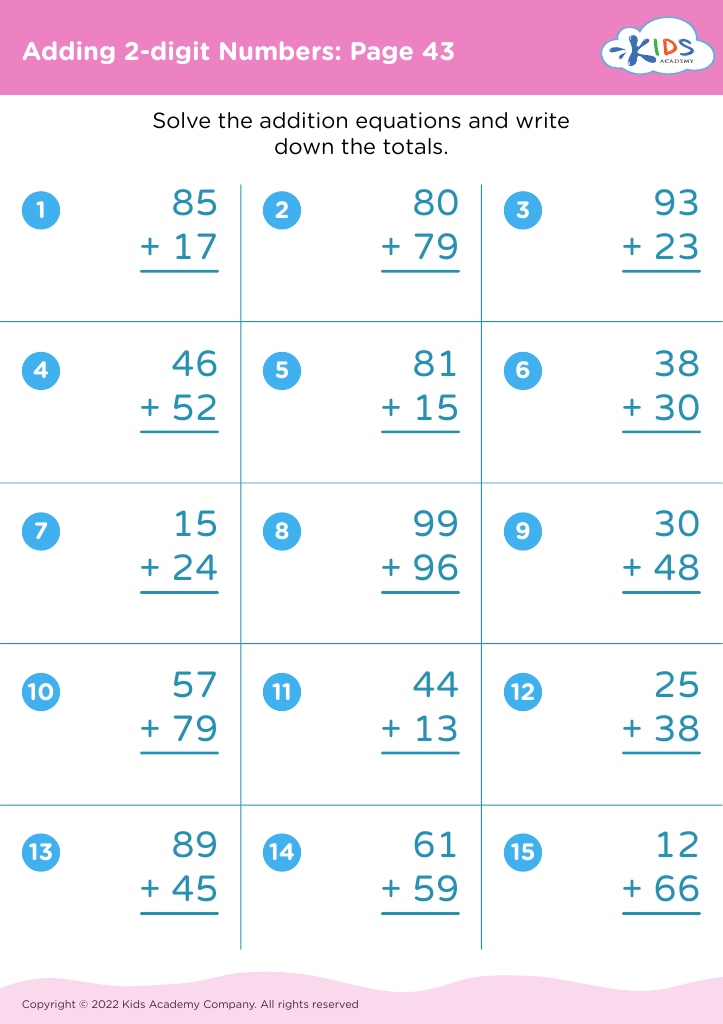
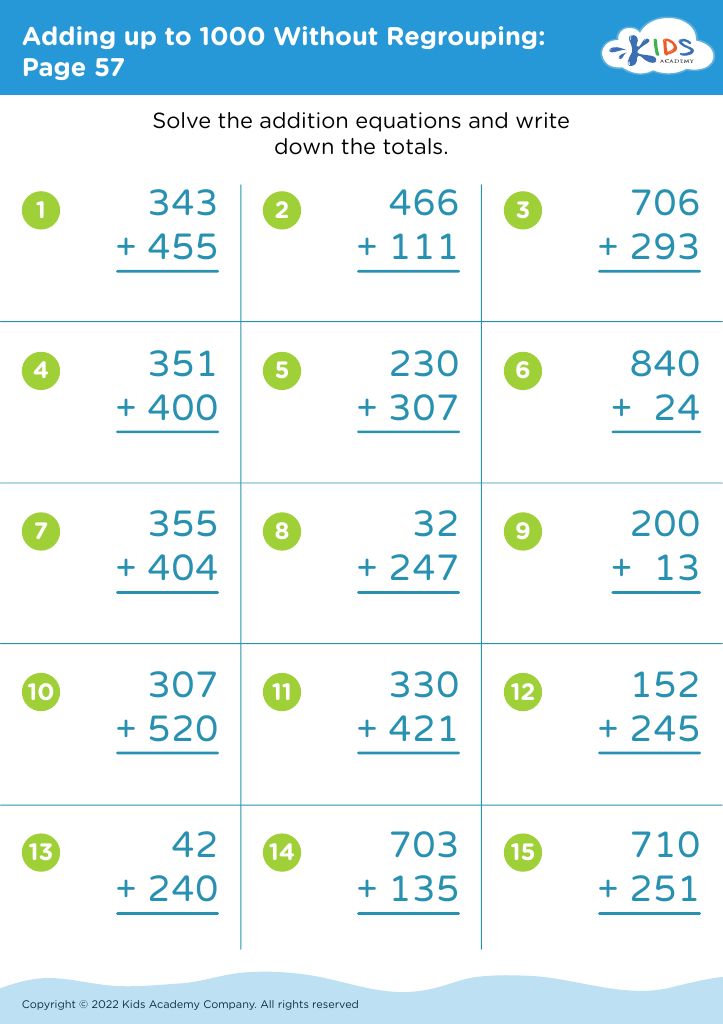
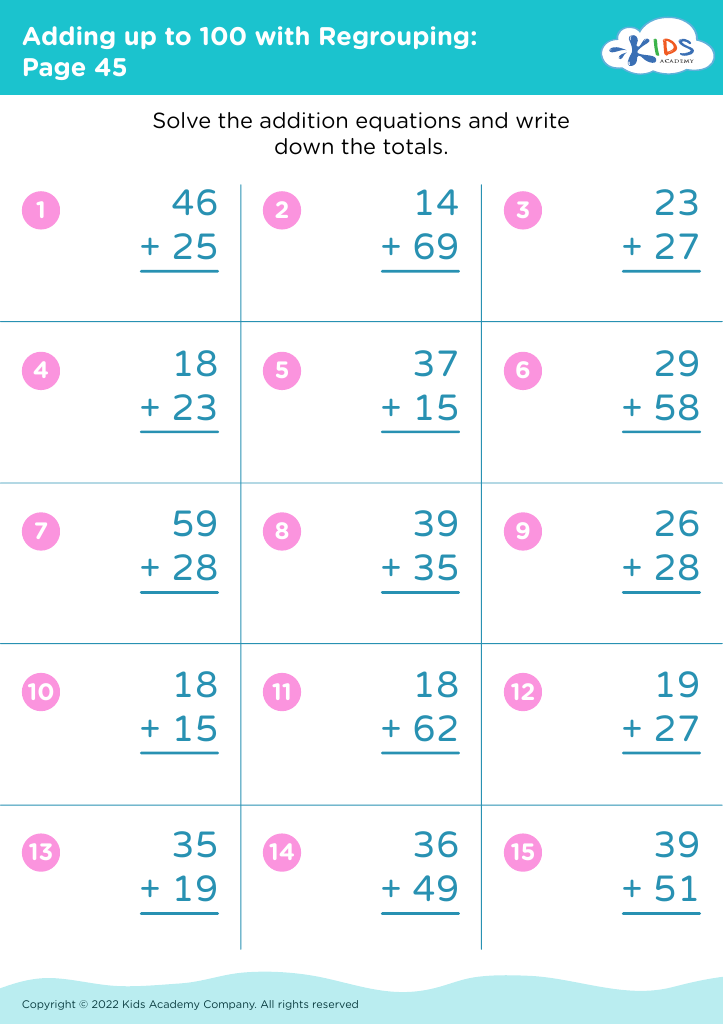
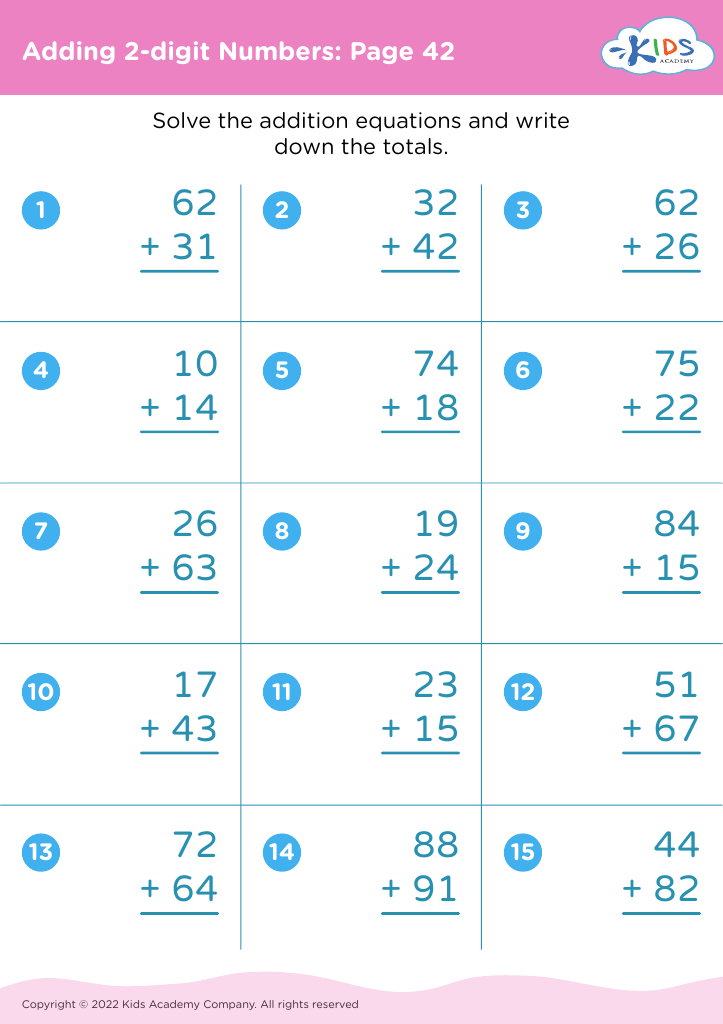
Shape Recognition Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-9 - Page 2
33 filtered results
-
From - To
Shape recognition and basic arithmetic skills are foundational components of early childhood education that play a significant role in a child's cognitive development. For children ages 6-9, grasping these concepts sets the stage for future academic success and everyday problem-solving.
