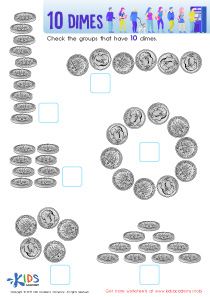
Develop fine motor skills Worksheets for Kids
13 filtered results
-
From - To
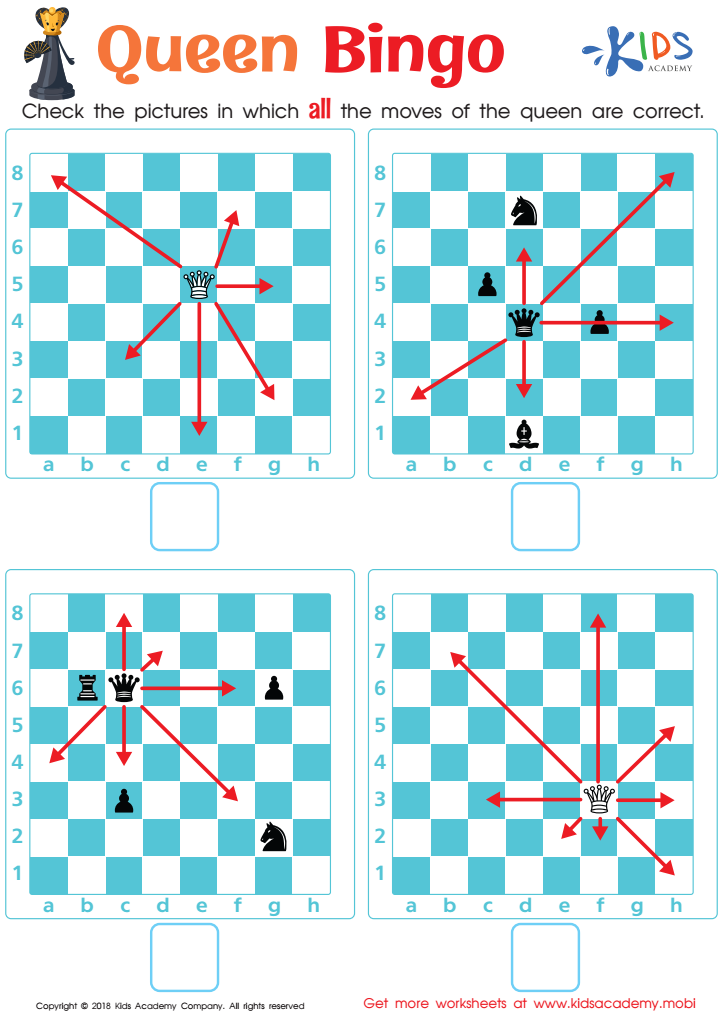

Queen Bingo Worksheet


Connecting the Monster's Socks Printable
Question/Answer
How does the mastery of the Develop fine motor skill affect a student's performance at an early age?
Mastery of fine motor skills at an early age significantly enhances a student's performance by improving handwriting, enabling better manipulation of tools like pencils and scissors, and facilitating tasks requiring hand-eye coordination. This development supports academic achievements, particularly in writing and art, and promotes independence and confidence in handling classroom activities and everyday tasks.
