Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To

6 Parrots Worksheet

Rapunzel Addition Maze Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet
Fine motor skills are integral for children ages 6-8, as they underpin foundational learning in mathematics, particularly in addition and subtraction. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for writing, drawing, and manipulating objects, which directly impacts a child's ability to engage with mathematical concepts.
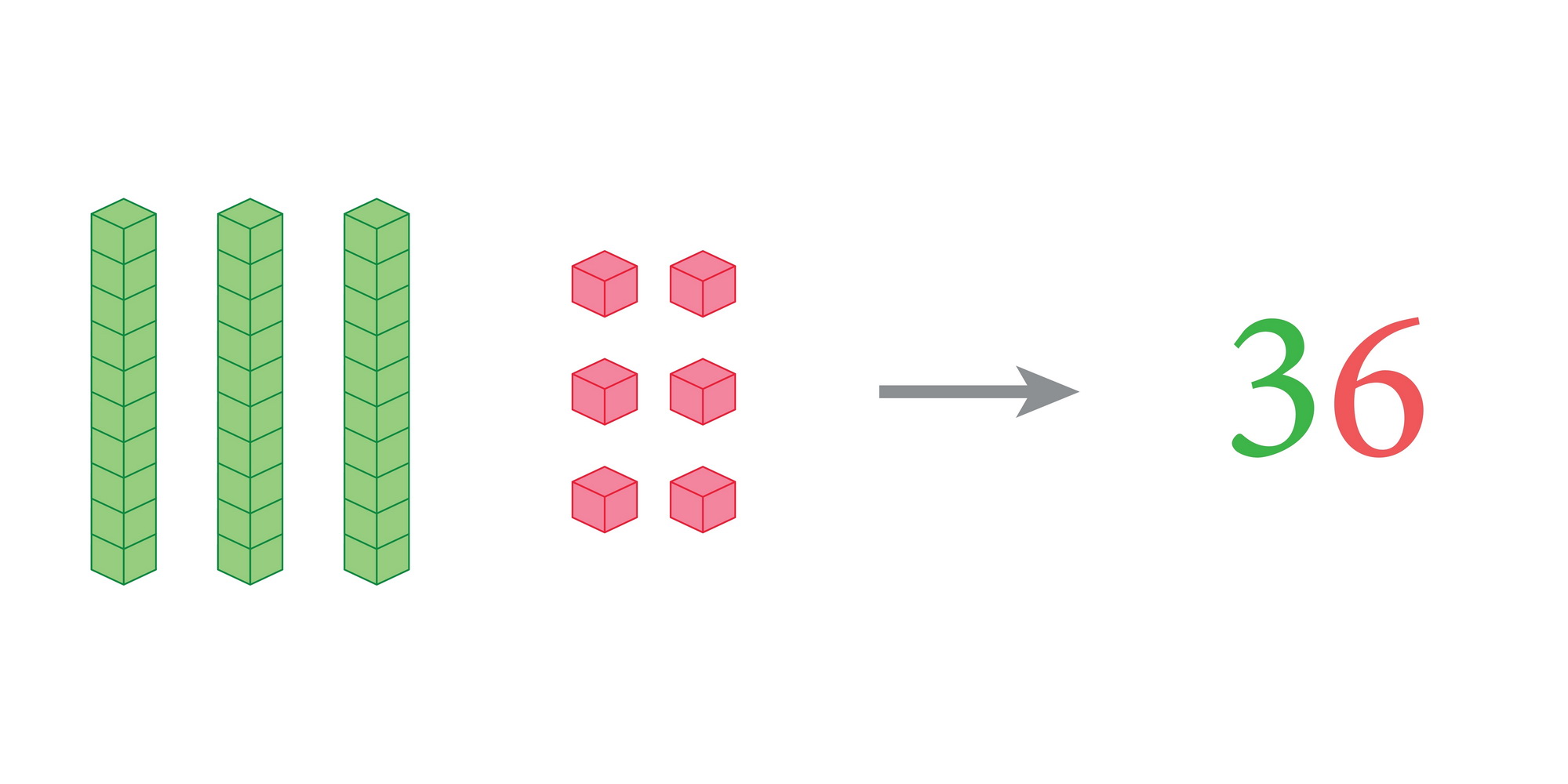
As children learn addition and subtraction, they often use manipulatives like blocks or counters. Effective handling of these tools necessitates developed fine motor skills. Furthermore, strong fine motor proficiency supports clearer writing, which is vital when solving math problems on paper and communicating solutions.
Teachers and parents should care about honing fine motor skills because such development can enhance a child’s confidence and enjoyment in learning. Kids who struggle with motor skills may become frustrated with arithmetic, leading to anxiety or aversion towards math altogether. By incorporating fun activities that promote fine motor growth, such as crafting or using finger paints, adults can create a more positive learning environment. Ultimately, fostering fine motor skills will not only aid academic success in addition and subtraction, but will also lay a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts in the future.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students