Shape Recognition Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-8 - Page 2
33 filtered results
-
From - To
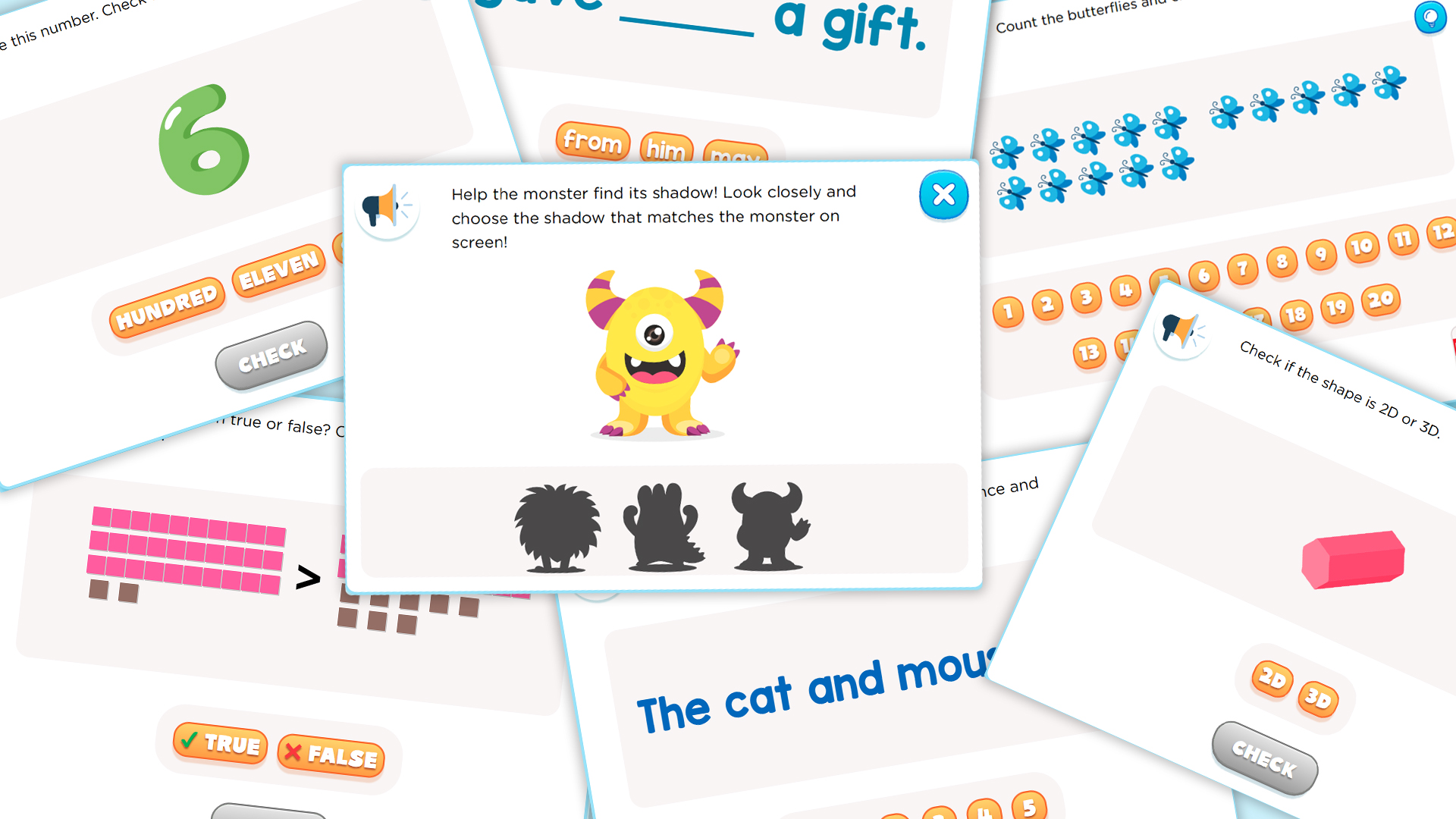
Parents and teachers should prioritize teaching shape recognition and basic arithmetic skills like addition and subtraction to children aged 6-8 because these foundational skills significantly enhance cognitive and academic development. Shape recognition helps children understand and organize the world around them by categorizing objects based on their characteristics. This cognitive skill is crucial for spatial awareness, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. Recognizing shapes also links directly to learning geometry, drawing, and reading, where identifying patterns and forms is essential.