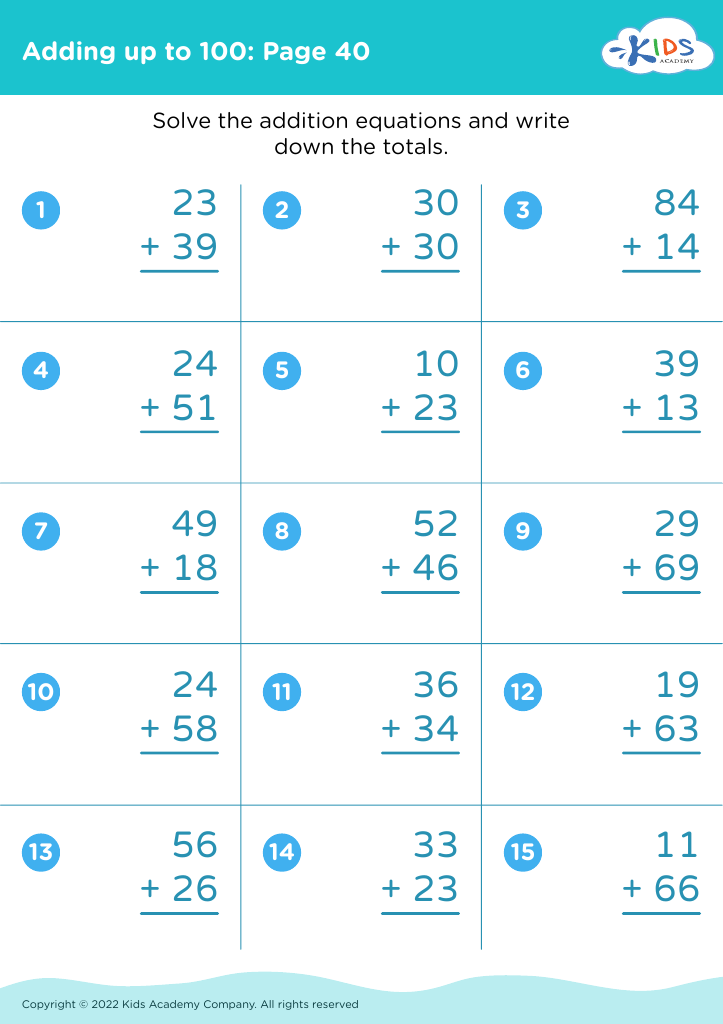
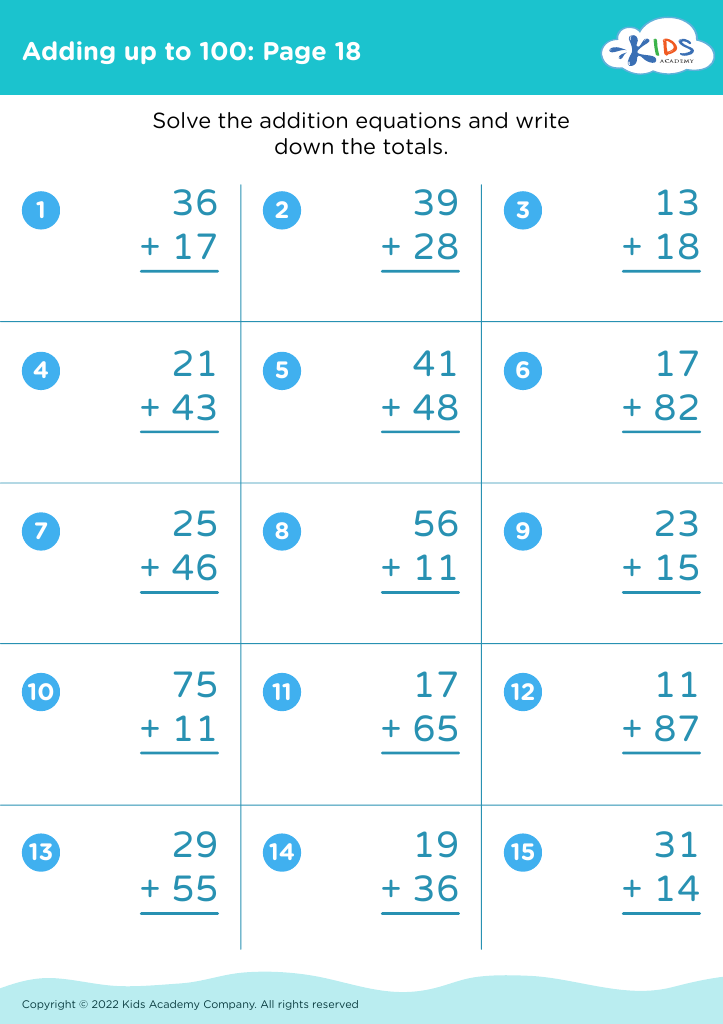
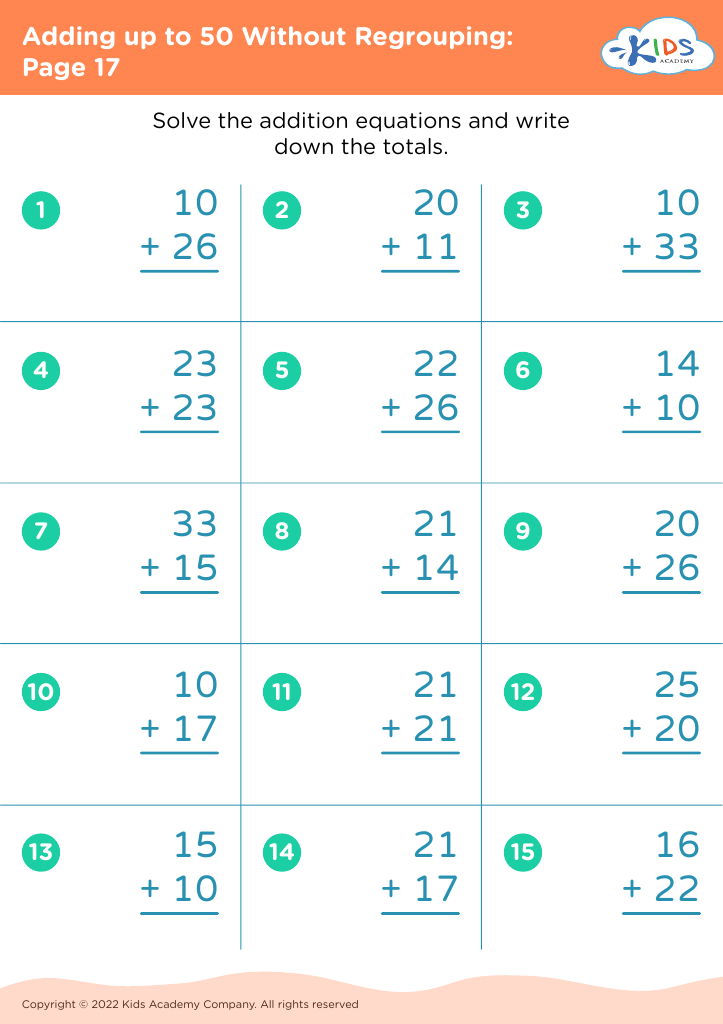
