Observational skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 7-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
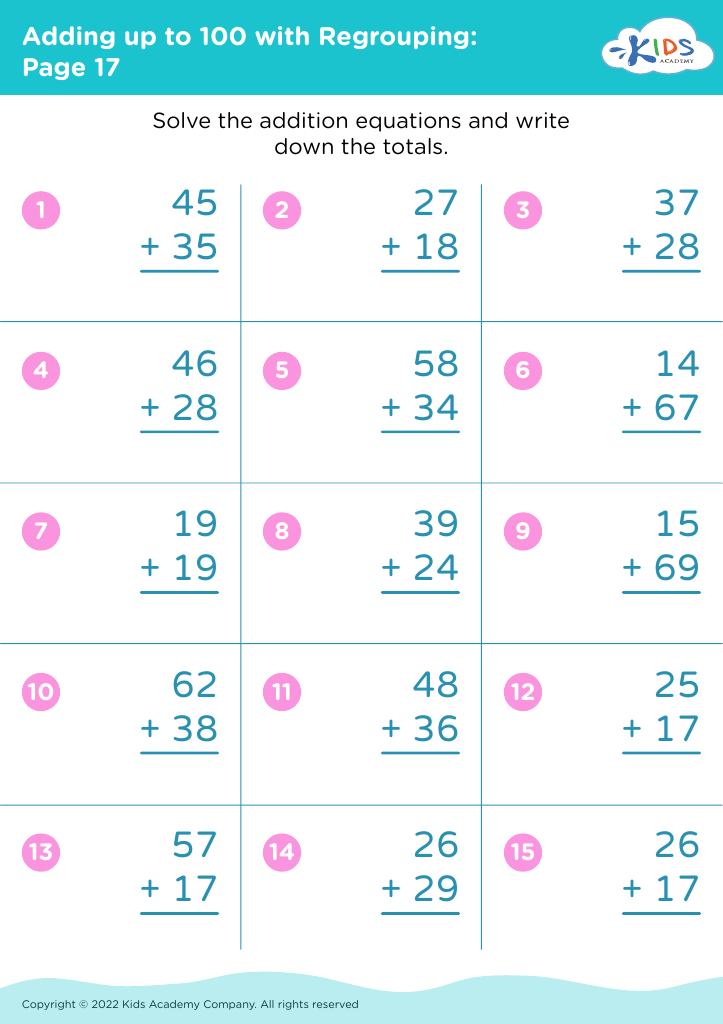
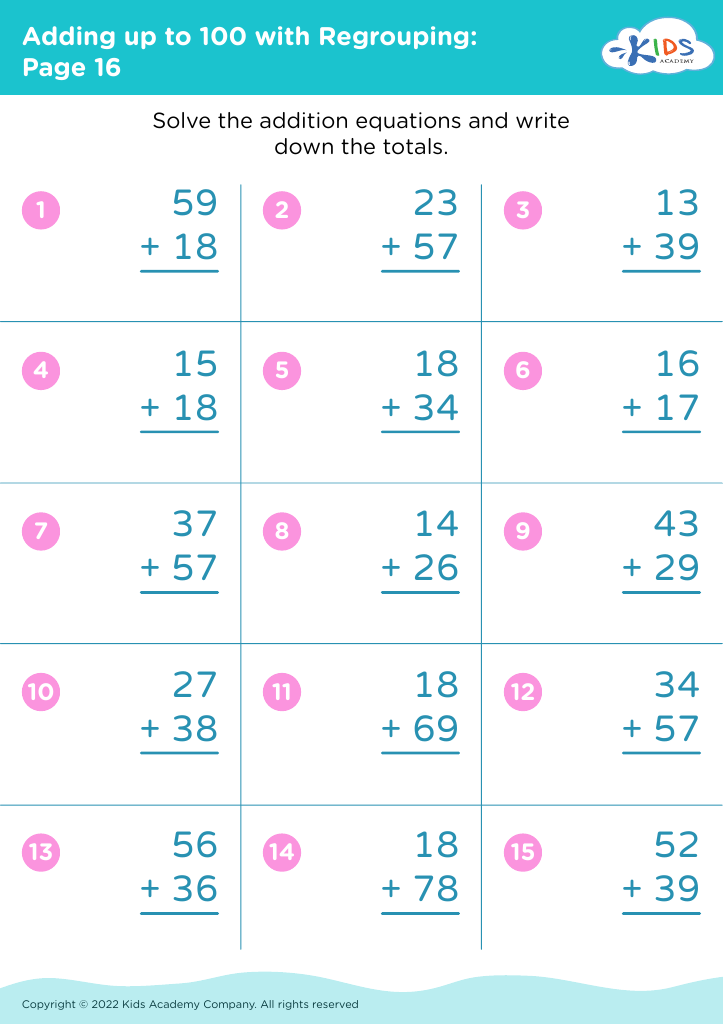
Enhance your child’s math abilities with our "Observational Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 7-9". These engaging worksheets combine fundamental math concepts with crucial observational skills, helping students to analyze and solve problems efficiently. Suitable for young learners, the carefully designed exercises feature colorful illustrations and interactive tasks to make learning fun and effective. By practicing these sheets, kids will improve their attention to detail, logical thinking, and problem-solving capabilities, building a strong foundation for future math success. Ideal for home or classroom use, these resources are perfect for nurturing confident, competent young mathematicians.


Count in the School of Magic Worksheet
Observational skills are crucial for children aged 7-9 as they enhance cognitive development and lay the groundwork for academic success. Fostering these skills specifically in the context of addition and subtraction equips young learners with practical tools to interpret their surroundings and solve real-world problems.
Attention to detail is fundamental in math; observing patterns, understanding numerical relationships, and recognizing errors strengthen a child's problem-solving capabilities. These observational skills not only help children perform accurate calculations but also support their ability to estimate and check their work—a critical aspect of developing mathematical proficiency.
Additionally, observational skills foster independence. As children learn to approach math problems with a keen eye, they become more self-reliant, reducing their dependence on parents and teachers for validation. This autonomy builds confidence and encourages a love for learning.
By investing time in nurturing observational skills related to addition and subtraction, parents and teachers are also laying a foundation for more advanced math concepts. Scaffolding these skills early promotes better academic outcomes and a deeper comprehension of math in future educational endeavors.
In summary, enhancing observational skills in young children through addition and subtraction is a proactive approach to education, fostering cognitive growth, problem-solving expertise, confidence, and a lifelong passion for learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students