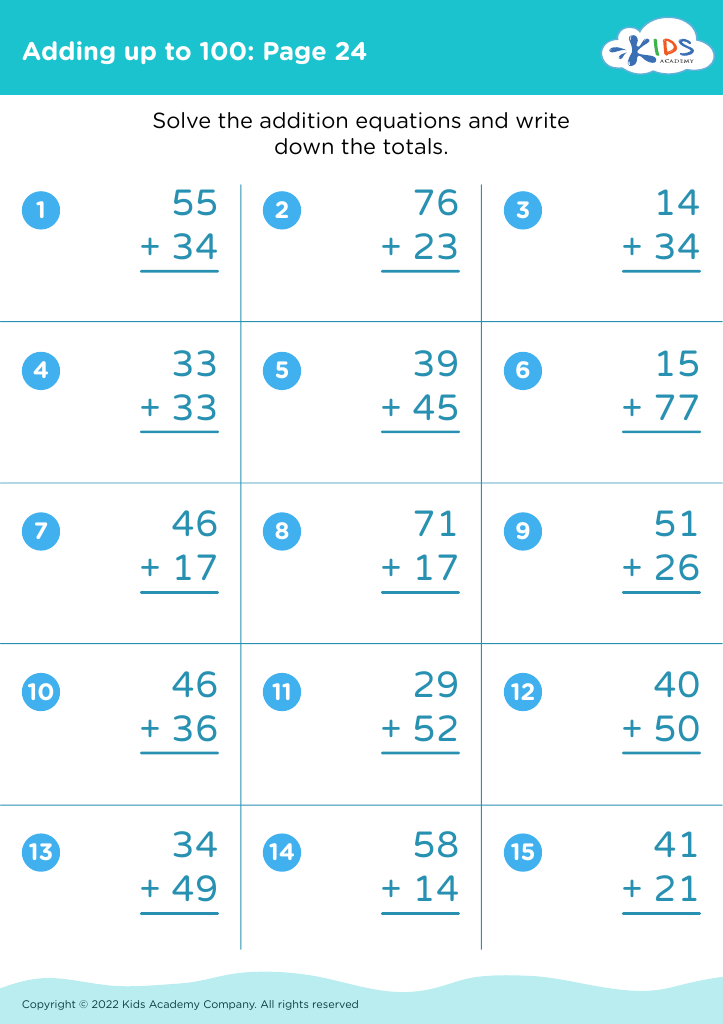
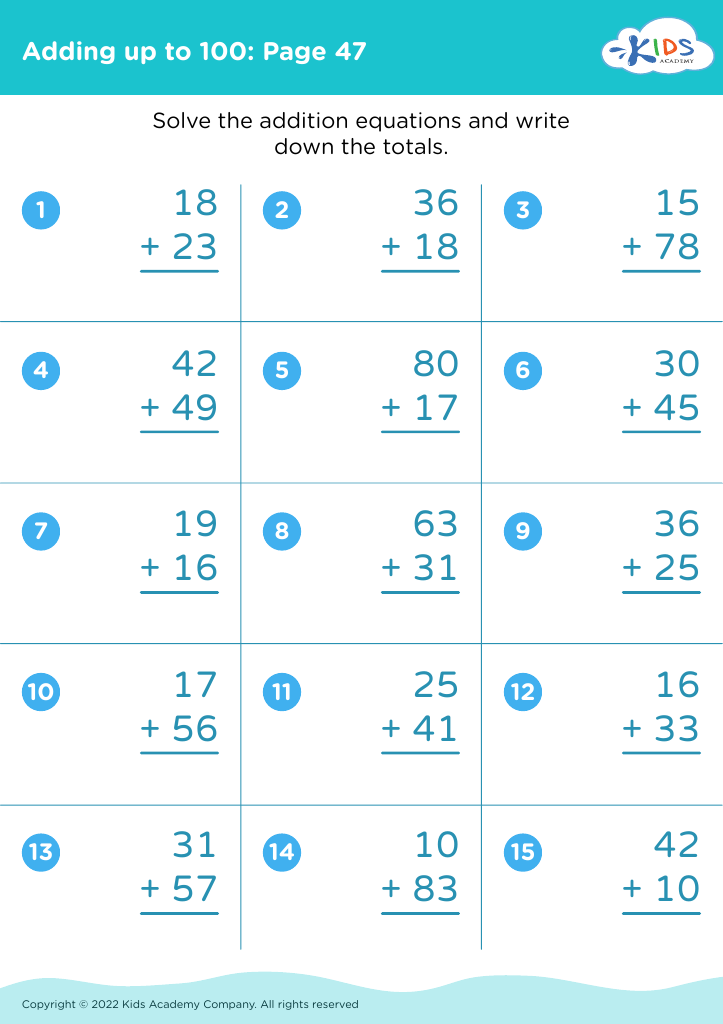
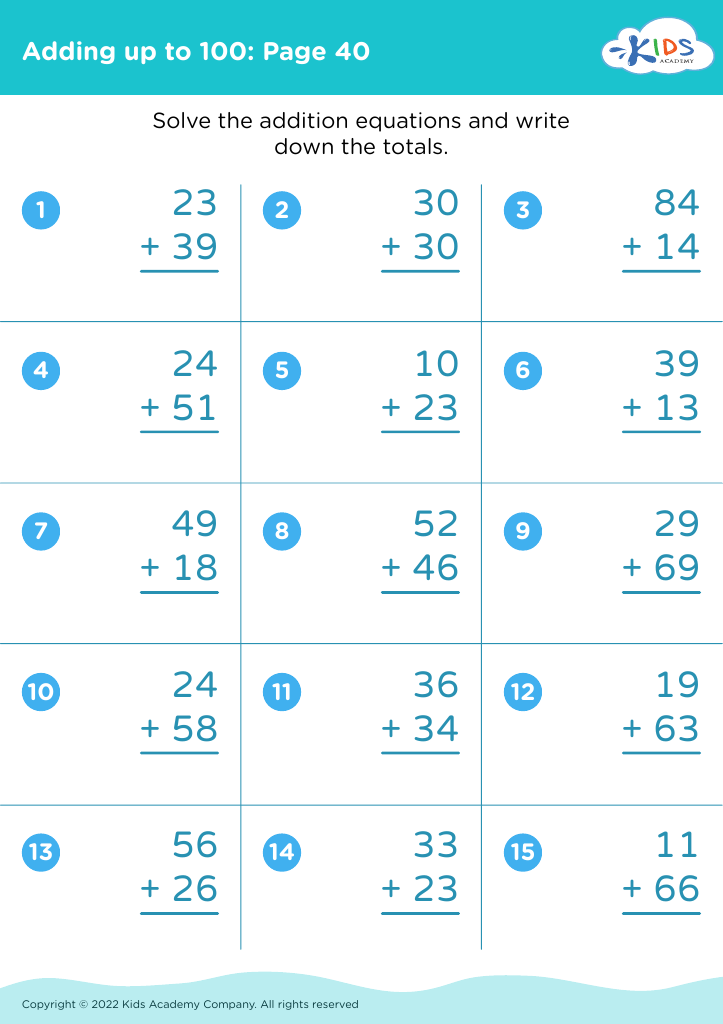
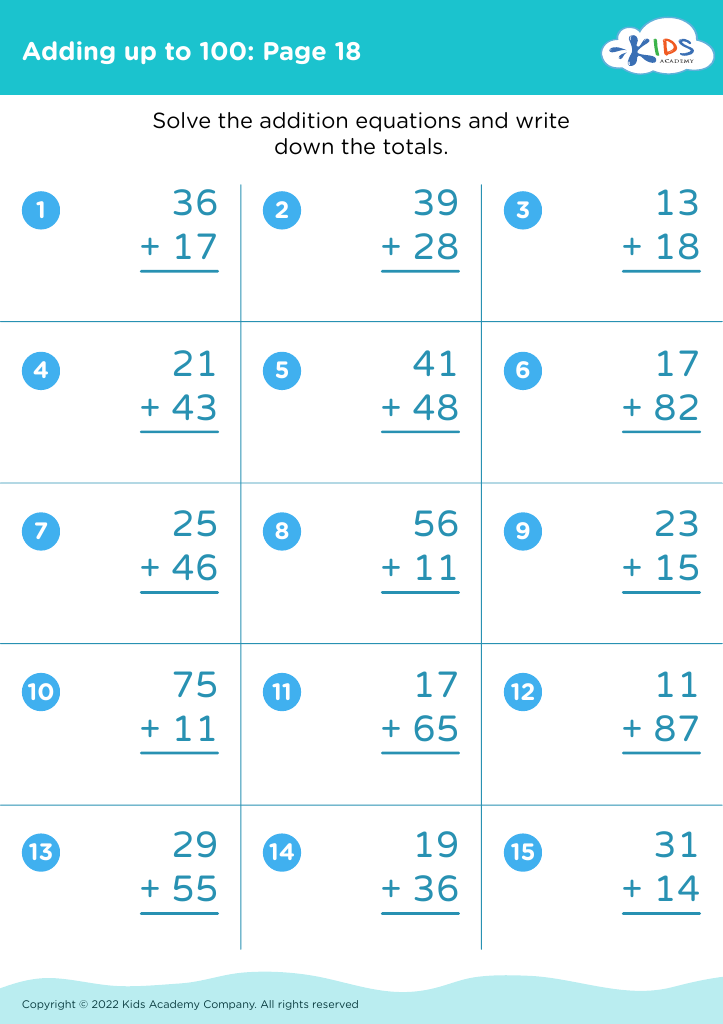
Develop fine motor skills Adding up to 100 Misc Worksheets for Ages 6-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging collection of "Adding Up to 100 Misc Worksheets" designed specifically for children aged 6-8 to help develop fine motor skills! These worksheets not only reinforce essential math concepts but also enhance hand-eye coordination, control, and dexterity through fun and interactive activities. With a variety of colorful exercises, kids can practice their counting, addition, and problem-solving skills while improving their writing and small motor movements. Ideal for both classroom settings and at-home learning, our worksheets make math enjoyable! Dive into these creative resources and watch as your child's abilities flourish through hands-on practice and dedicated learning!
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for children aged 6-8 as these skills directly impact their ability to perform everyday tasks and engage in more complex activities. Fine motor skills involve small muscle movements, particularly those of the hands and fingers. For parents and teachers, nurturing these skills during this critical developmental stage is paramount for several reasons.
Firstly, fine motor skills are foundational for academic success. Activities such as writing, drawing, and handling classroom materials require precision and control that stem from strong fine motor abilities. Improved skills boost children's confidence and enable them to participate more fully in classroom activities.
Secondly, fine motor development has meaningful implications for self-care tasks, such as buttoning shirts, tying shoelaces, and using utensils. As children gain independence in these areas, it fosters resilience and self-esteem.
Additionally, engaging in activities that enhance fine motor skills—like arts and crafts, building with blocks, or playing simple games—mirrors social interactions and collaborative learning. This not only promotes social skills but also encourages cognitive development.
In summary, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skill development, as it plays a crucial role in children's holistic growth, supporting academic, social, and life skill achievement.