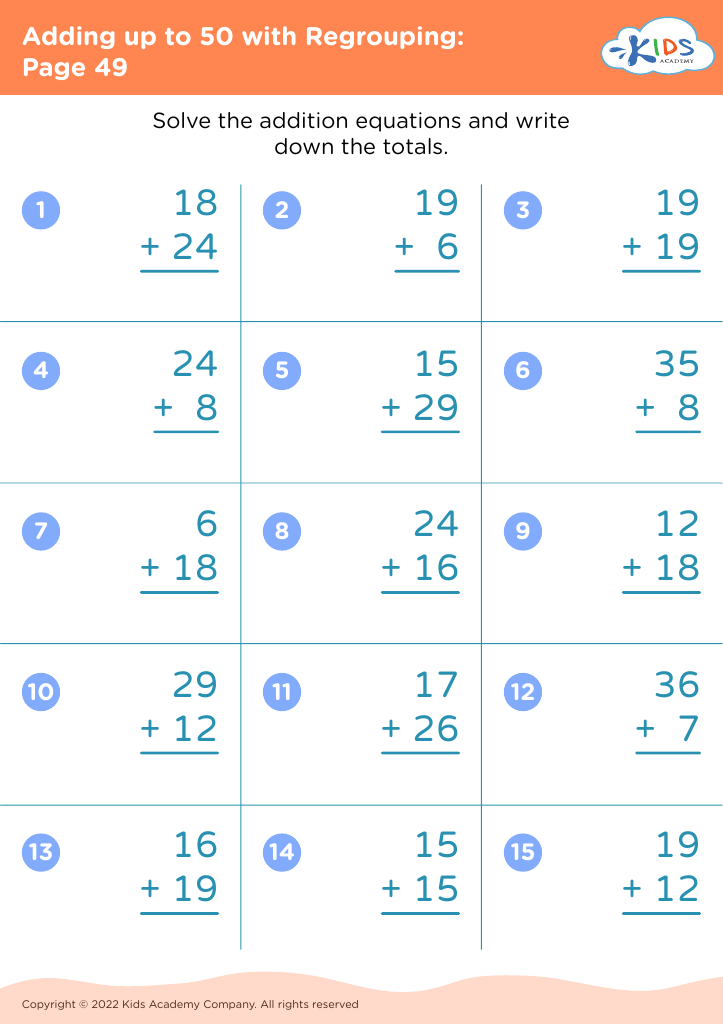
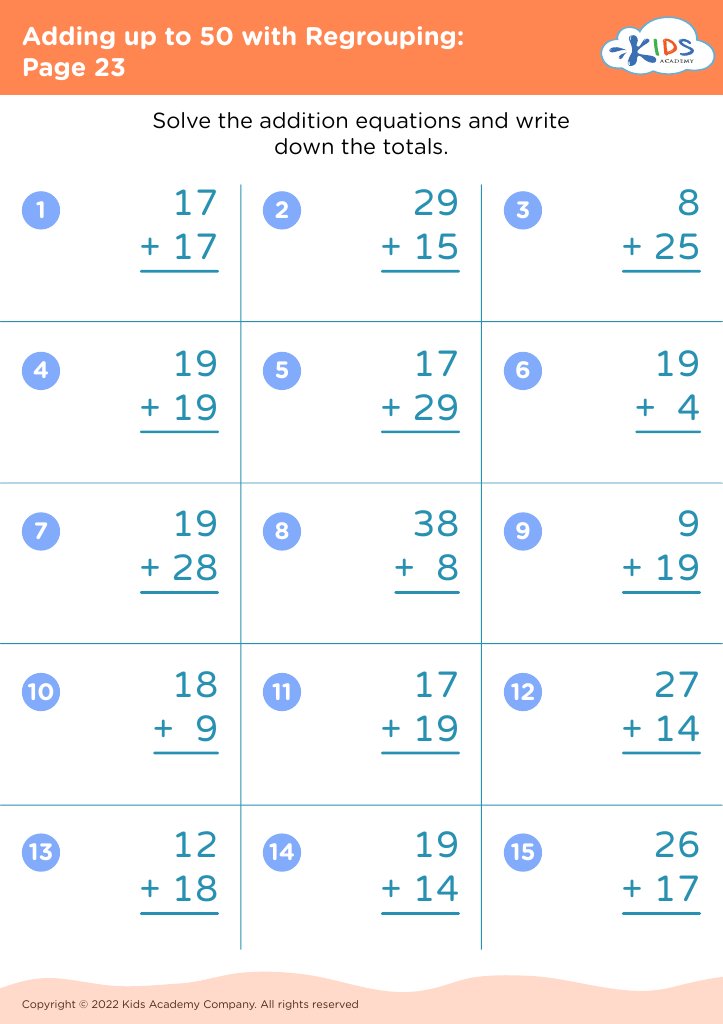
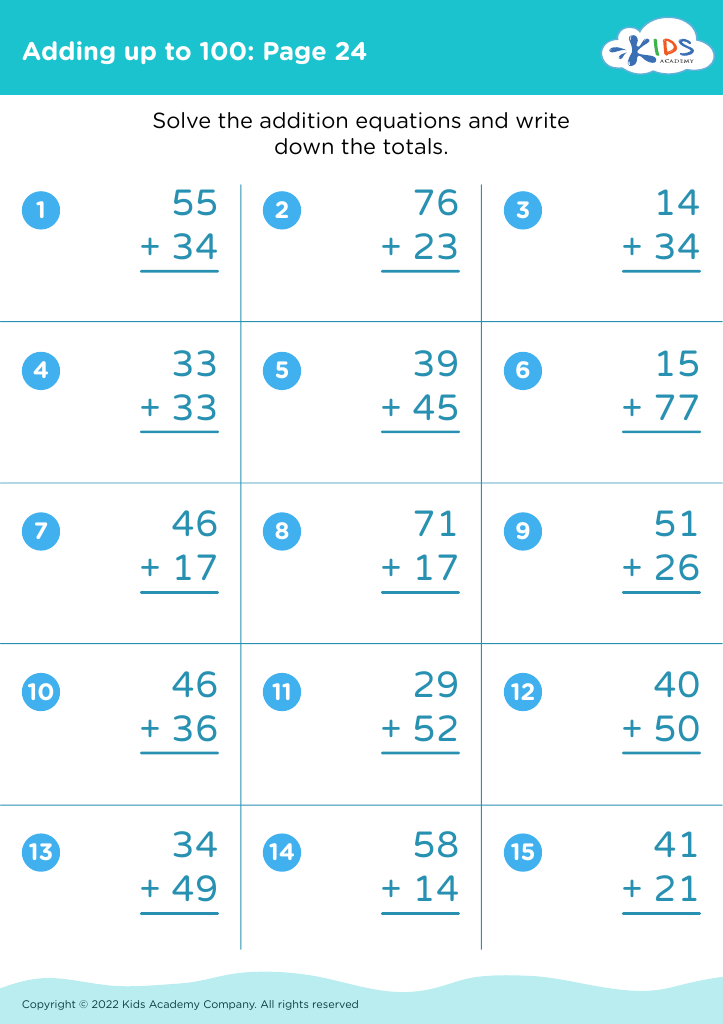