First, shape recognition is more than just identifying circles and squares; it enhances spatial awareness, which is crucial for understanding mathematics, particularly geometry. Knowing how to recognize and manipulate shapes aids in the development of skills such as symmetry, patterning, and spatial relationships, fostering a strong mathematical foundation.
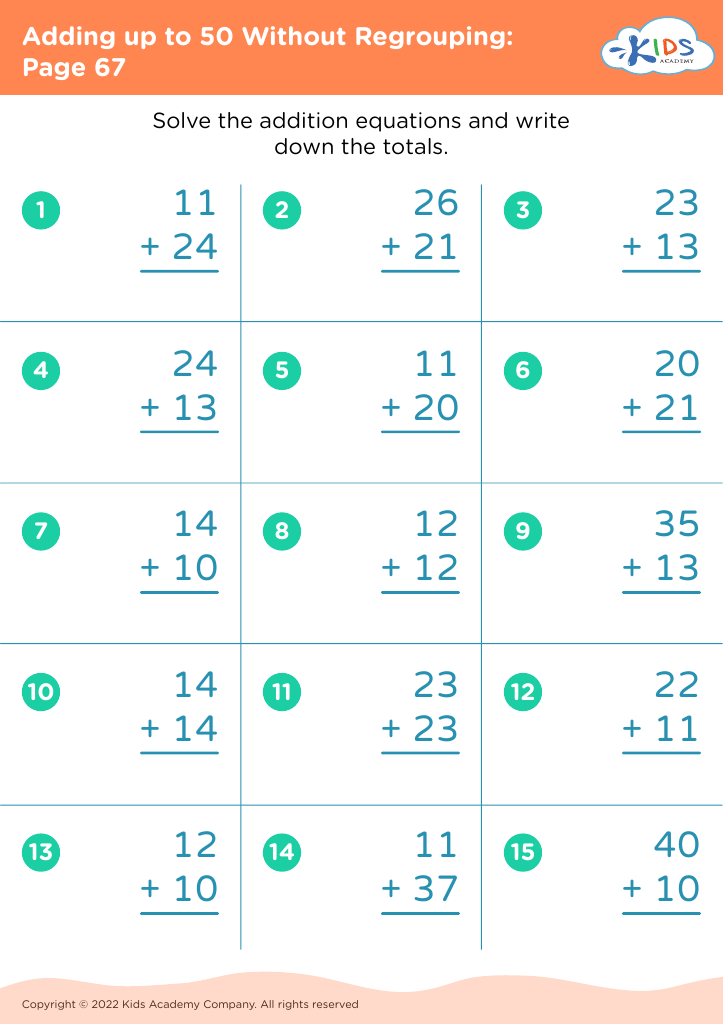
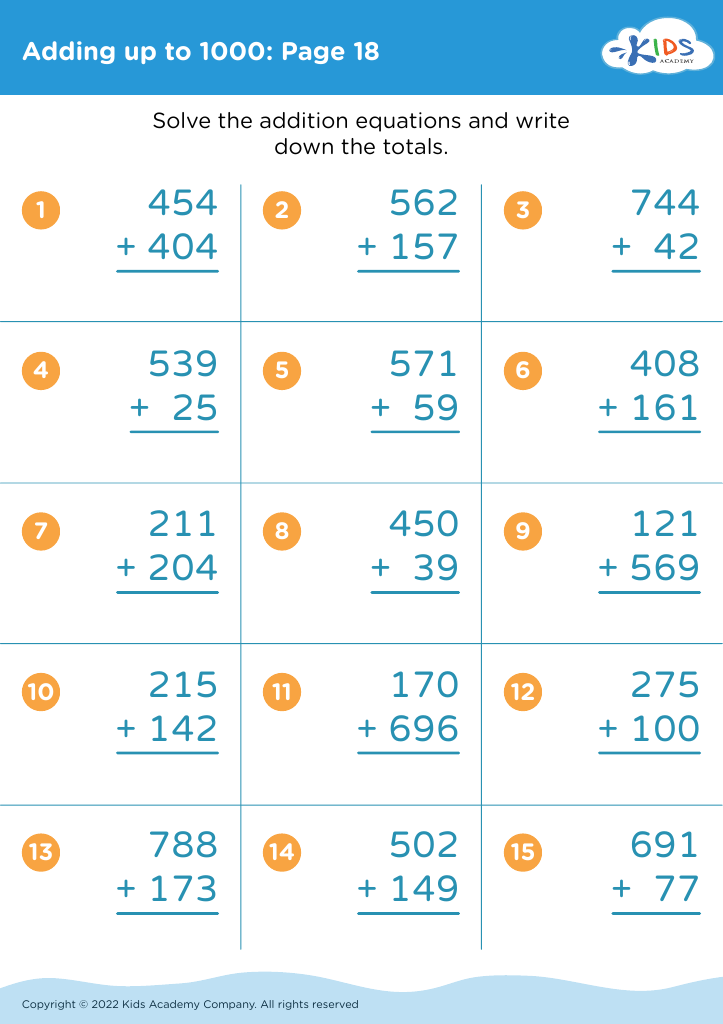
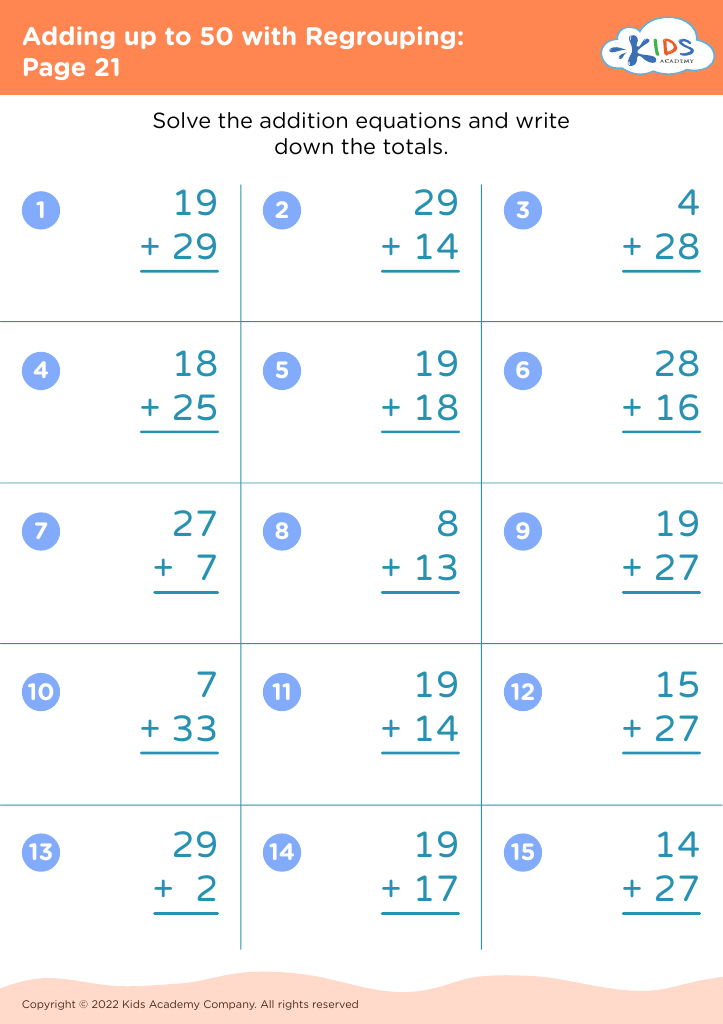
