Counting practice Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-9 - Page 3
59 filtered results
-
From - To
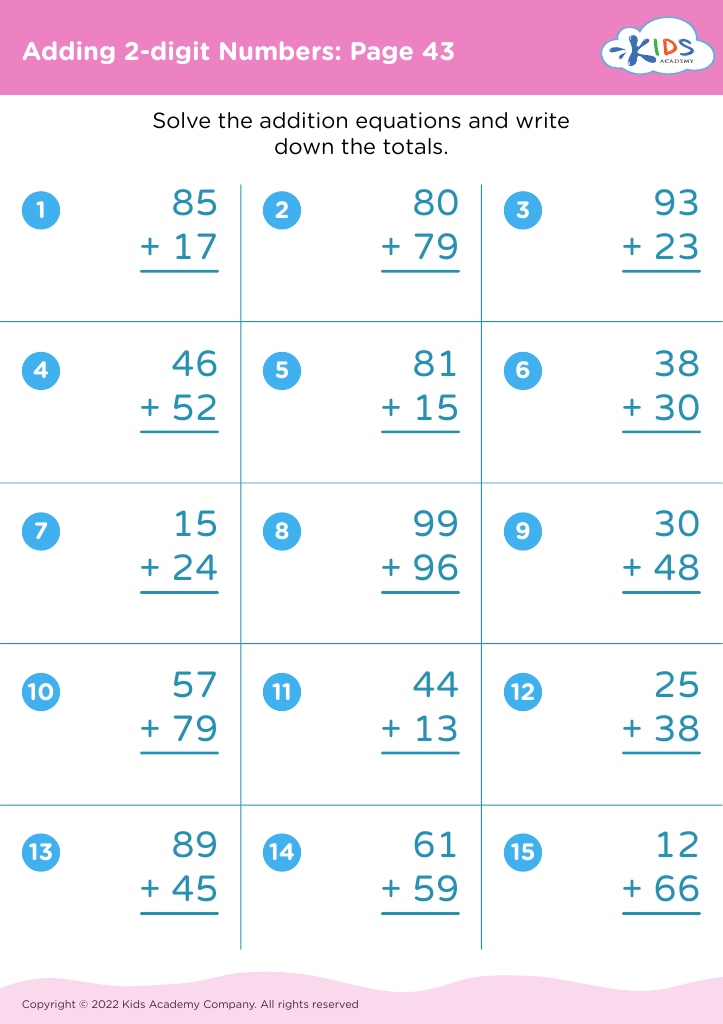
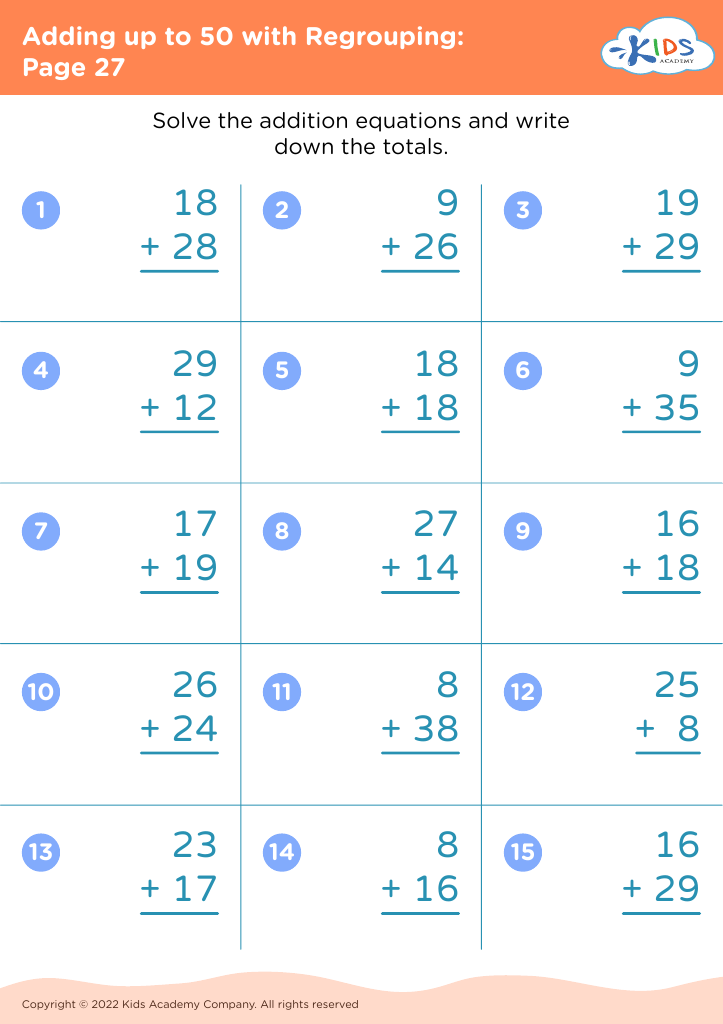
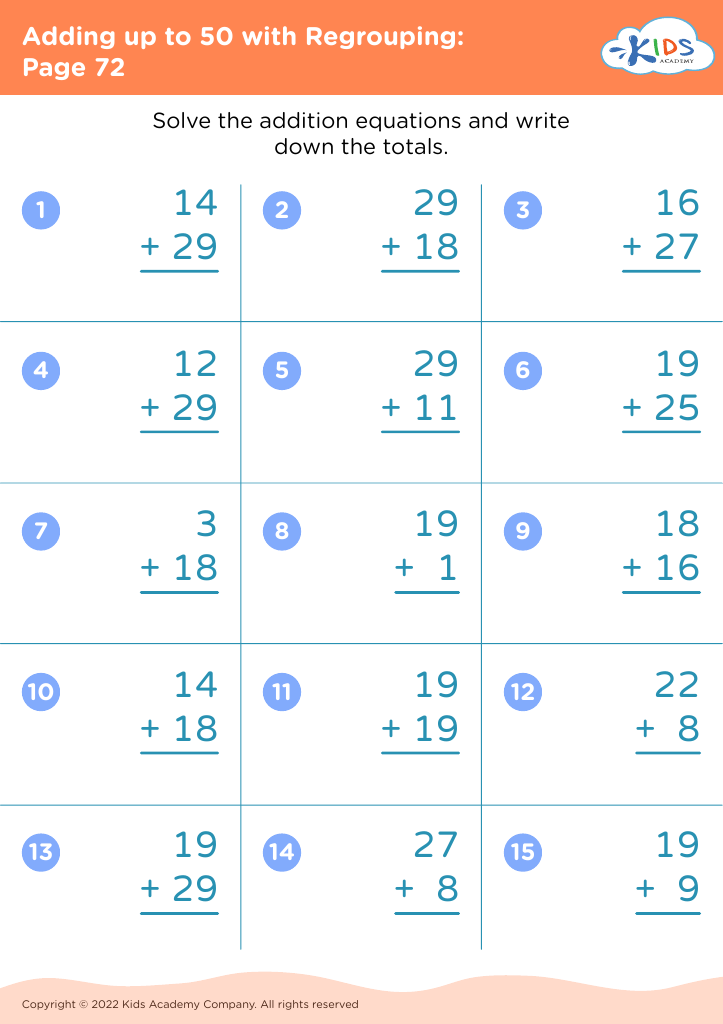
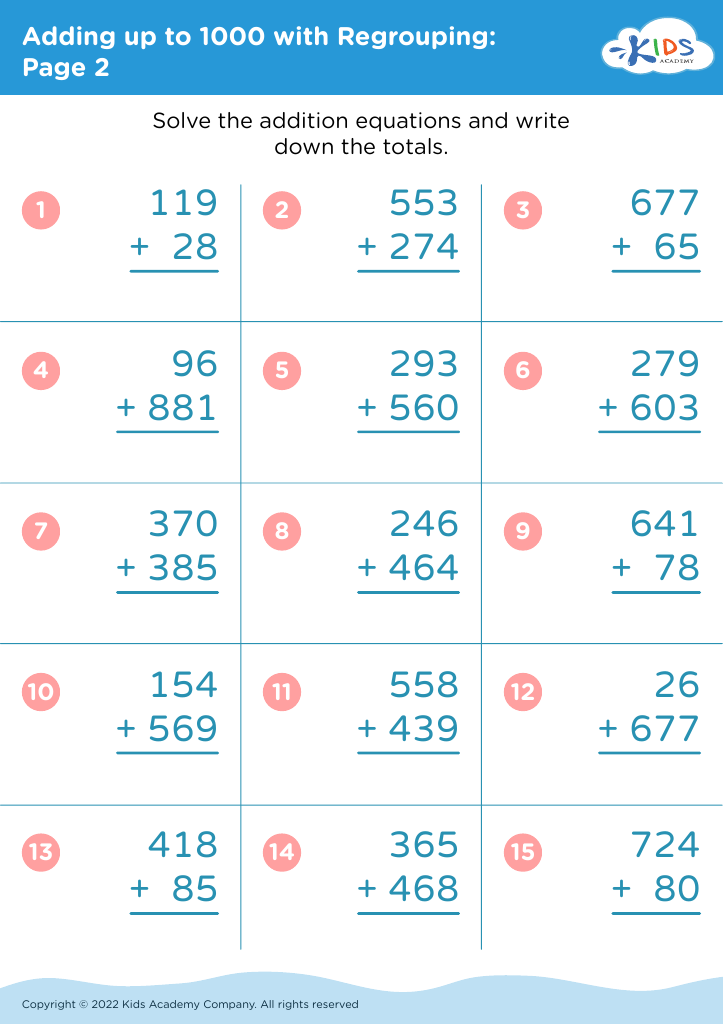
Counting practice and basic addition are fundamental skills for children aged 6-9, forming the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts they will encounter later in their education. Teachers and parents should prioritize these skills for several key reasons. First, proficiency in counting and addition supports the development of number sense, which is the intuitive understanding of numbers, their magnitude, relationships, and how they are affected by operations. This understanding is critical for mastering concepts in all branches of mathematics.
Second, early competence in addition helps build confidence. A child who feels comfortable with numbers is more likely to tackle new and challenging mathematical problems with a positive attitude. This confidence can extend beyond math, fostering an overall love for learning and perseverance in other academic areas.
Third, early math skills correlate with overall academic success. Studies show that children who enter school with strong counting and addition skills are better prepared for more advanced topics. These skills also support problem-solving and critical thinking abilities that are applicable in everyday life and essential for future academic and career success.
Additionally, engaging young children in counting and addition activities promotes a strong parent-child or teacher-student bond through collaborative, rewarding experiences. These interactions can make learning fun, reduce math anxiety, and instill a lifelong appreciation for mathematics.