Phonics Skills Building Vocabulary Worksheets for Ages 6-7
7 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our Phonics Skills Building Vocabulary Worksheets tailored for ages 6-7! Designed to make learning fun and effective, these worksheets strengthen children's phonics abilities while expanding their vocabulary. Each engaging activity helps kids recognize sounds, blend them into words, and enhance reading fluency. Perfect for independent practice or guided lessons, these printable resources align with educational standards, making them ideal for home or classroom use. Foster a love for reading and build a strong phonetic foundation with our expertly crafted worksheets, setting your young learner on the path to literacy success. Get started today and watch them thrive!


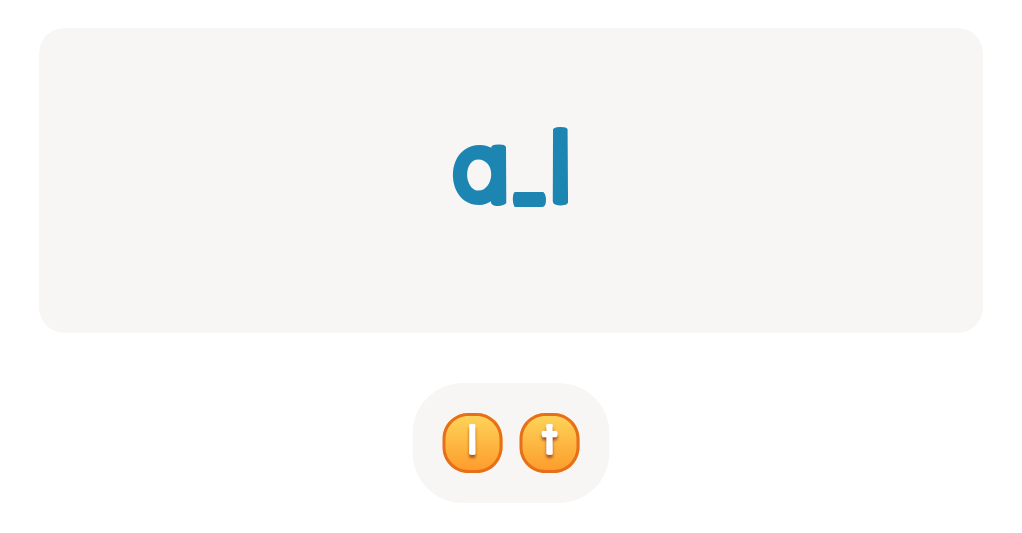
Long /u/ Words Worksheet
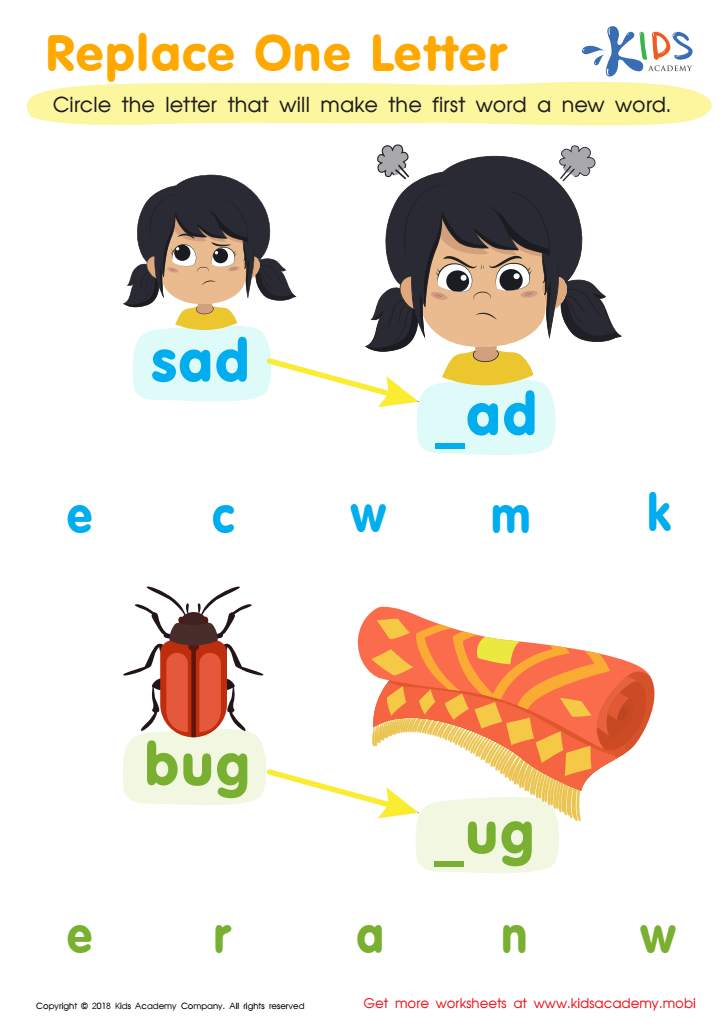

