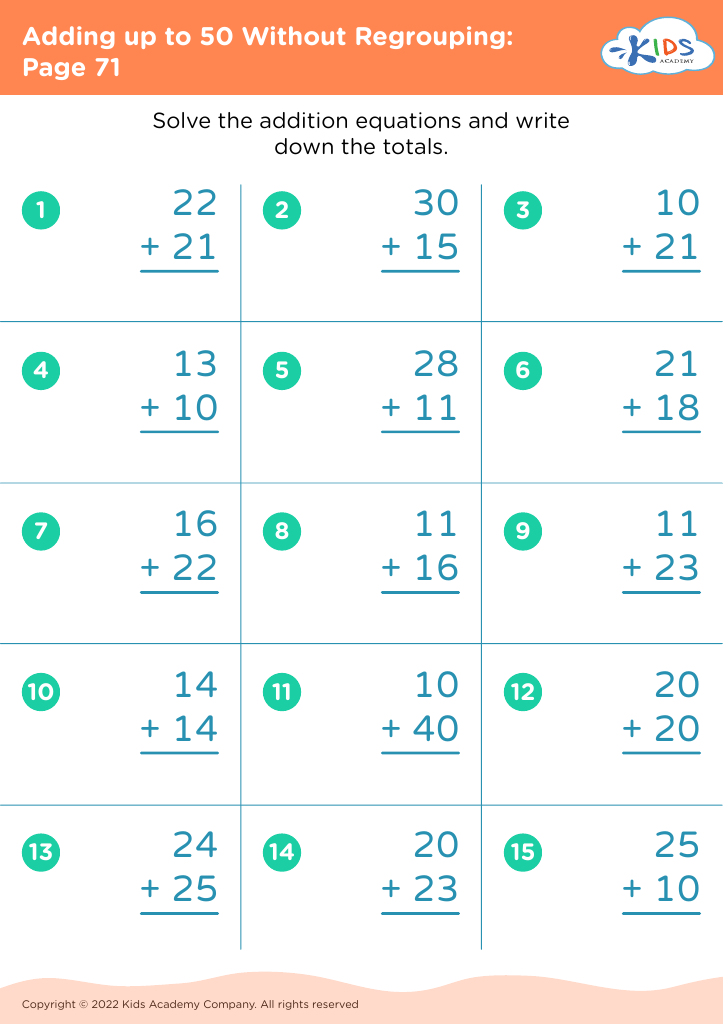
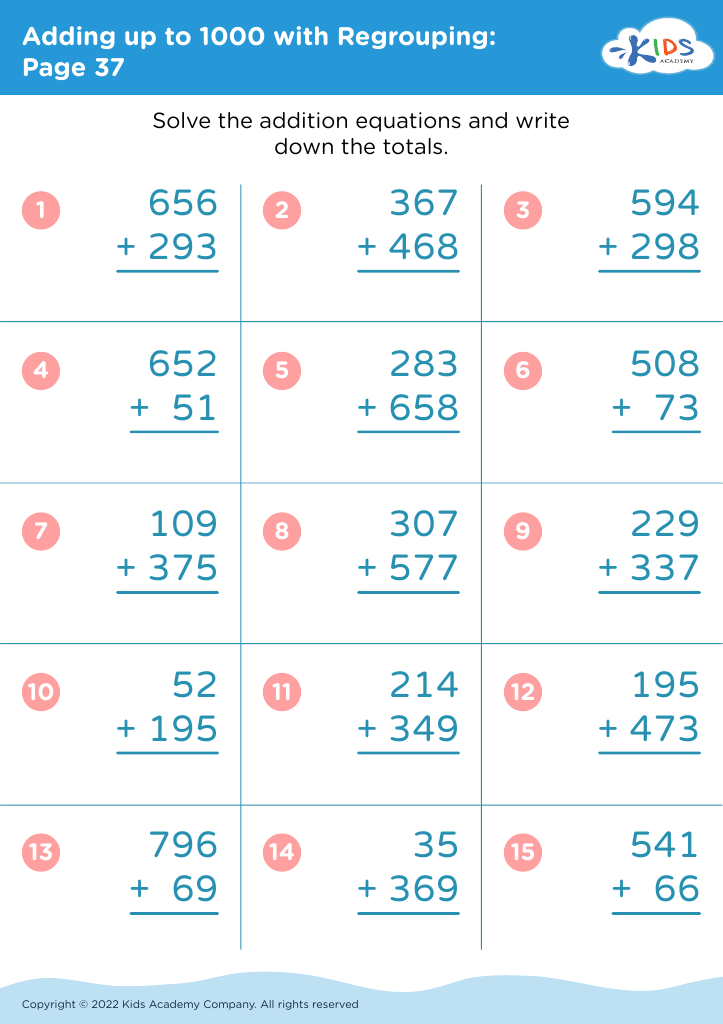
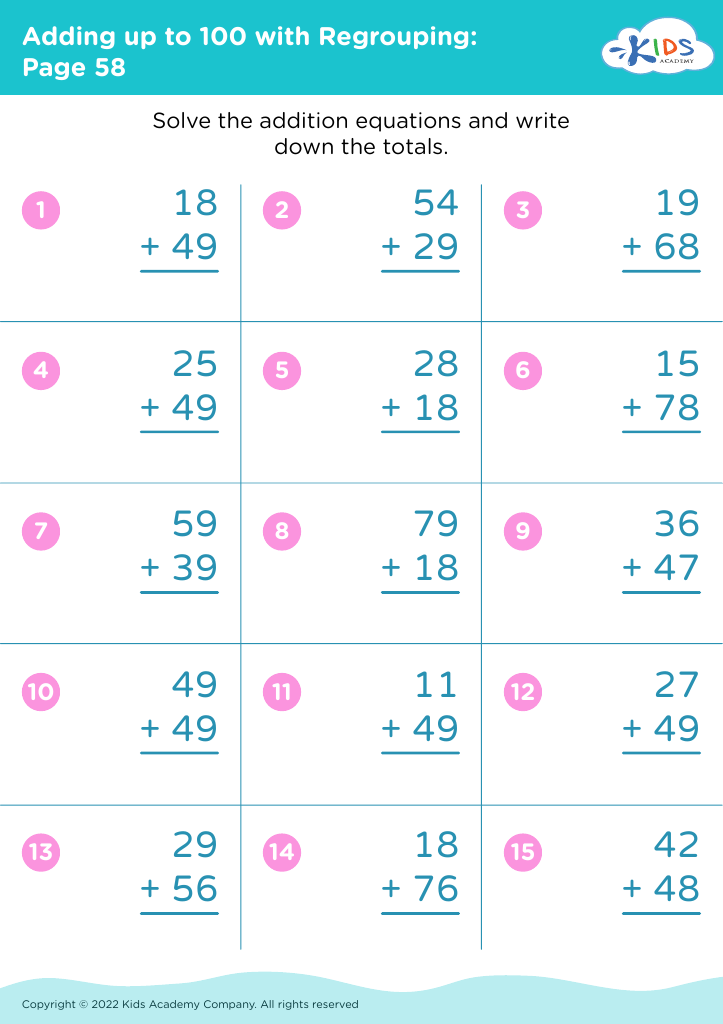
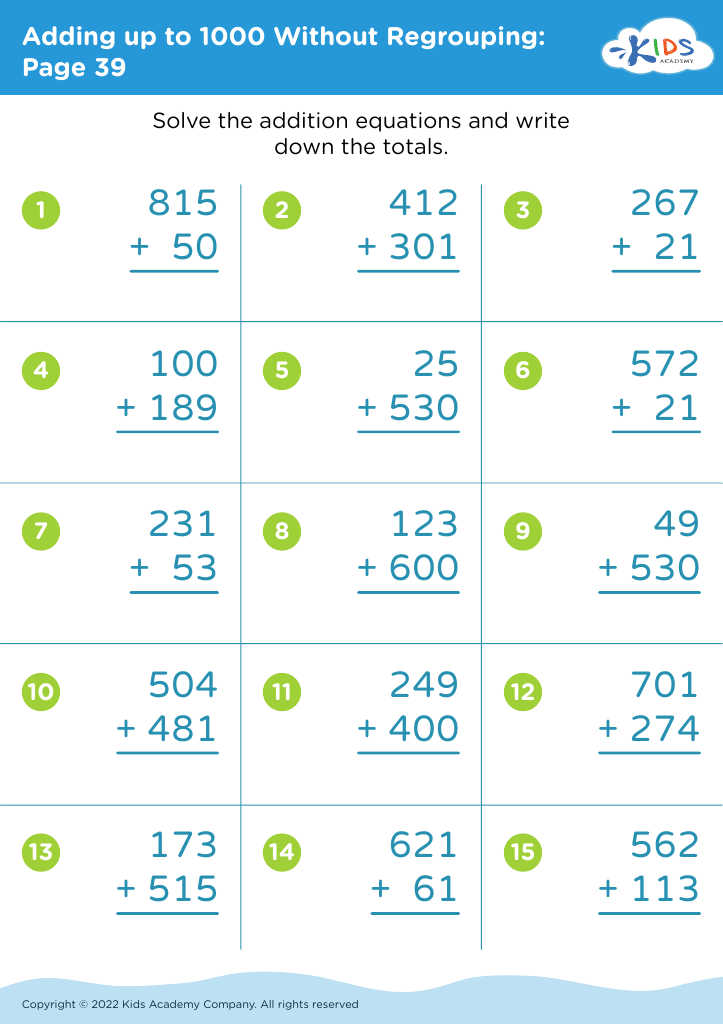
Enhance your child's handwriting and math skills with our Handwriting Improvement Addition Worksheets for ages 6-7. Combining crucial handwriting practice with foundational addition exercises, these worksheets offer a dual benefit. Children will trace and write numbers, improving their penmanship while solving engaging addition problems. Ideal for reinforcing classroom learning or as a supplementary home activity, our worksheets make mastering these essential skills fun and exciting. Tailored to fit the developmental needs of 6-7-year-olds, each worksheet invites young learners to confidently explore math concepts while honing their handwriting. The perfect resource for parents and teachers aiming to boost academic success!
Parents and teachers should prioritize handwriting improvement for children aged 6-7 because it lays the groundwork for their future academic success and personal development. During this developmental stage, children are refining their motor skills and muscle memory, which are critical for writing legibly and fluently. Well-developed handwriting ensures that students can efficiently record their thoughts and ideas, aiding in clearer communication and reducing frustration.
Handwriting practice enhances fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination, skills that are vital not only for writing but for various everyday tasks. It also aids in cognitive development. For instance, forming letters by hand is a multi-sensory activity that strengthens neural pathways, supporting memory retention and understanding. This cognitive engagement deepens learning and can improve reading and spelling skills.
Additionally, neat, readable handwriting can boost a child’s self-esteem. Poor handwriting often leaves children feeling self-conscious and reluctant to share their work, potentially hindering classroom participation and academic growth. By improving handwriting, students gain confidence in their abilities and tend to show greater interest and pride in their assignments.
Supporting children in mastering handwriting fosters a foundation of academic skills and positive self-image, giving them essential tools for succeeding inside and outside the classroom.