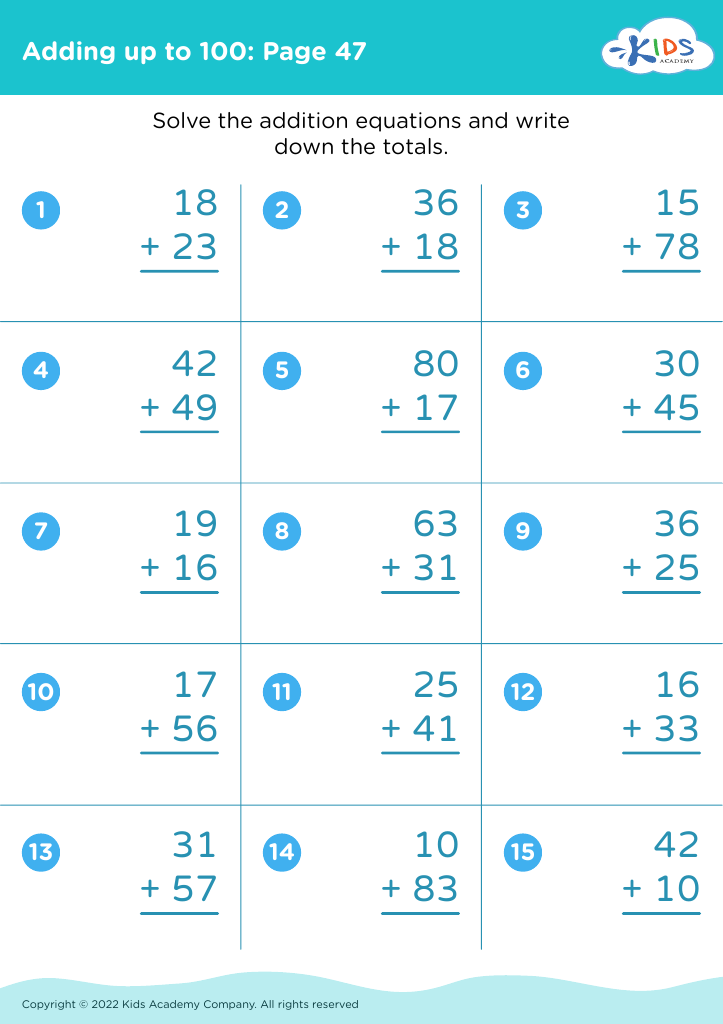
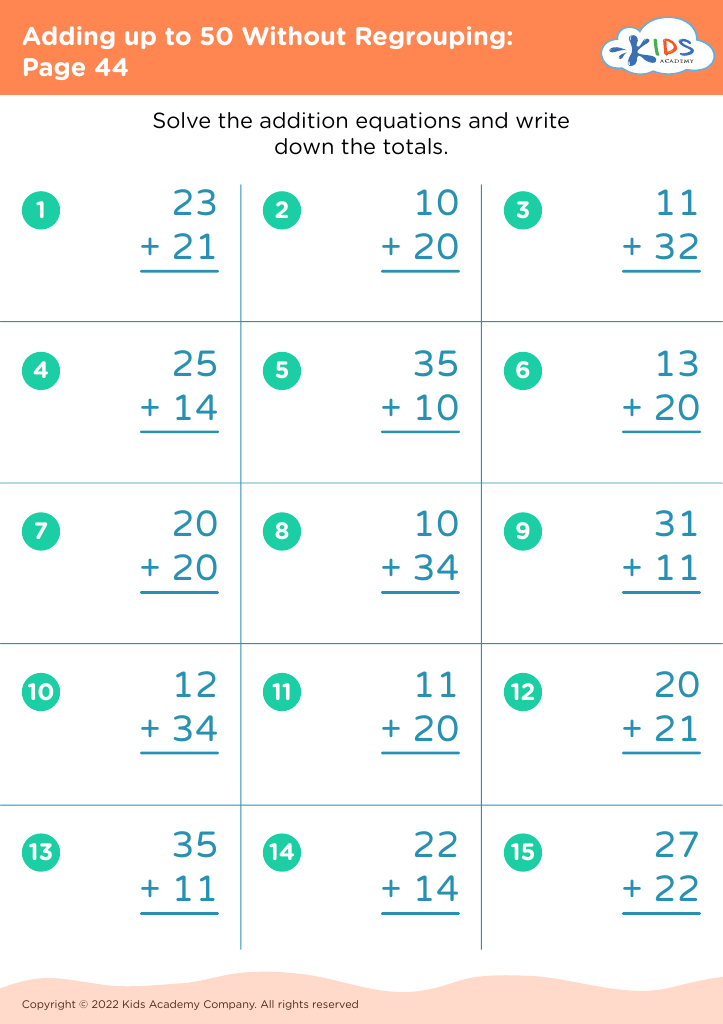
What are some effective activities to train students’ Develop fine motor skill when teaching them about Adding up to 50 Without Regrouping?
