Categorization skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 6-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's geometry understanding with our engaging Categorization Skills worksheets designed specifically for ages 6-7. These worksheets focus on helping young learners identify and categorize shapes, improving their critical thinking and organizational skills. Through fun exercises featuring various geometric forms, children will develop foundational skills in recognizing similarities and differences among shapes. Our user-friendly resources encourage independent practice while reinforcing essential math concepts in a playful and interactive way. Designed by educators, these worksheets align with age-appropriate standards, ensuring that every child receives the support they need to succeed. Start cultivating your child's geometric cognition today!
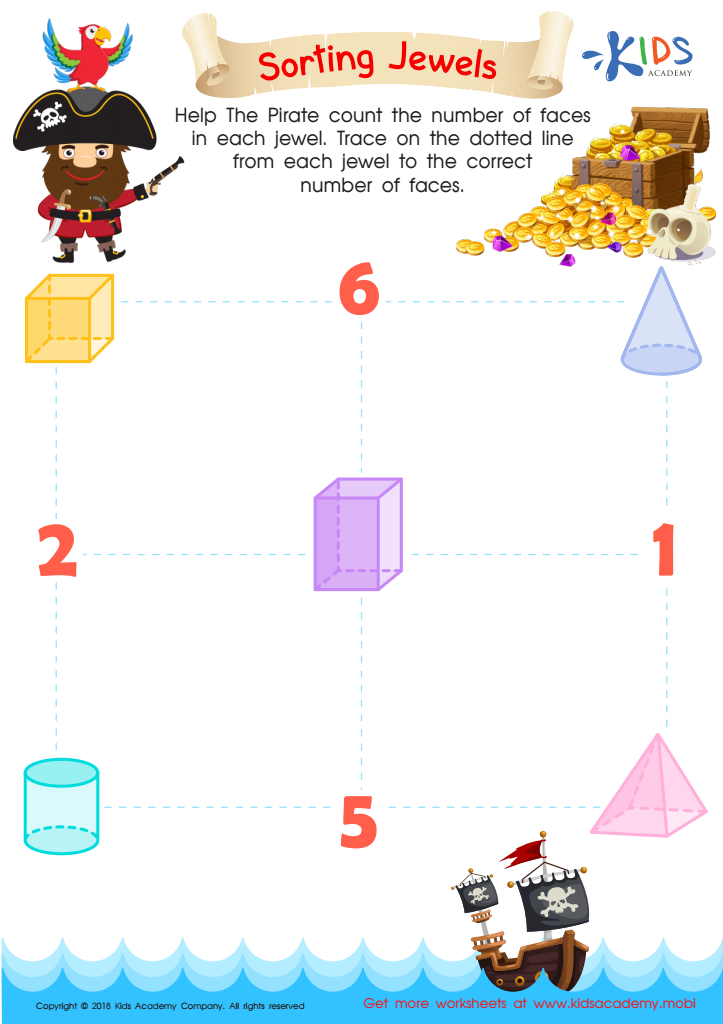

