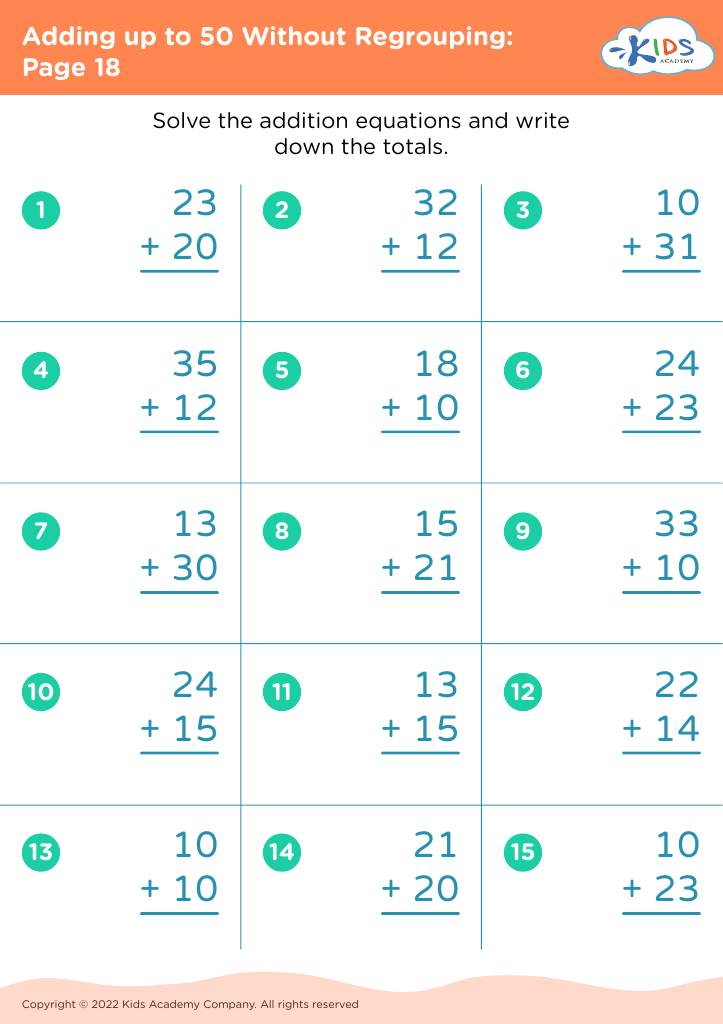
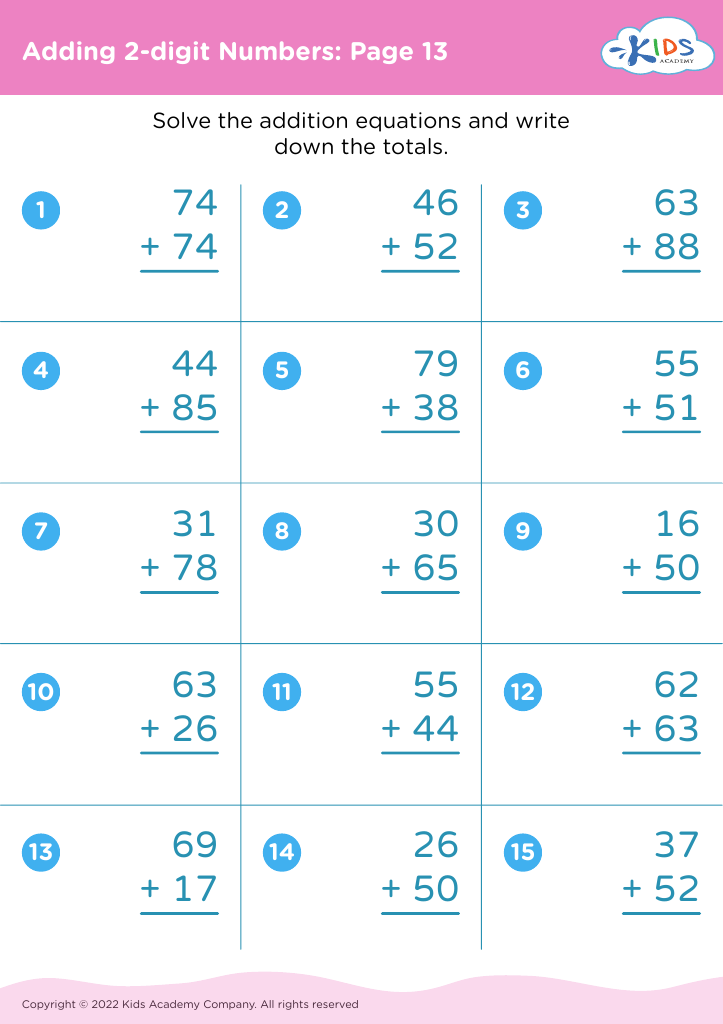
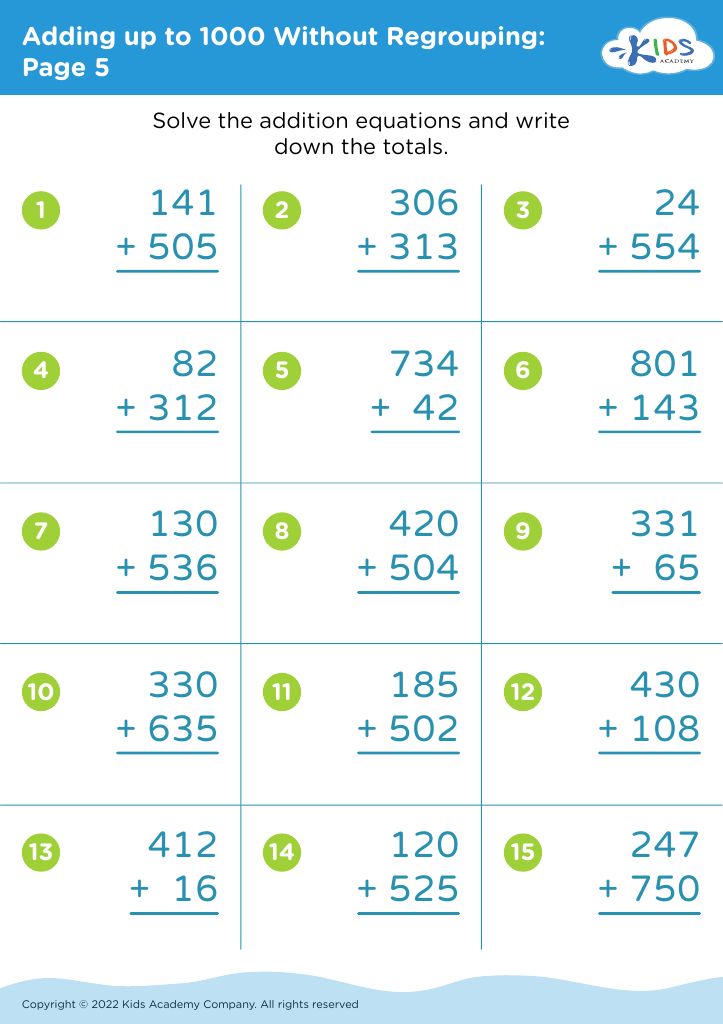
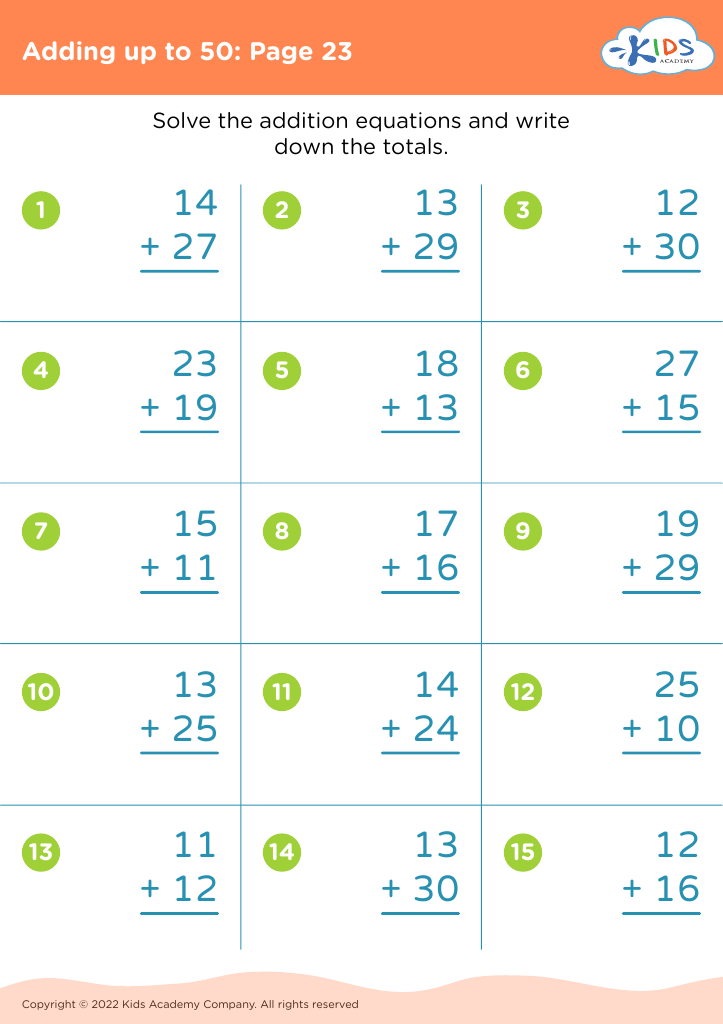
Visual representation comprehension Addition Worksheets for Ages 8-9
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's math skills with our Visual Representation Comprehension Worksheets for ages 8-9. Carefully designed, these worksheets aid in understanding addition through engaging visual aids. Students will visualize problems using diagrams, pictures, and charts, making abstract concepts easier to grasp. By offering step-by-step challenges, we ensure a solid foundation in math fundamentals, enhancing both critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Perfect for classroom use or home learning, these fun, interactive exercises will captivate young learners, building confidence and competence in their addition skills. Enhance your child’s learning journey today!
Visual representation comprehension in addition for ages 8-9 is crucial because it lays the foundation for mathematical understanding and problem-solving skills. At this developmental stage, children are transitioning from concrete thinking to more abstract reasoning. Visual aids, such as number lines, counting bars, and pictorial representations, help bridge this gap by providing tangible links between abstract numbers and real-world quantities.
Incorporating visual aids makes the concept of addition more accessible and less intimidating. It allows children to see the practical applications of addition, enhancing their engagement and motivation to learn. This form of visual learning aligns with multiple learning styles—kinesthetic, visual, and even auditory when combined with verbal explanations—therefore reaching a broader range of students.
Moreover, visual representation promotes critical thinking and cognitive development. It encourages children to identify patterns, make predictions, and understand the properties of operations, such as commutativity (understanding that 3+4 is the same as 4+3). This foundational understanding is essential for future mathematical learning, including more complex operations like multiplication and division.
Parents and teachers must pay attention to visual representation comprehension for ensuring that foundational skills are robust. Building these early mathematical competencies equips children with the necessary tools for academic success and problem-solving abilities applicable beyond the classroom.