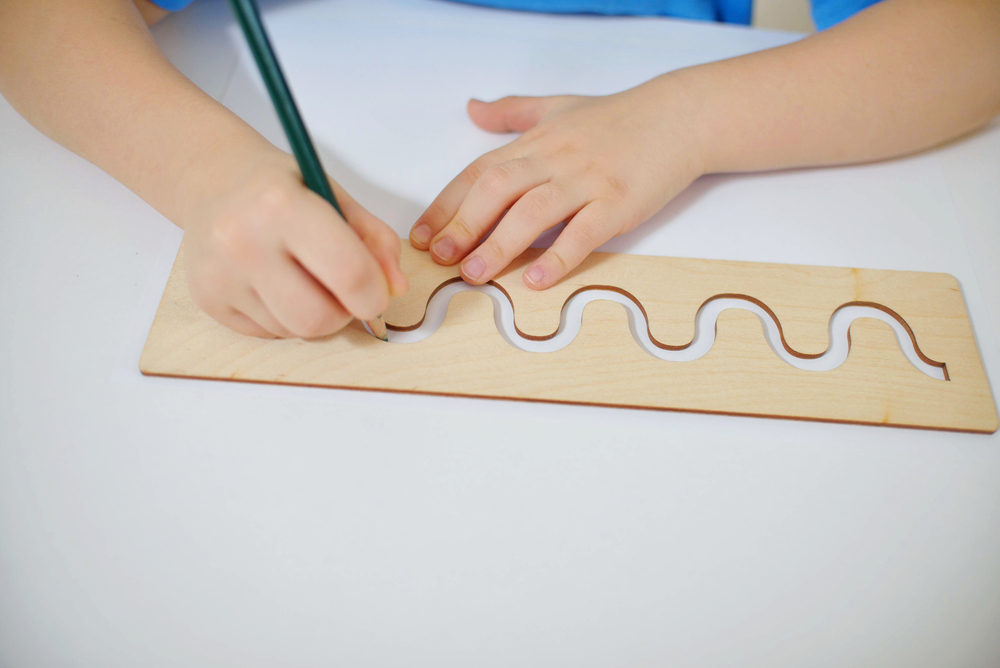
Motor skills development Normal Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Foster your child's motor skills development with our engaging Normal Alphabet Worksheets designed for ages 3-8. These worksheets provide exciting activities that help young learners practice essential writing techniques while becoming familiar with the alphabet. By tracing and writing letters, children enhance their fine motor skills, hand-eye coordination, and spatial awareness—all vital for early literacy success. Our user-friendly format encourages creativity and makes learning fun! Ideal for home or classroom use, these printable resources support physical development and pave the way for a strong educational foundation. Download now and watch your child thrive as they explore the world of letters!
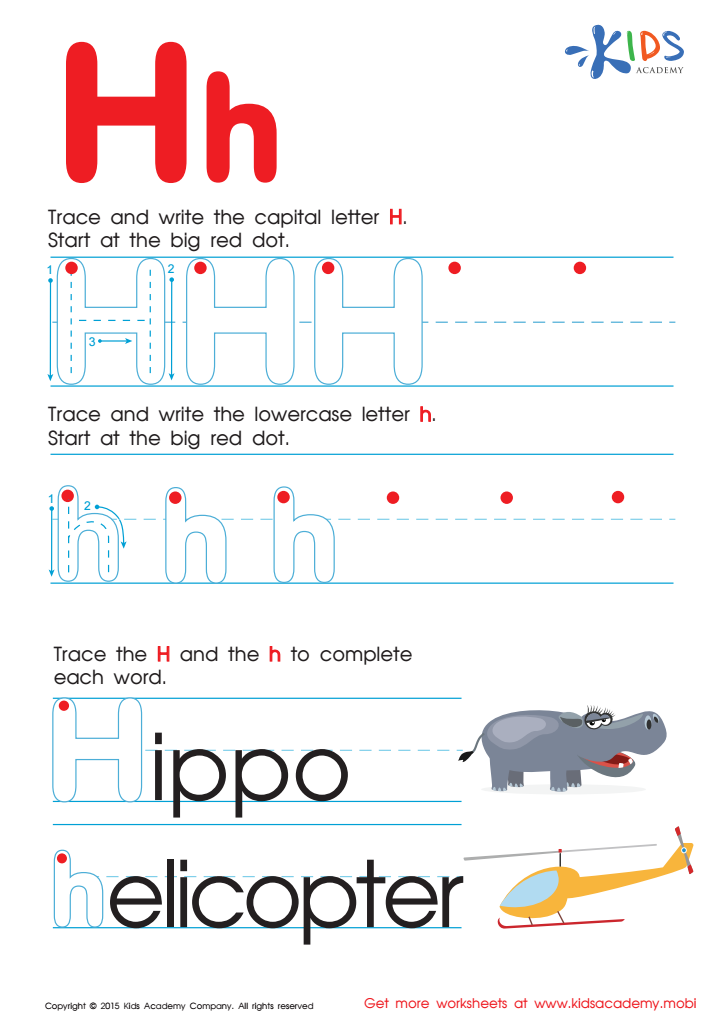