To train students' fine motor skills while teaching adding up to 50 without regrouping, incorporate activities such as using tweezers to move small objects like beads into numbered sections (up to 50) based on addition problems, threading beads on strings to match answers, and using playdough to form numbers and solve addition problems.
Why is the Develop fine motor skill important for Grade 2 students?
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for Grade 2 students as it enhances their ability to perform tasks requiring small muscle movements, such as writing, cutting, and buttoning. These skills are foundational for academic success, enabling students to complete schoolwork with greater efficiency and independence. Improving fine motor skills also supports the development of hand-eye coordination and cognitive abilities.
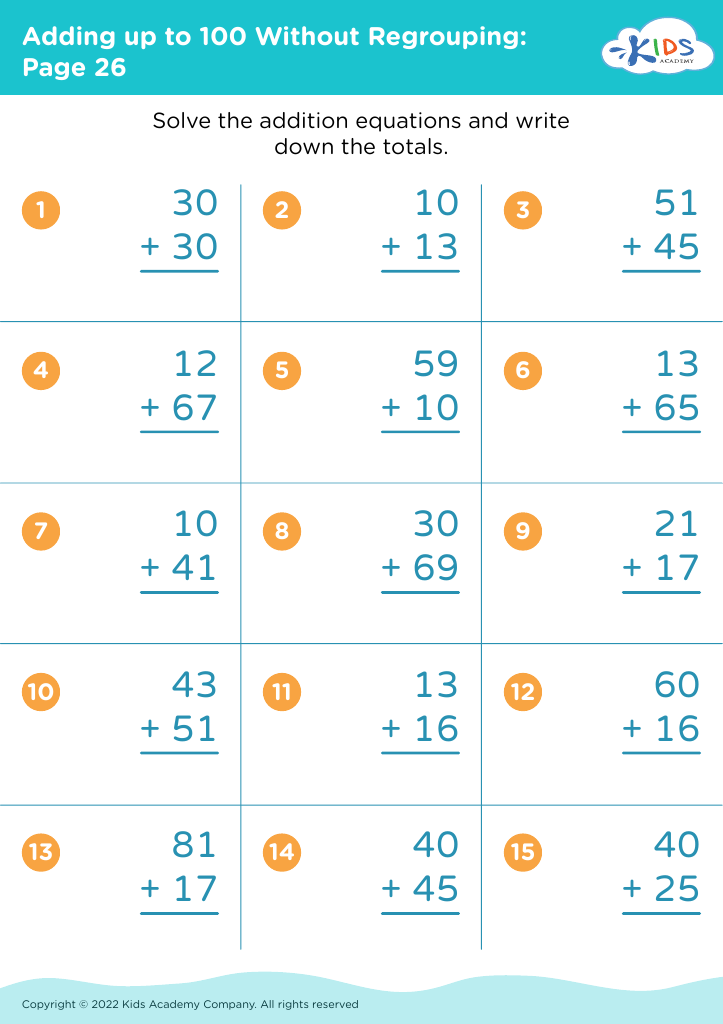
 Assign to the classroom
Assign to the classroom