Understanding bar graphs Grade 3 Graphs Worksheets
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Explore our "Understanding Bar Graphs Grade 3 Graphs Worksheets" designed to enhance your child's data interpretation skills! This comprehensive set of worksheets helps third graders grasp the essentials of reading, creating, and analyzing bar graphs. Through engaging activities and practical examples, young learners can practice comparing quantities, interpreting information, and making informed conclusions. Perfect for classroom use or extra practice at home, these worksheets cover key concepts aligned with grade-level math standards. Boost your child's confidence and proficiency in math with our fun and educational bar graph resources today. Visit and download now!
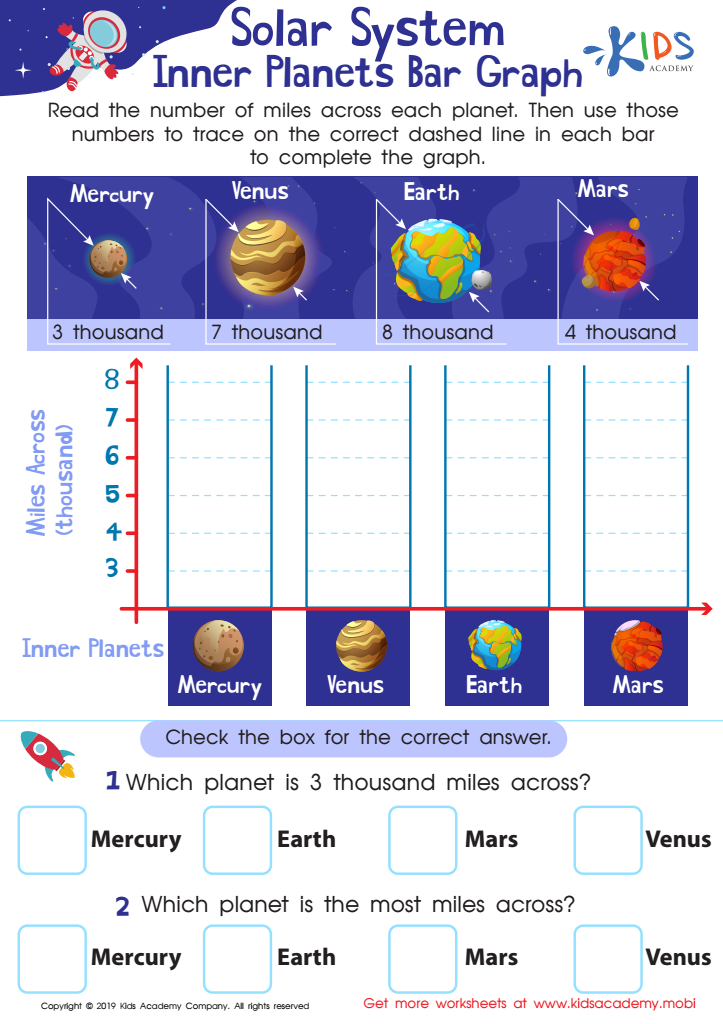

Planets Bar Graph Worksheet
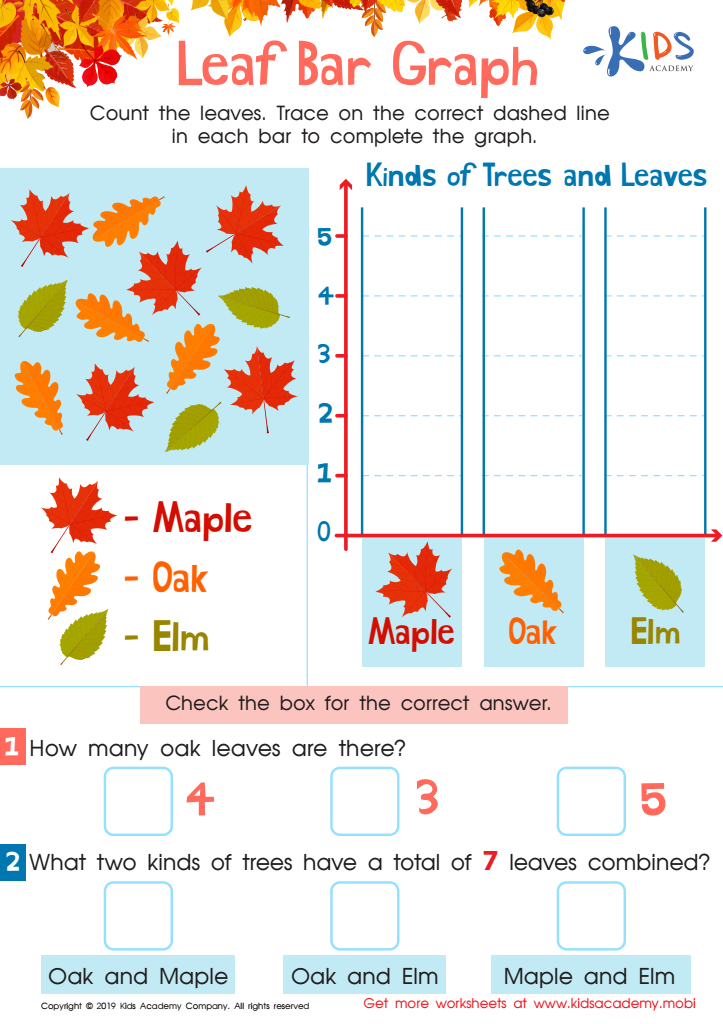

Leaf Bar Graph Worksheet


Egyptian Bar Graph Worksheet
Understanding bar graphs by third grade is crucial for several reasons. Bar graphs are fundamental tools in teaching children how to visualize and interpret data, which are valuable skills in both academic and real-world contexts. By learning how to read and create bar graphs, children enhance their math and analytical capabilities. This early exposure helps them with future subjects that rely on data representation, such as science and social studies.
In everyday life, bar graphs are everywhere—commercials comparing products, reports in news articles, and even weather forecasts. Encouraging graph literacy helps children become informed, thoughtful citizens who can critically evaluate the information presented to them. Moreover, understanding bar graphs enhances organizational skills. For instance, when a child learns to gather information, categorize it, and display it clearly, they are organizing their thoughts and presenting them coherently.
Additionally, mastering bar graphs involves several core math skills: counting, comparing numbers, addition, and perhaps even introduction to concepts like average and range. These skills serve as building blocks for more complex mathematical concepts in the future.
Thus, while it may seem simple, competence with bar graphs opens doors to numerous educational and practical opportunities, making it an essential component of the curriculum at an early age. Parents and teachers who support the development of these skills are preparing children not just for academic success but for thoughtful, data-informed living.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students