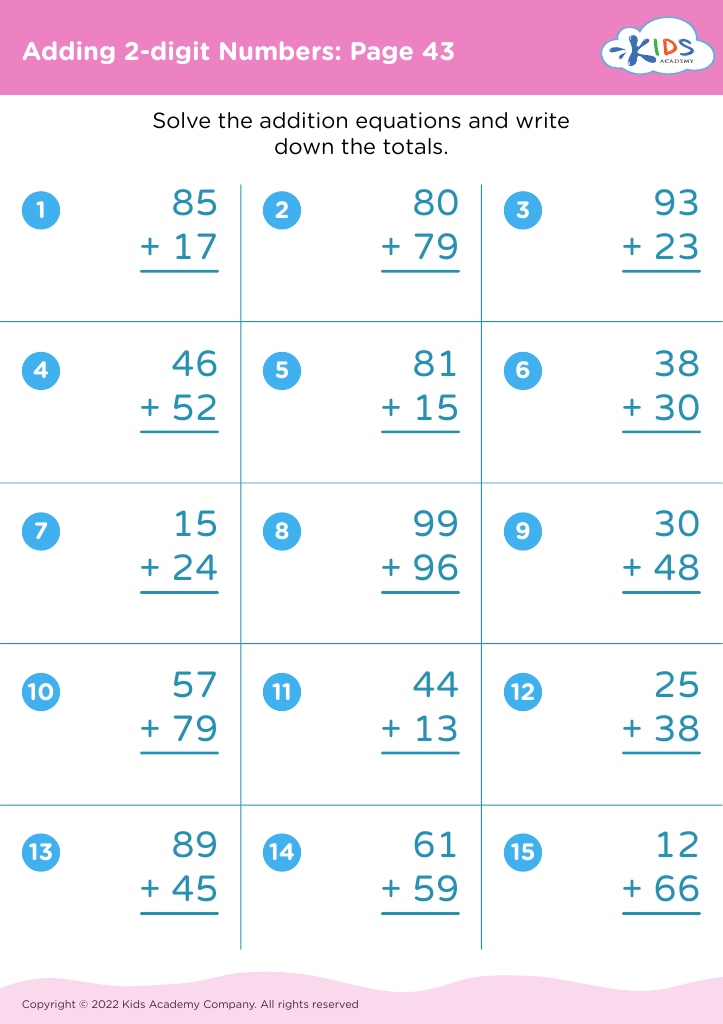
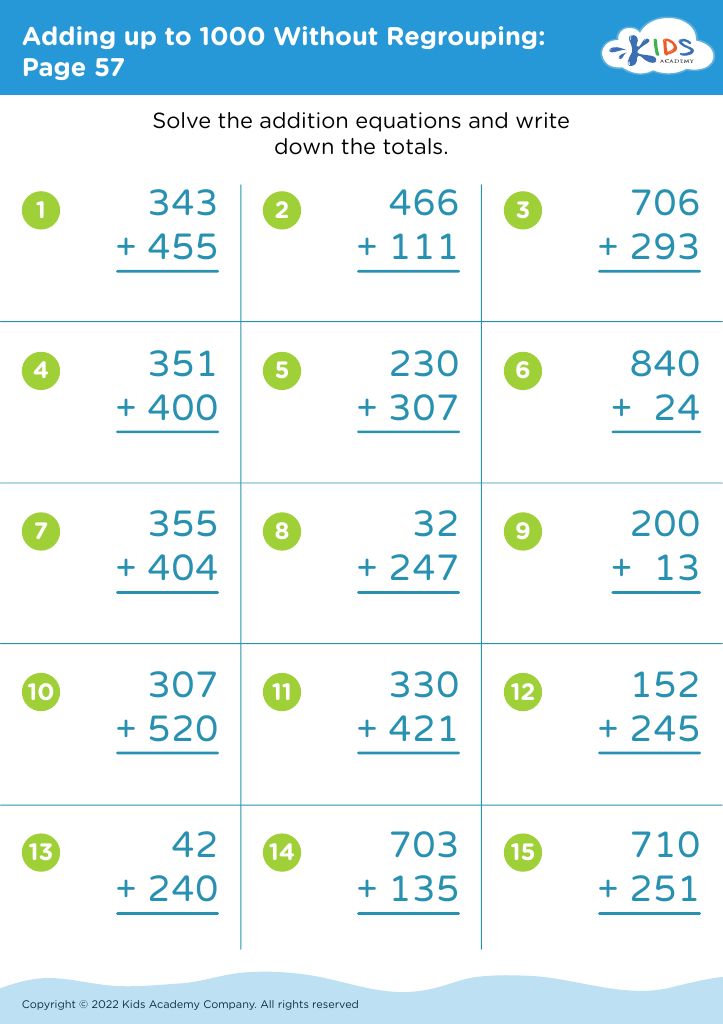
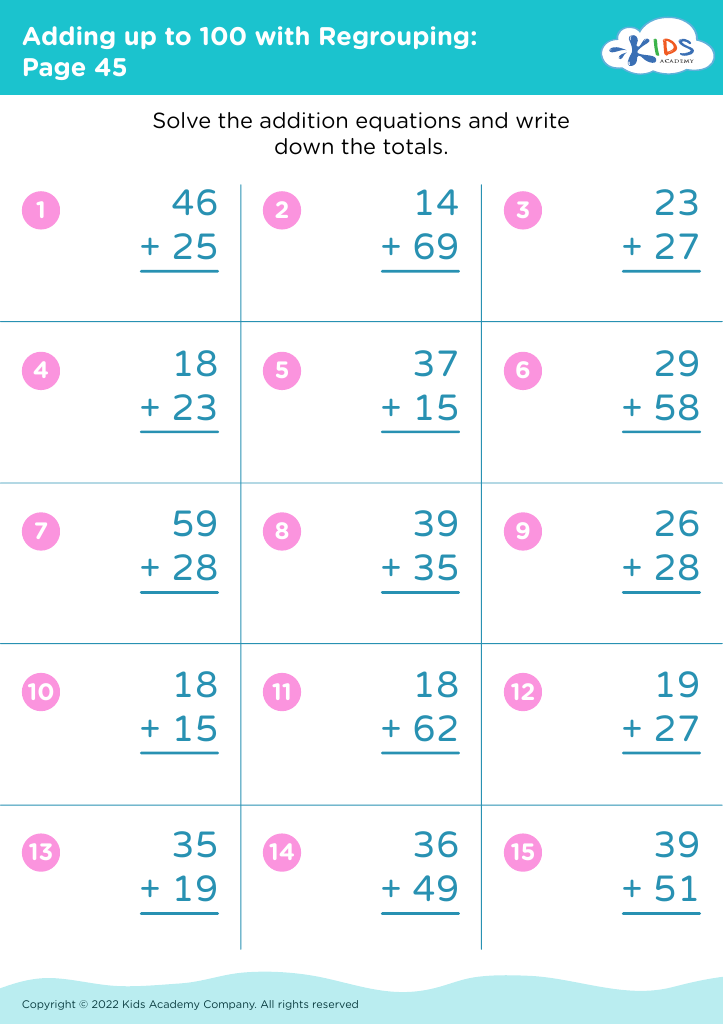
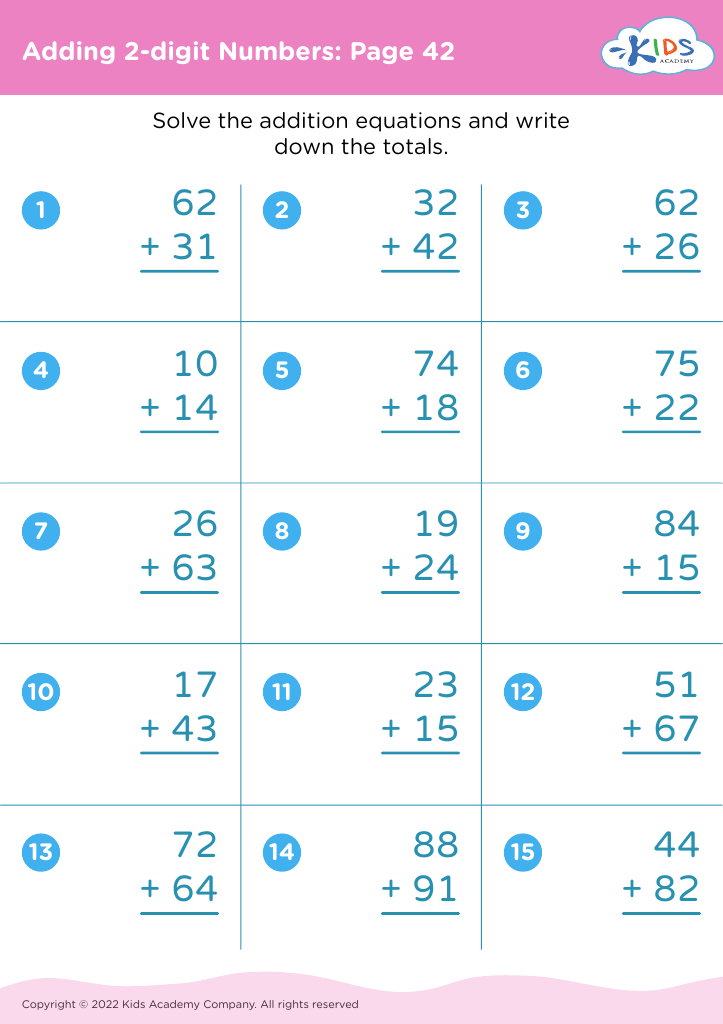
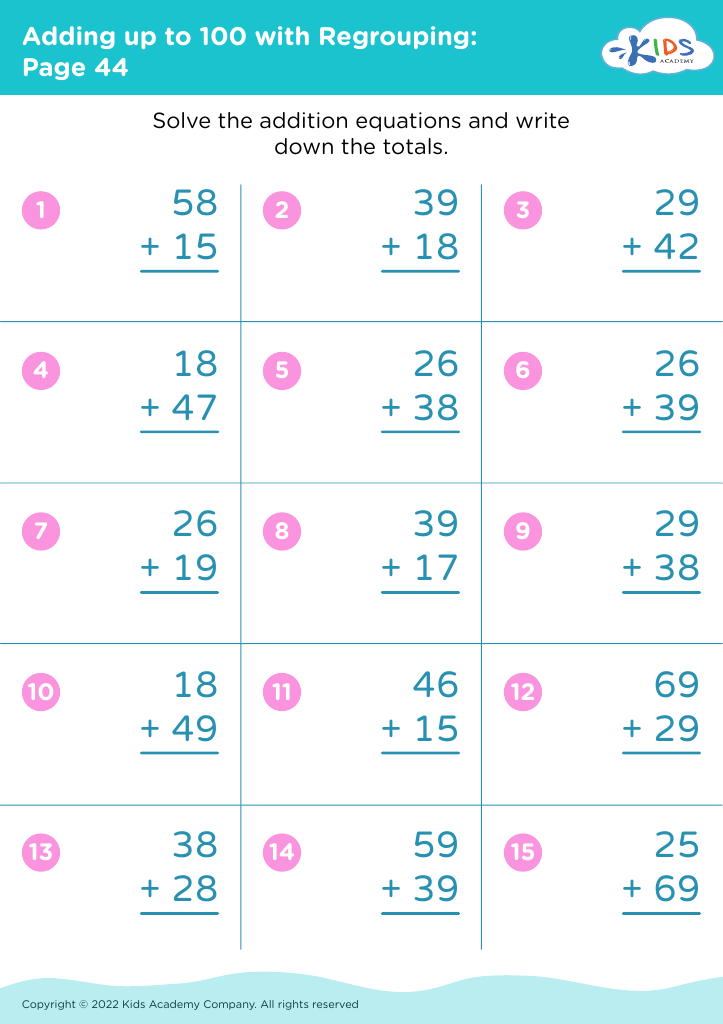
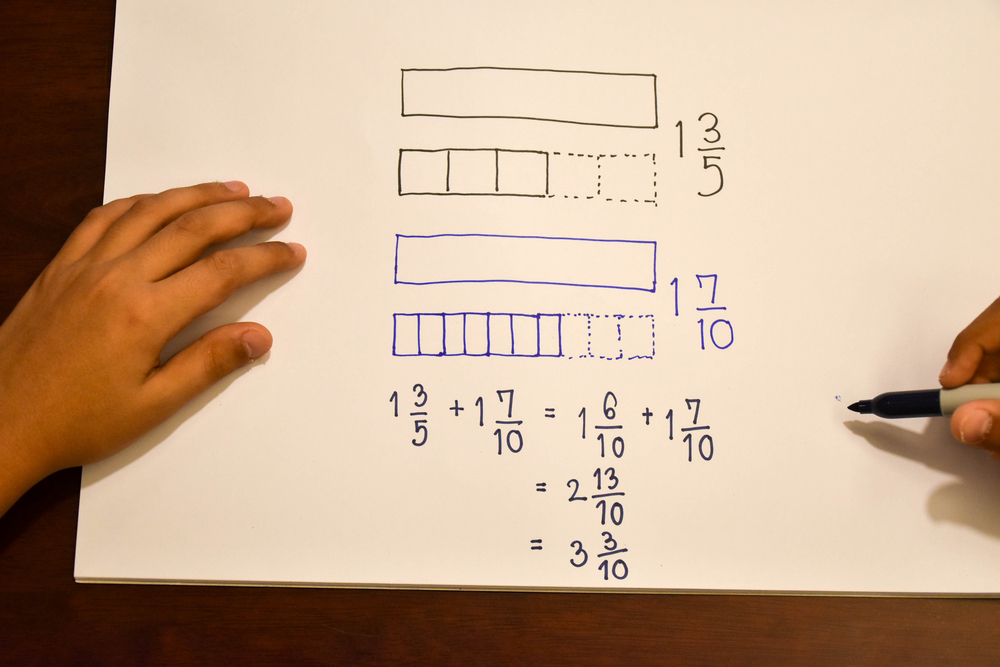
Meanwhile, addition and subtraction are core components of early arithmetic, forming the basis for all future mathematical learning. Mastering these skills at a young age fosters a child's numerical literacy, enabling them to perform more complex operations with confidence as they progress in their education. Understanding these basics also bolsters a child's ability to follow instructions, solve problems, and think analytically. When combined, shape recognition and arithmetic help solidify a child's logical reasoning, spatial reasoning, and number fluency.
Early engagement in these areas through fun, interactive lessons can also help kids develop a positive attitude toward learning and they are more likely to perform well in school. A strong start in these critical skills lays the groundwork for academic success in various subjects, including science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).