Handwriting practice Reading Worksheets for Ages 6-9
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Handwriting Practice and Reading Worksheets, designed specifically for children aged 6 to 9! These interactive resources combine the joy of reading with essential handwriting skills, making learning fun and effective. Tailored to enhance fine motor skills, our worksheets encourage young learners to practice letter formation, sentence structure, and proper spacing while reading captivating texts. With colorful illustrations and age-appropriate exercises, kids will enjoy developing their writing proficiency alongside their reading comprehension. Ideal for teachers and parents alike, these worksheets will foster a love for language and set a strong foundation for academic success. Start your child’s writing journey today!
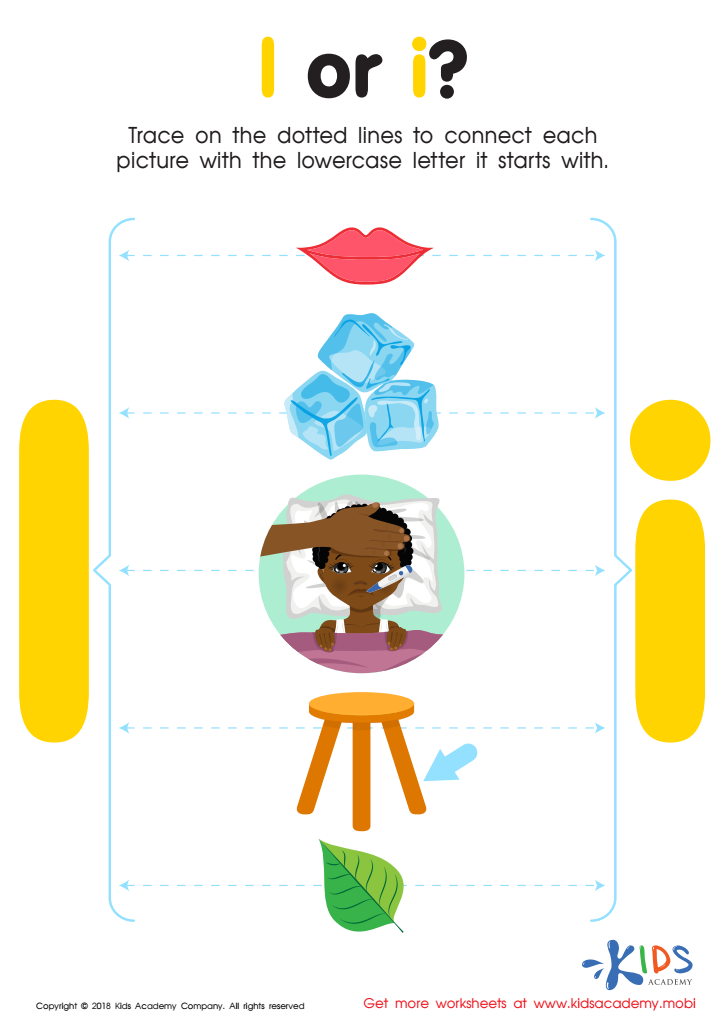


l or i? Worksheet


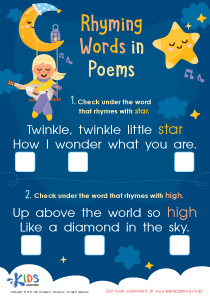
Bat Rhyming Words Worksheet


Chinese Word Tracing: Ni Hao Worksheet


Upon, Around, Off Sight Words Worksheet


"B" Words Printable Sight Words Worksheet


Trace Read You Like Worksheet
Handwriting practice is crucial for children aged 6-9 as it significantly impacts their overall academic success and cognitive development. This developmental stage is key for refining fine motor skills, essential for writing legibly and confidently. Improved handwriting boosts children’s ability to express their thoughts clearly, fostering effective communication skills.
Moreover, handwriting practice enhances reading comprehension. When children write by hand, they engage in a deeper processing of words, leading to improved retention and understanding. This connection between reading and writing aids in vocabulary acquisition and spelling, as students learn to recognize patterns in language.
In addition, mastering handwriting lays the groundwork for future learning. With technology becoming increasingly prevalent, the importance of legible writing should not be overlooked. Handwriting is a fundamental academic skill that children will utilize throughout their educational journey.
Lastly, writing regularly supports a child’s emotional and cognitive growth. It provides a creative outlet, allowing self-expression and boosting confidence. For all these reasons, parents and teachers should prioritize handwriting practice as an essential component of literacy development in young learners.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students




.jpg)