Fine Motor Skills Normal Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-9
22 filtered results
-
From - To
Empower your child's learning journey with our "Fine Motor Skills Normal Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets," designed for ages 3-9. These engaging worksheets focus on developing essential fine motor skills while helping young learners recognize and write both upper and lowercase letters. With a variety of interactive activities, children will practice tracing, coloring, and writing letters, enhancing their dexterity and hand-eye coordination in a fun, educational way. Perfect for preschool and early elementary environments, our worksheets are easy to access and print, providing a valuable resource for parents and educators alike. Foster your child's love for learning today!


Lowercase Letters Maze Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


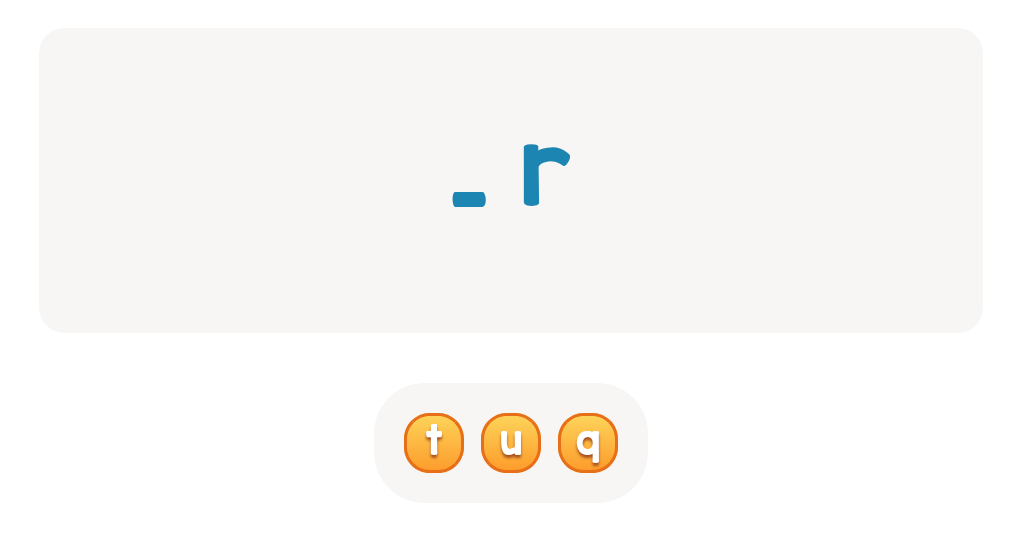
Find lowercase Letters p q r Worksheet


Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet
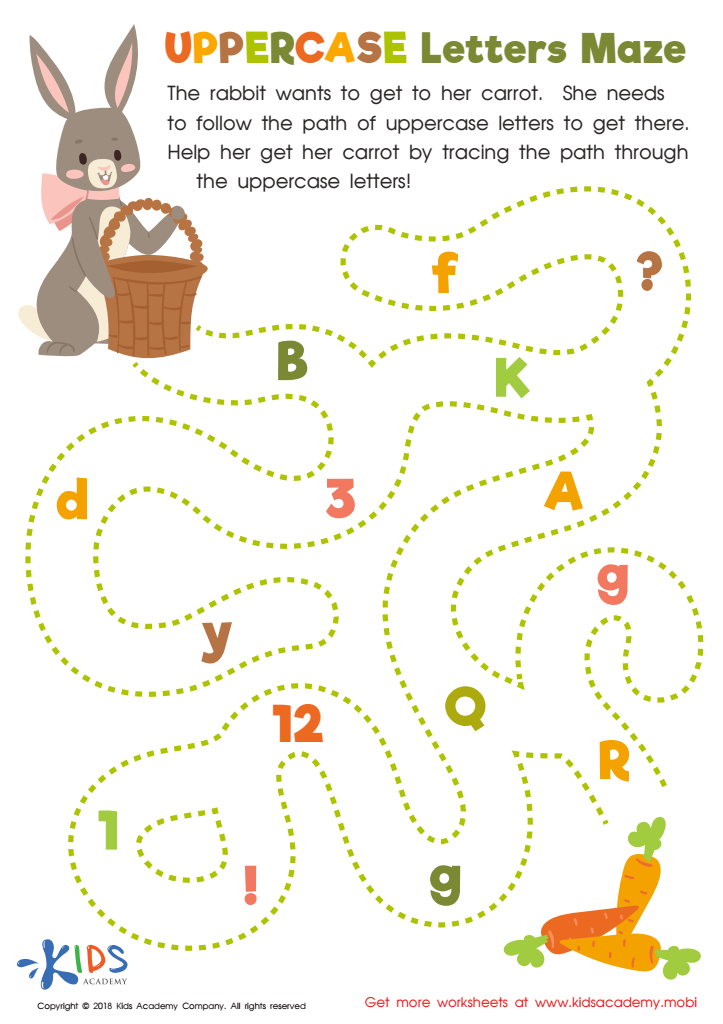

