Fine Motor Skills Easy Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Big City Buildings Worksheet


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize Fine Motor Skills development for children aged 3-4 because these skills lay the foundation for essential daily activities and academic readiness. Fine motor skills involve the small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling children to perform tasks like buttoning clothes, using utensils, and handwriting. Mastery of these skills enhances children's independence and confidence in their ability to manage personal care tasks.
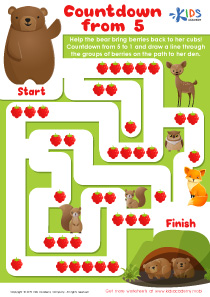
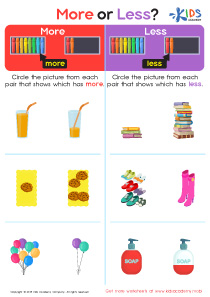
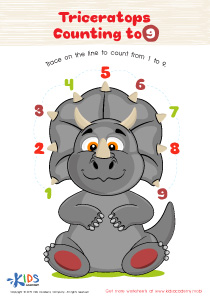
Additionally, fine motor skills are closely linked to cognitive development, particularly in early math and literacy. Activities that target these skills, such as tracing numbers, drawing shapes, and manipulating small objects, also improve hand-eye coordination and concentration. An early focus on recognizing and writing easy numbers through playful, hands-on activities prepares children for more complex mathematical concepts they will encounter in school.
Interventions and structured activities aimed at developing fine motor skills reduce the risk of learning difficulties later on. Therefore, investing time and effort into nurturing these skills offers long-term benefits, helping children succeed academically and develop essential life skills. Early childhood is a crucial period for laying the groundwork, and a solid foundation in fine motor skills significantly contributes to a child's holistic development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students