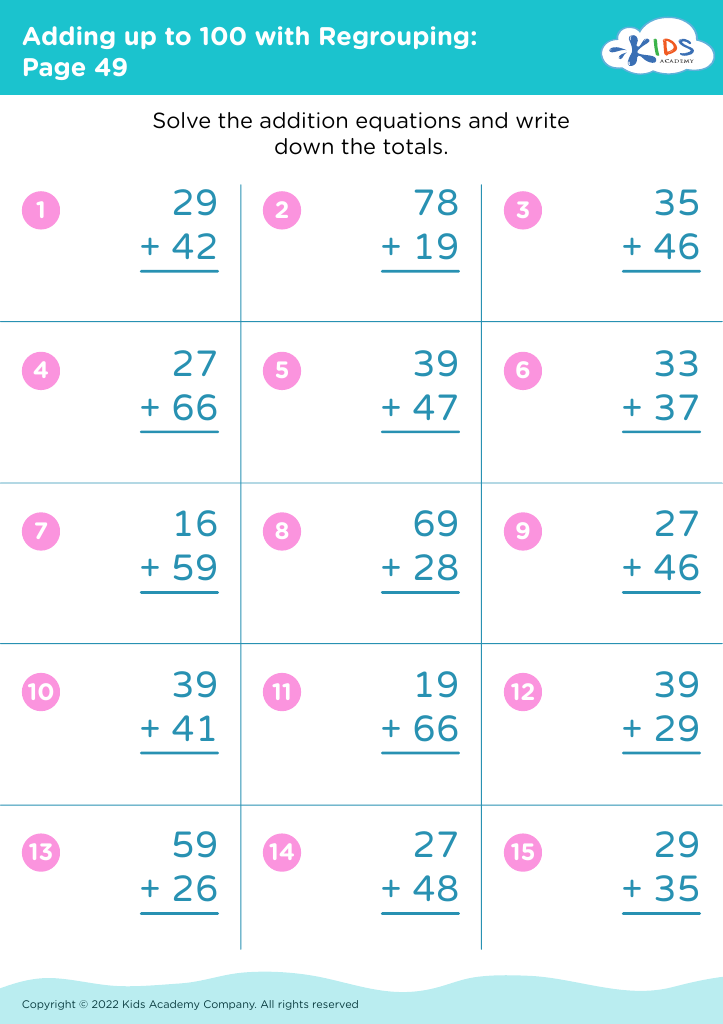
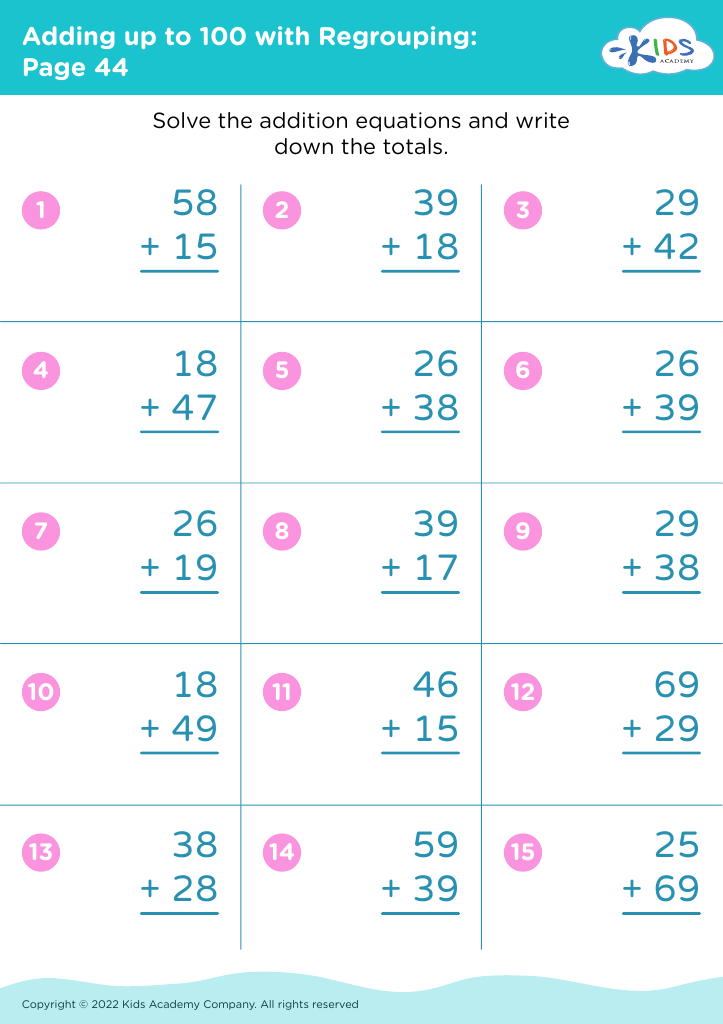
Second, addition and subtraction are the building blocks of all higher-level mathematics. Early competency in these areas leads to a better understanding of more advanced math concepts like multiplication, division, and fractions. These operations develop critical thinking and logical reasoning skills, which are essential not only in math but across all academic subjects and real-life situations.
For teachers and parents, engaging children in activities that blend shape recognition with addition and subtraction maximizes learning experiences. Games, puzzles, and hands-on activities make math fun and interactive, thereby increasing a child's engagement and retention. Investing time in these areas during the formative years ensures that children are well-prepared for the educational challenges ahead, fostering both academic aptitude and a positive attitude towards learning.