Uppercase Letters Maze Worksheet


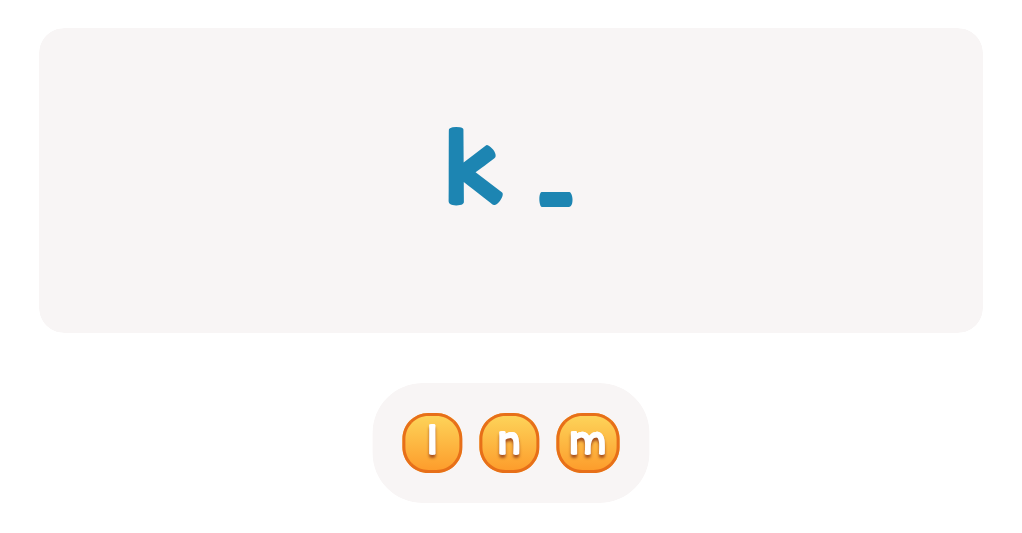
Lowercase Letters j k l Worksheet


Find lowercase Letters s t u Worksheet


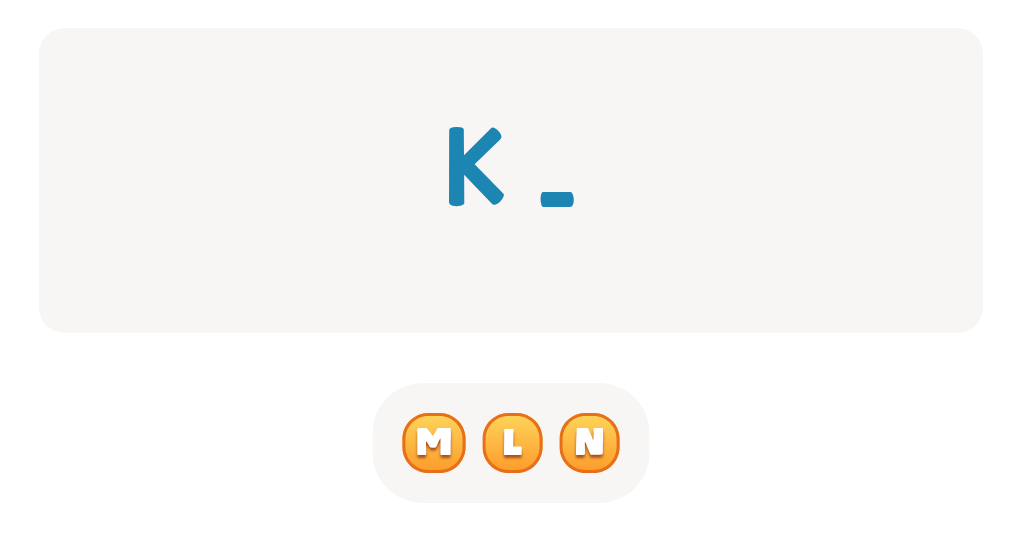
Uppercase Letters M, N, and O Worksheet


Find Uppercase Letters A, B, and C Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet


Let's Review! Big Letters Worksheet


Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Find Uppercase Letters V, W, X Worksheet


