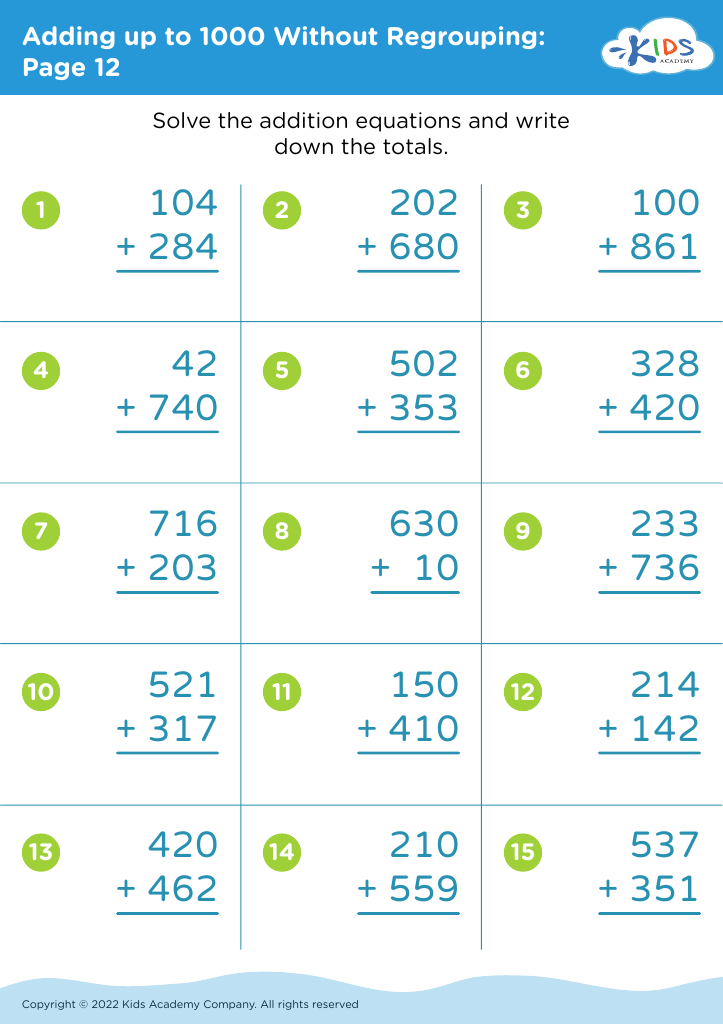
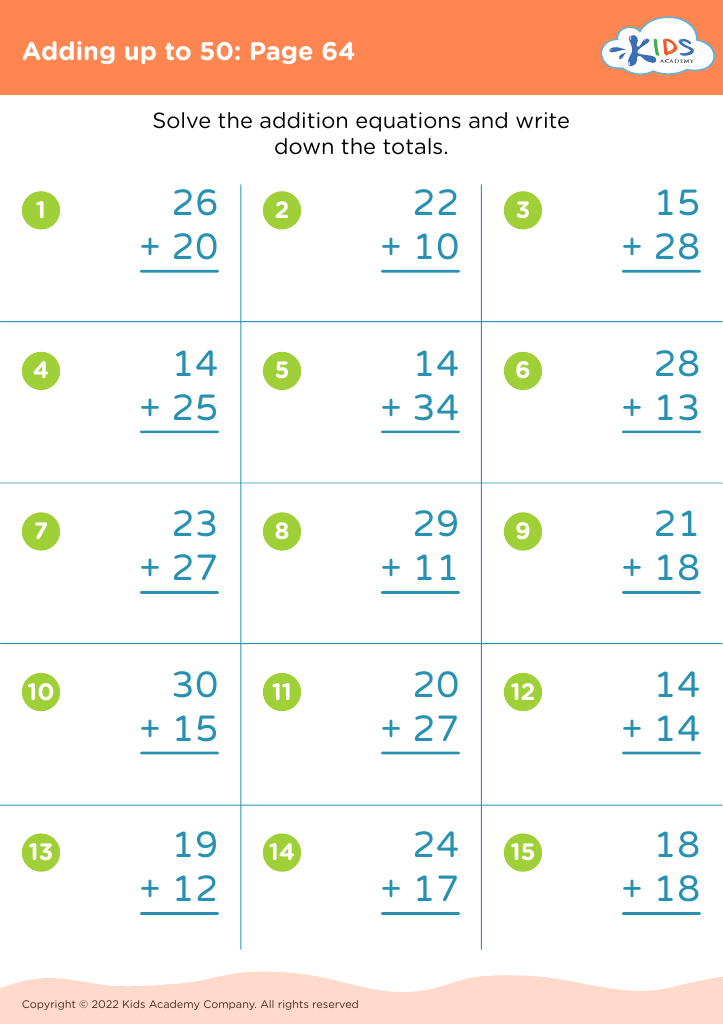
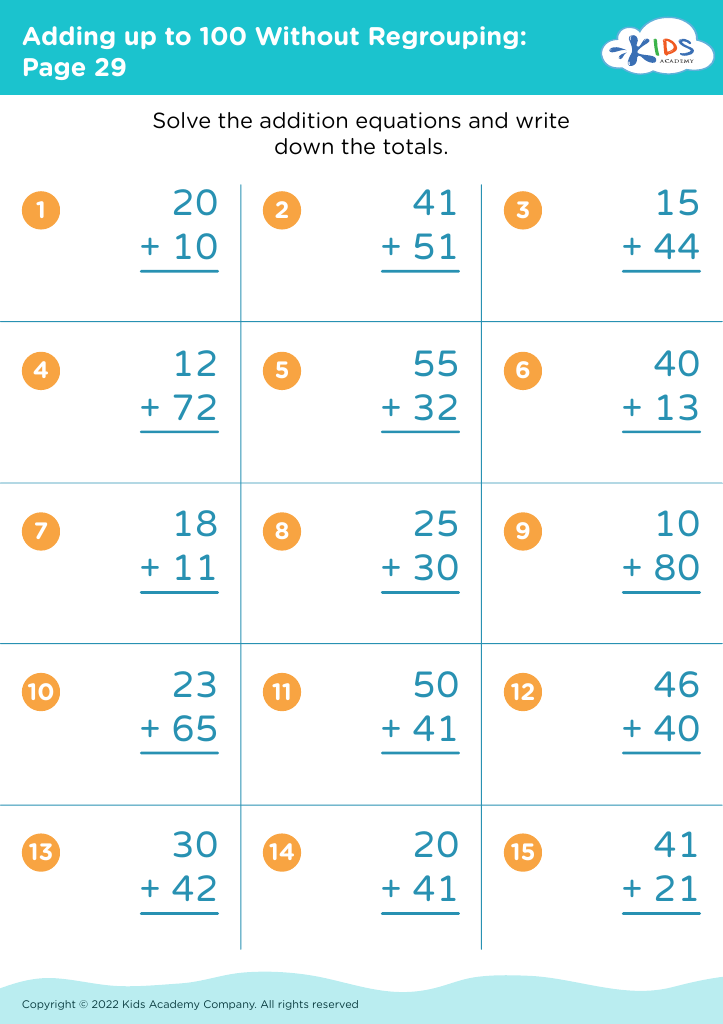
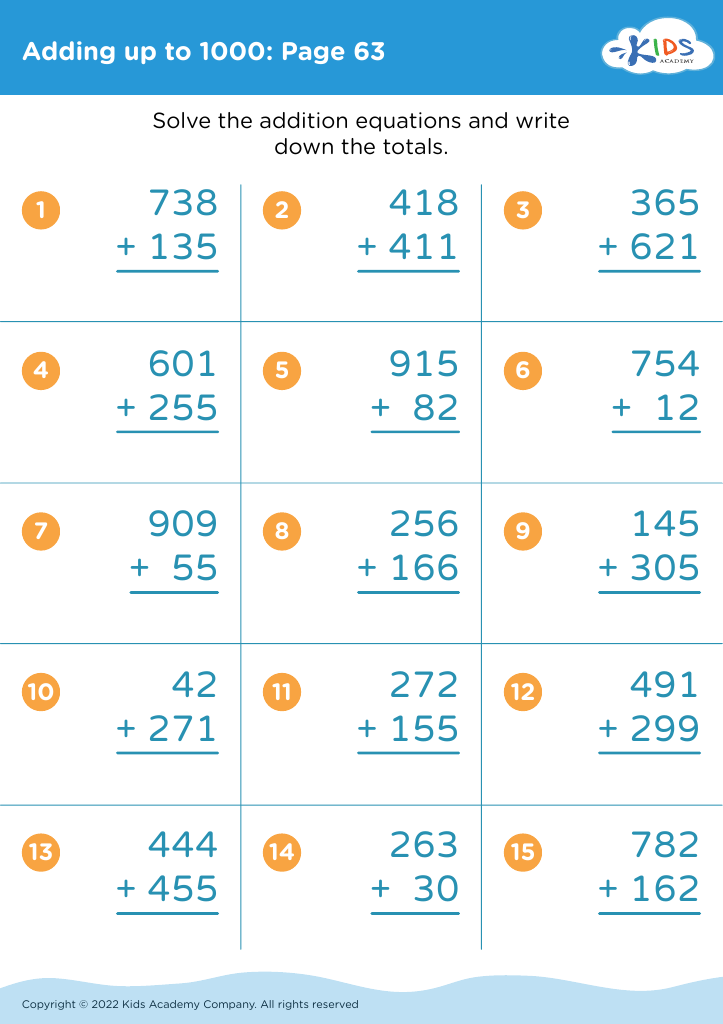
Comparing numbers Addition Worksheets for Ages 7-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock the fun of learning with our Comparing Numbers Addition Worksheets designed for children ages 7-8! These engaging worksheets help young learners sharpen their math skills by comparing and adding numbers in a variety of interactive ways. As students practice recognizing greater and lesser values, they build a solid foundation for more advanced math concepts. Our resources feature vibrant illustrations and easy-to-follow instructions to inspire curiosity and foster critical thinking. Ideal for classroom settings or home learning, these worksheets are a perfect tool to enhance your child’s mathematical confidence and fluency. Let’s make math an enjoyable journey together!
Parents and teachers should care about comparing numbers and addition for children ages 7-8 because these foundational skills are critical for mathematical development and cognitive growth. At this age, children are beginning to build a more concrete understanding of values, number relationships, and basic arithmetic operations, which are essential for later math concepts.
Understanding how to compare numbers helps children develop good number sense, enabling them to identify larger or smaller quantities and quantify objects accurately. Mastering addition promotes skills like problem-solving, logical thinking, and pattern recognition. These abilities are not just important for mathematics; they also foster critical cognitive skills that benefit learning in various subjects.
Additionally, proficiency in these areas can boost a child's confidence in their academic abilities. It can also help them engage in a variety of everyday situations—like budgeting their allowance, measuring ingredients for cooking, or telling time.
When parents and teachers prioritize comparative and additive reasoning in early education, they lay the groundwork for future learning, enabling children to tackle the increasing complexity of mathematics confidently. In essence, nurturing these skills now empowers children for both current and future academic challenges.