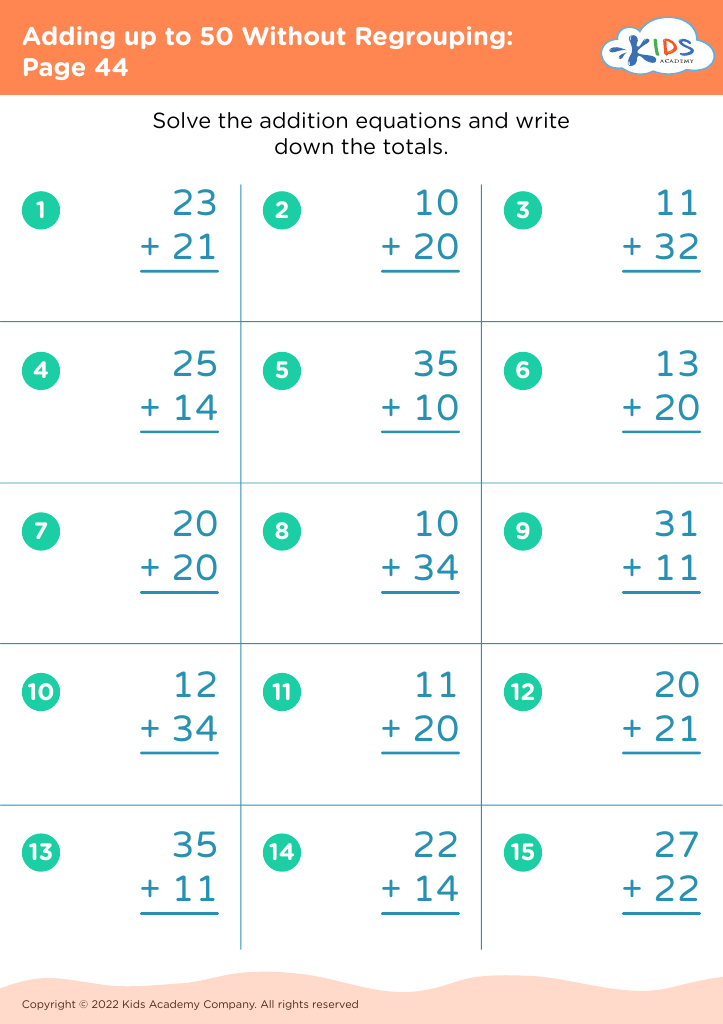
Practice handwriting numbers Worksheets for Kids
2 filtered results
-
From - To
Question/Answer
Why is the Practice handwriting numbers skill important for Grade 2 students?
The practice of handwriting numbers is important for Grade 2 students because it helps them develop fine motor skills, ensures they can accurately represent mathematical concepts, and aids in their ability to perform calculations.
What are some effective activities to train students’ Practice handwriting numbers skill when teaching them about Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping?
Effective activities for training students in handwriting numbers while teaching them addition up to 50 without regrouping include number tracing worksheets, fill-in-the-blank addition problems, collaborative number writing games, and interactive whiteboard exercises. Additionally, practicing number writing through directed drawing of objects that add up to sums within 50 can be both engaging and educational.
How does the mastery of the Practice handwriting numbers skill affect a student's performance at an early age?
Mastering the Practice handwriting numbers skill at an early age significantly enhances a student's numerical literacy, fine motor skills, and overall academic performance. It facilitates easier learning of mathematical concepts, promotes confidence and independence in numerical tasks, and supports the development of good study habits. This foundation is crucial for future success in more complex mathematical operations and academic pursuits.