Sorting Jewels Worksheet
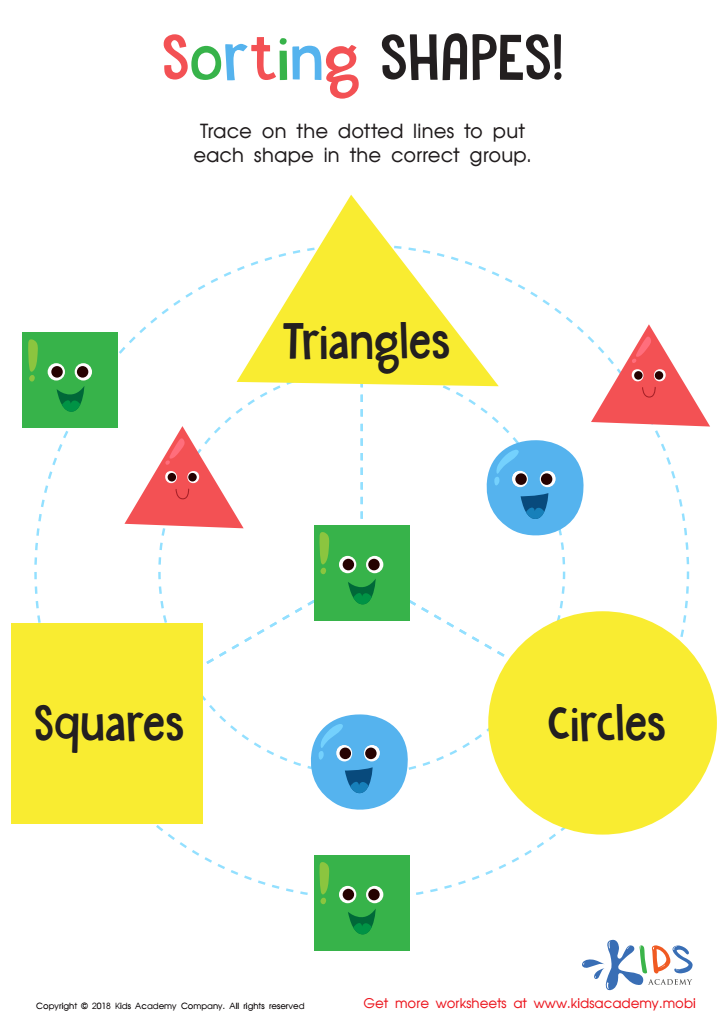

Sorting Shapes - Part 3 Worksheet
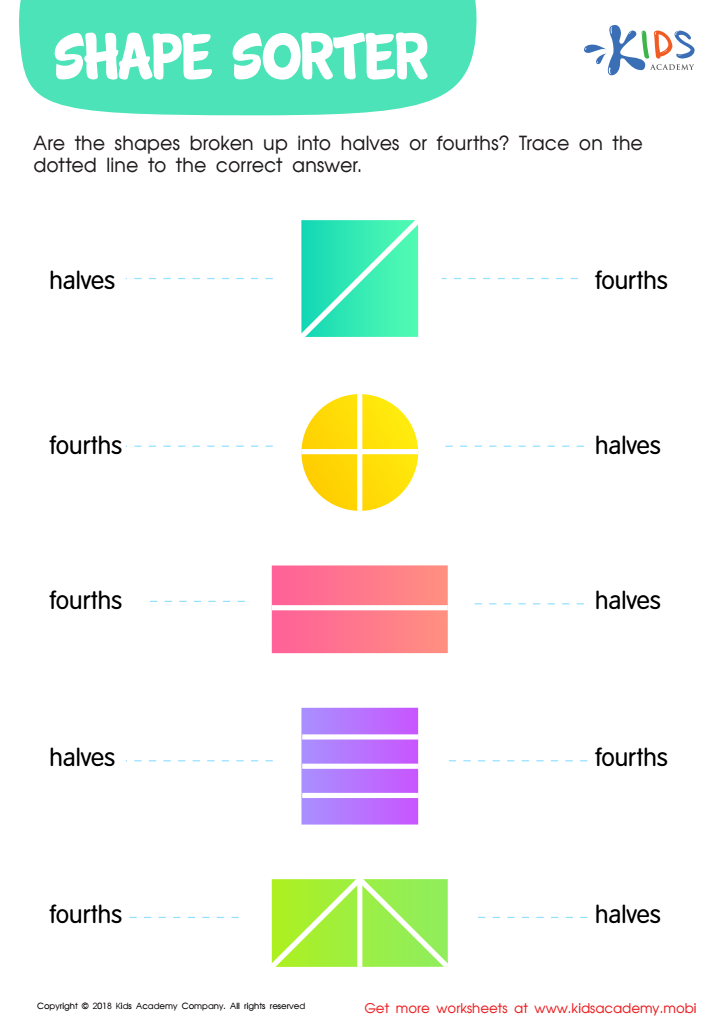

Shape Sorter Worksheet
Categorization skills in geometry are crucial for children aged 6-7 as they lay the foundation for critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. At this stage of development, children begin to understand shapes, sizes, and spatial relationships, which are essential components of geometry. When parents and teachers emphasize the importance of categorization, they help children to organize and make sense of the visual world around them.
Learning to categorize shapes and objects enhances a child's ability to differentiate and identify properties, such as sides, angles, and patterns. This skill not only supports mathematical learning but also boosts cognitive development and improves observational skills. Children learn to recognize similarities and differences among shapes, enabling deeper understanding and more effective reasoning.
Moreover, strong categorization skills foster creativity, as children learn to classify objects based on various attributes. This can enhance their artistic expression and encourage spatial awareness. Additionally, these foundational skills in geometry can correlate with success in higher-level math concepts down the line.
In summary, prioritizing categorization skills in geometry helps young learners build essential competencies that influence both their current educational experiences and future academic endeavors. Parents and teachers play a pivotal role in nurturing these skills, benefiting children in multiple dimensions of learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students