Letter H Tracing Page


Letter O Coloring Sheet
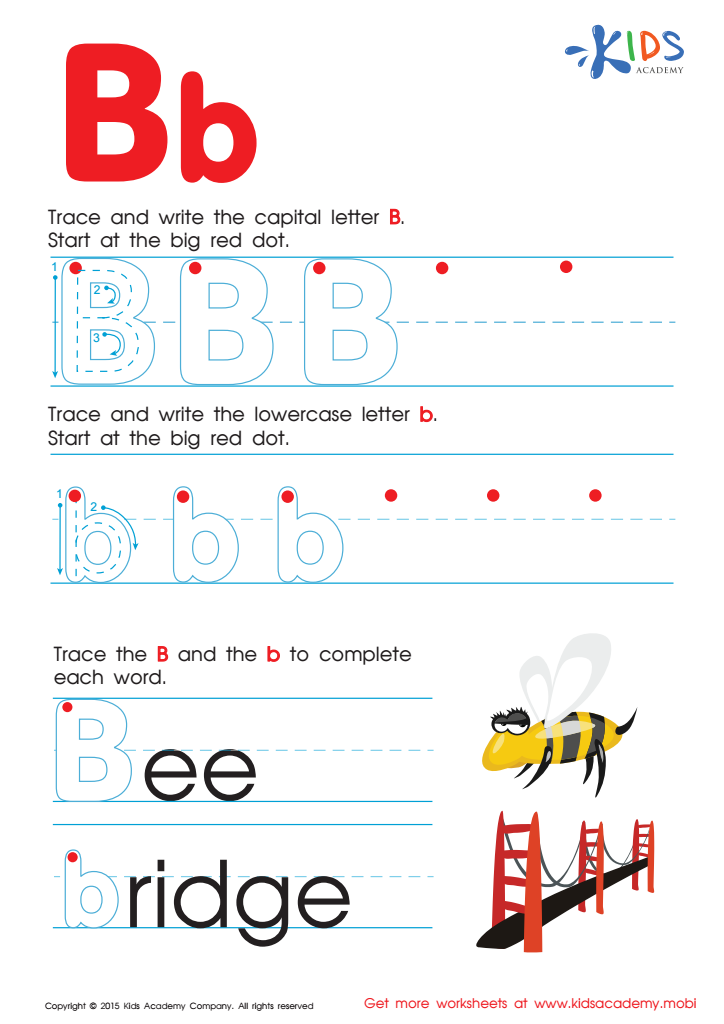

Letter B Tracing Page
Motor skills development is crucial for children aged 3-8, and both parents and teachers should take it seriously due to its far-reaching implications. Fine motor skills, like using scissors or writing, help children develop independence and confidence in their abilities. Gross motor skills, like running or jumping, are essential for overall physical health and coordination.
At this age, children are not just playing; they are learning foundational skills that affect their academic performance and social interactions. Strong motor skills enable better focus in the classroom, as children who can manipulate objects effortlessly often feel less frustration while learning. Furthermore, these skills contribute to emotional well-being, as children gain confidence when they master physical tasks.
Supporting motor skills development also fosters creativity and problem-solving abilities, essential traits for lifelong learning. Parents and teachers should provide opportunities for activities that boost these skills, such as arts and crafts, outdoor play, and interactive games. Engaging in these activities together can strengthen the bond between adult and child while nurturing a holistic approach to development.
In conclusion, prioritizing motor skills development leads to improved academic success, emotional health, and social skills—making it critical for parents and educators to engage actively in this phase of learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students