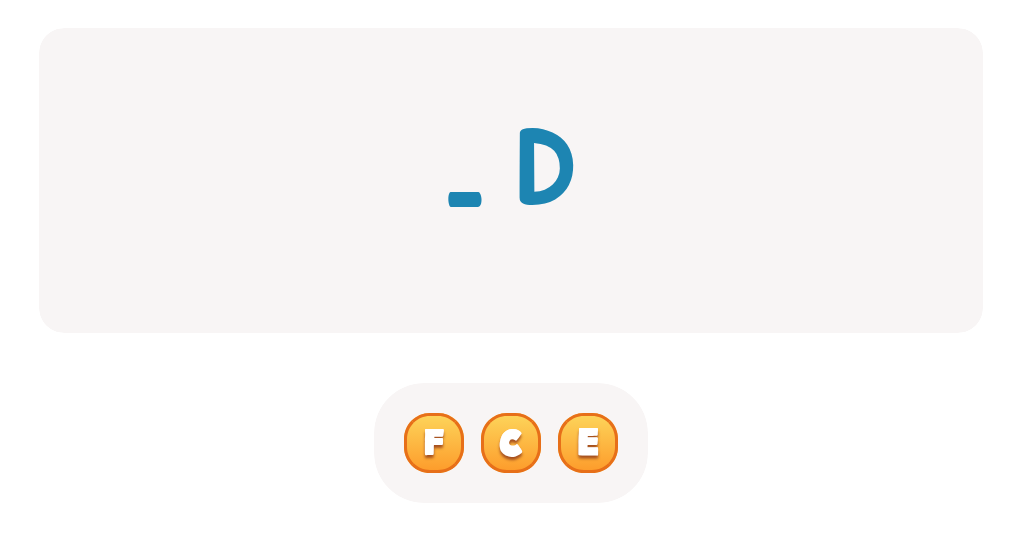
Lowercase Letters d e f Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Identifying Uppercase Letters Worksheet


Find lowercase letters a b c Worksheet


Lowercase Letters s t u Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet


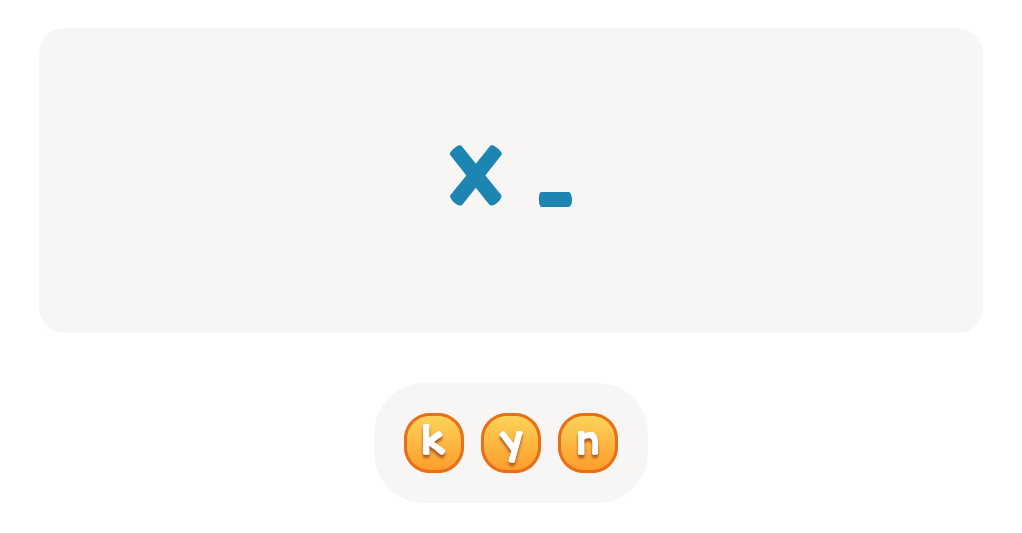
Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet


Uppercase Letters V, W, and X Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 3-9 as they lay the foundation for various everyday tasks, including writing. Developing the ability to write both uppercase and lowercase letters is crucial during this age, as it boosts not only writing strength but also hand-eye coordination and dexterity. These skills help children grasp pencils properly, control their writing movements, and maintain appropriate pressure while writing.
For parents and teachers, paying attention to fine motor skills can significantly influence a child’s academic success and self-esteem. Mastering letter formation enhances a child's confidence in their ability to express themselves through writing, laying the groundwork for future learning in literacy and mathematics, where clear, legible writing is paramount. Moreover, early mastery can prevent frustration, as children later contend with more complex writing tasks.
Fostering these skills in a fun and engaging manner—through activities such as coloring, cutting, and crafting—can promote a positive learning environment. As children show progress in handling their writing tools and forming letters, they also develop persistence and a sense of achievement, qualities beneficial for lifelong learning. Hence, focusing on fine motor development at this age is a priority for fostering holistic growth in children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students