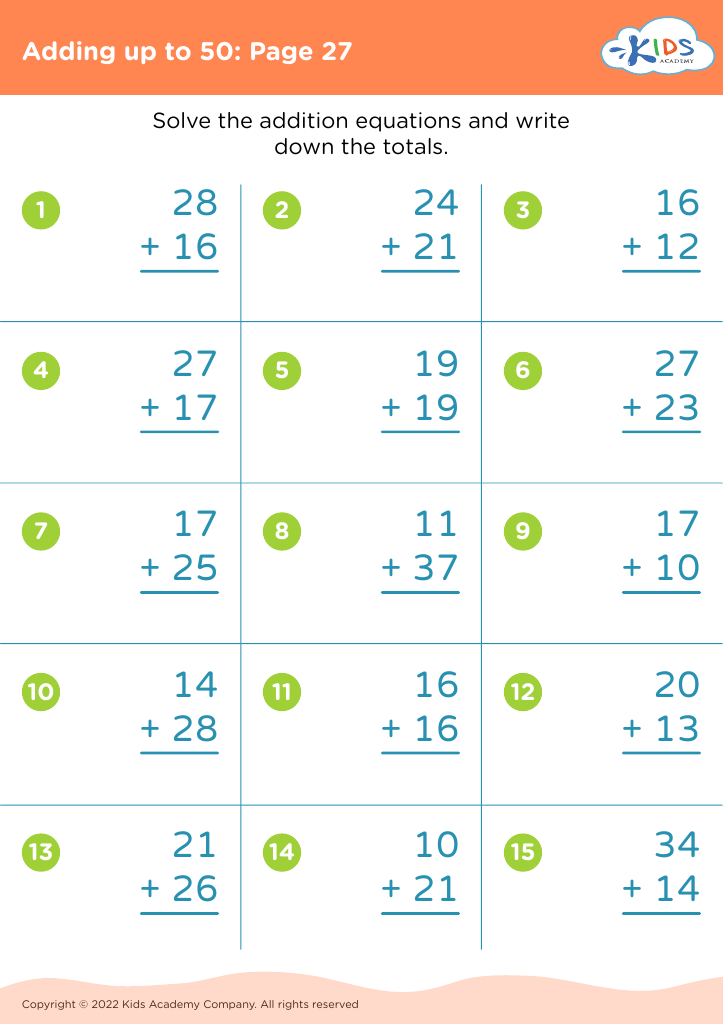
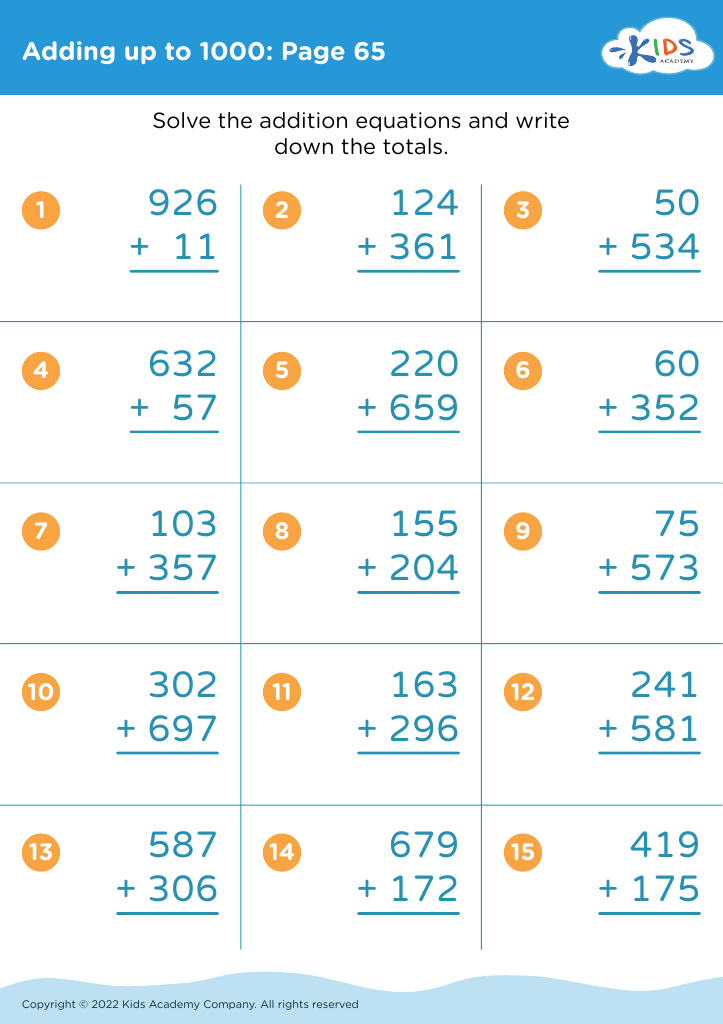
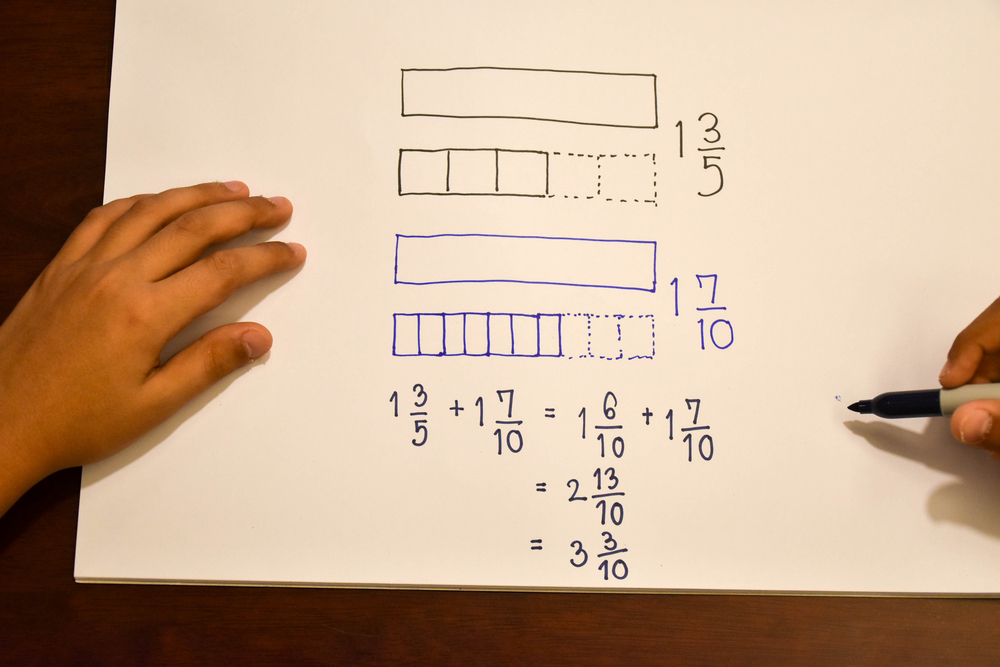
Sequencing Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's understanding of addition with our Sequencing Skills Addition Worksheets, designed specifically for ages 6-9. These engaging worksheets help develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities by guiding children through the order of operations in addition. With age-appropriate challenges, your young learner will build confidence in their math skills while they practice sequencing numbers and solving addition problems. Each worksheet is designed to reinforce foundational math concepts in a fun and interactive manner, making learning enjoyable. Discover how our printable resources can effectively support your child's academic growth and boost their love for math!
Sequencing skills are crucial for children aged 6-9 as they serve as the foundation for a range of cognitive and academic abilities. This age is pivotal in developing logical thinking, problem-solving, and comprehension—not just in mathematics but across all subjects. Mastering sequencing in addition helps children recognize patterns, understand the relationships between numbers, and develop strategies for solving problems more efficiently.
When parents or teachers prioritize sequencing skills in addition, they foster a child's ability to break down complex tasks into manageable steps. This is particularly important in math, where understanding the order of operations can significantly affect the outcome of calculations. By enhancing these skills, children also improve their overall confidence in mathematics, making them more likely to engage actively in learning.
Furthermore, strong sequencing skills are transferable. They aid in reading comprehension—understanding the sequence of events in a story enhances interpretation and memory retention. Moreover, these skills support everyday decision-making and critical thinking. By focusing on sequencing skills during these formative years, parents and teachers play an essential role in equipping children with the tools they need for future educational challenges, thereby laying the groundwork for lifelong learning.