Observational skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
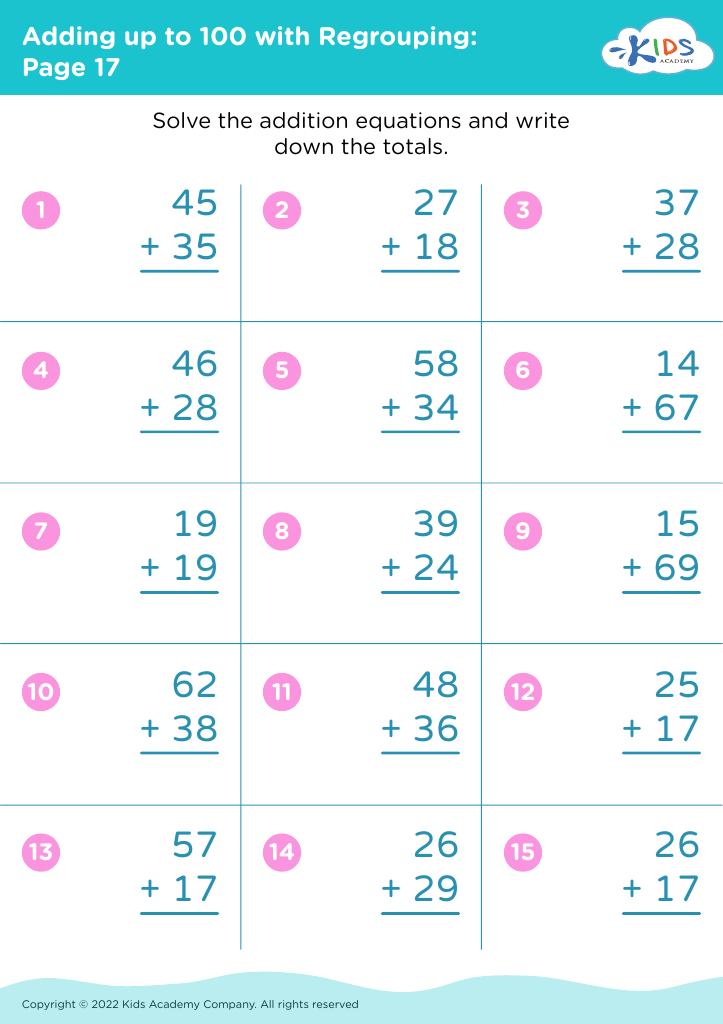
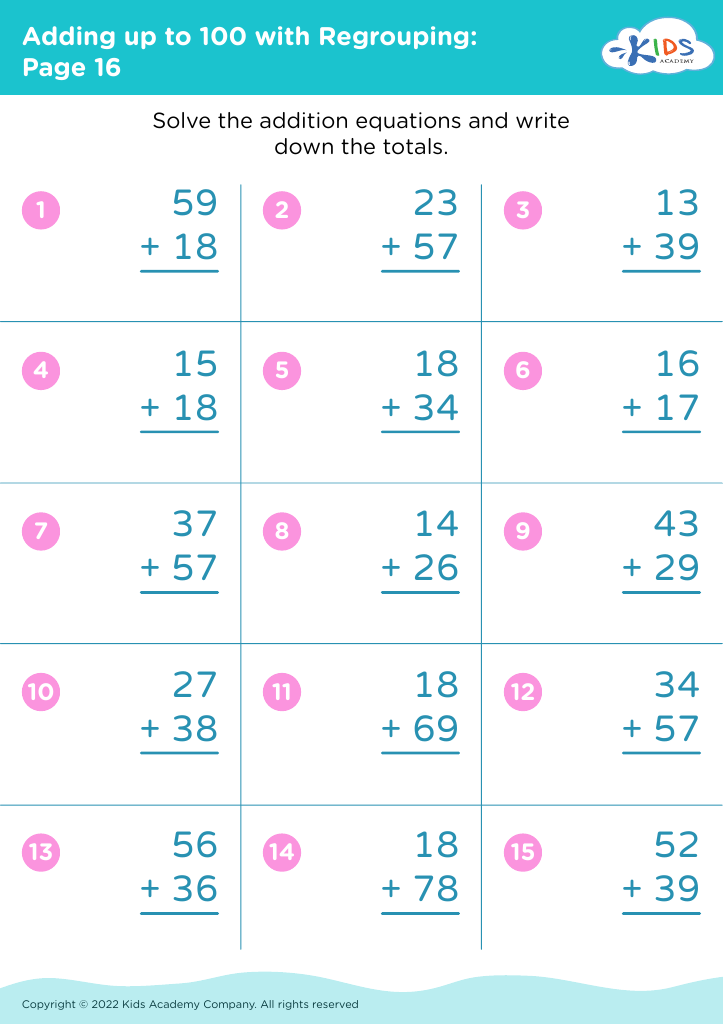
Boost your child's math prowess with our Observational Skills Addition Worksheets designed for ages 6-7. These engaging worksheets help young learners enhance their addition skills while fine-tuning their observational abilities. Each worksheet features vibrant illustrations and fun activities that challenge children to spot patterns, compare numbers, and solve puzzles. Perfect for early grade students, these resources promote critical thinking and attention to detail, making learning math a delightful adventure. Ideal for both classroom use and at-home practice, our worksheets offer a seamless blend of education and entertainment, paving the way for academic success.


Count in the School of Magic Worksheet
Observational skills addition for ages 6-7 is crucial for cognitive and social development. At this formative stage, children are naturally curious but need guidance to sharpen their focus and understanding of the world around them. Enhancing observational skills aids in improving attention to detail, critical thinking, and the ability to notice and interpret subtle cues in their environment.
For parents and teachers, fostering these skills is foundational. By encouraging close observation, children learn to analyze information before forming conclusions, an essential skill for academic success. For example, a child who can observe details in a story can better understand narratives and answer comprehension questions more accurately, bolstering literacy skills.
Moreover, observational skills extend beyond academics. They help children in social settings, making them more empathetic and understanding peers’ emotions through non-verbal cues like facial expressions and body language. This social awareness fosters healthier interpersonal interactions and builds emotional intelligence, which is invaluable throughout life.
Additionally, when kids practice attentive observation, they become more curious and engaged learners. This intrinsic motivation can lead to lifelong learning, a quality every parent and teacher desires. By prioritizing observational skills, parents and teachers lay the groundwork for well-rounded, perceptive, and resilient individuals.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students