Replace One Letter Worksheet
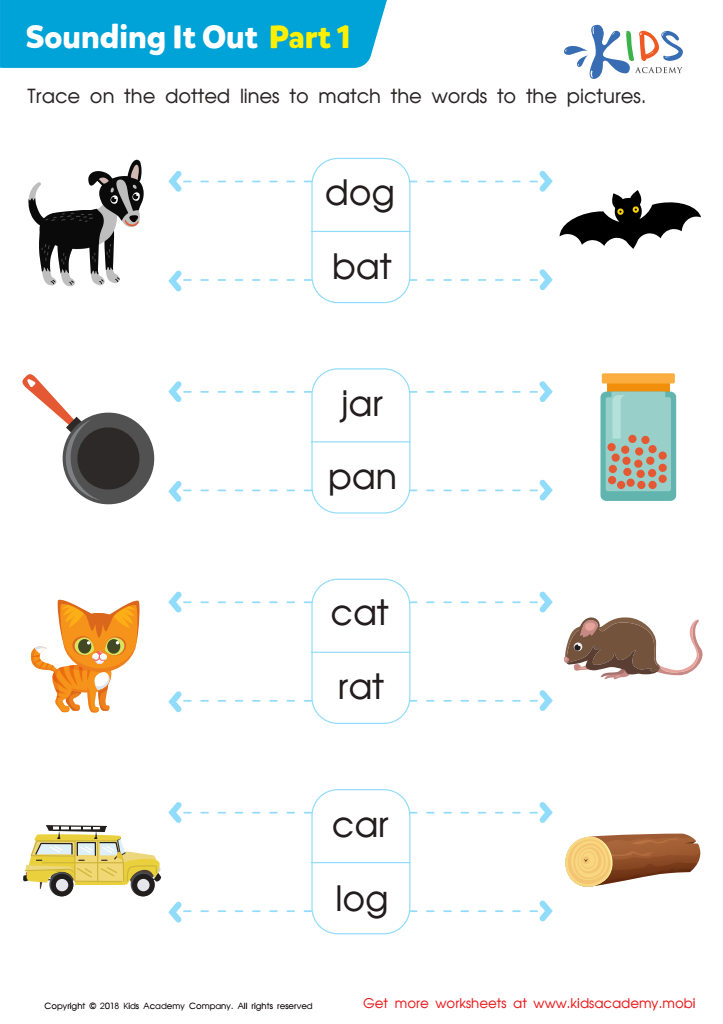

Sounding it Out: Part 1 Worksheet


Reading: Break Them Apart Worksheet

Sounding it Out: Part 3 Worksheet


Long Vowel Sound A Worksheet Worksheet


Reading: AW Words Worksheet
Phonics skills are essential building blocks for young readers, particularly around ages 6-7, where foundational literacy skills are developed. Phonics, the relationship between letters and sounds, helps children decode words, which is paramount for reading fluency. When children understand phonics, they can segment and blend sounds, enabling them to read unfamiliar words more easily. This confidence in decoding facilitates early reading success and fuels a love for reading.
Building a robust vocabulary at this stage complements phonics by enhancing comprehension. As children decode and read new words, a rich vocabulary helps them to understand the context and meaning, turning simple reader into fluent, confident readers. Decoding and comprehension skills combined enable children to engage with text more deeply, leading to better academic performance across all subjects.
Investing in phonics skills and vocabulary for 6-7-year-olds paves the way for lifelong literacy and learning. It ensures that children do not just learn to read but also read to learn. Hence, parents and teachers should prioritize strategies that integrate phonics and vocabulary to foster a comprehensive, effective approach to early literacy, creating strong readers who possess both the technical skills and the understanding necessary for academic and personal growth.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students