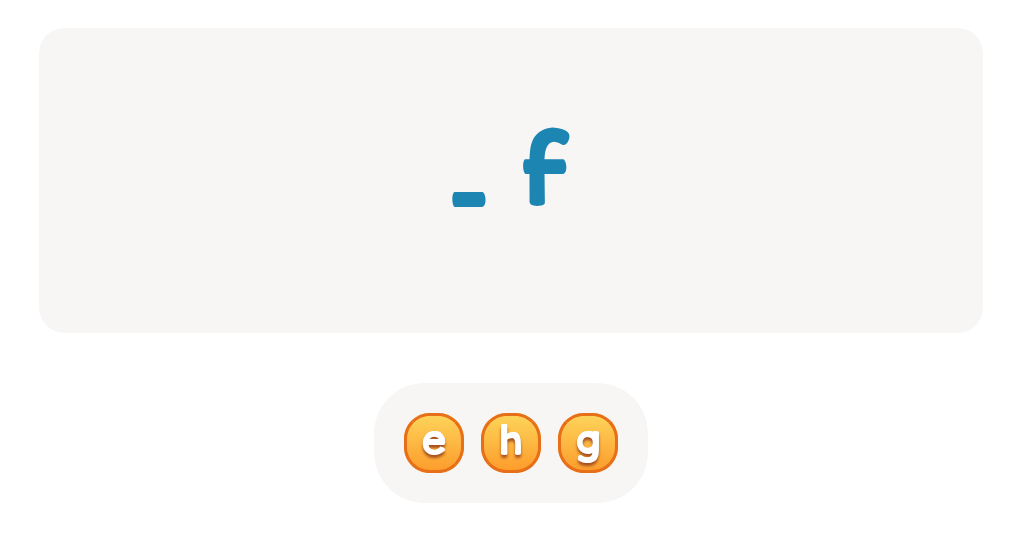
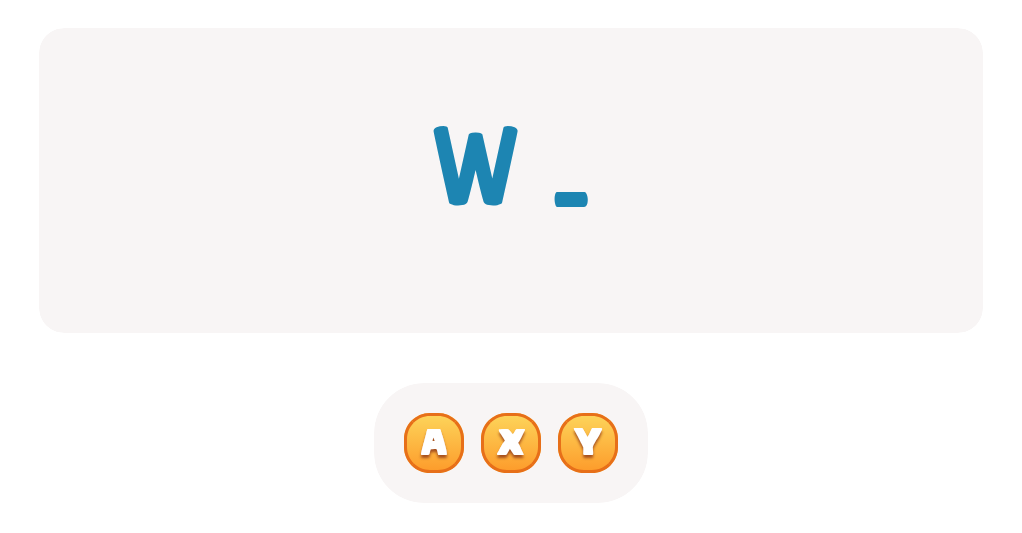
Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-5 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


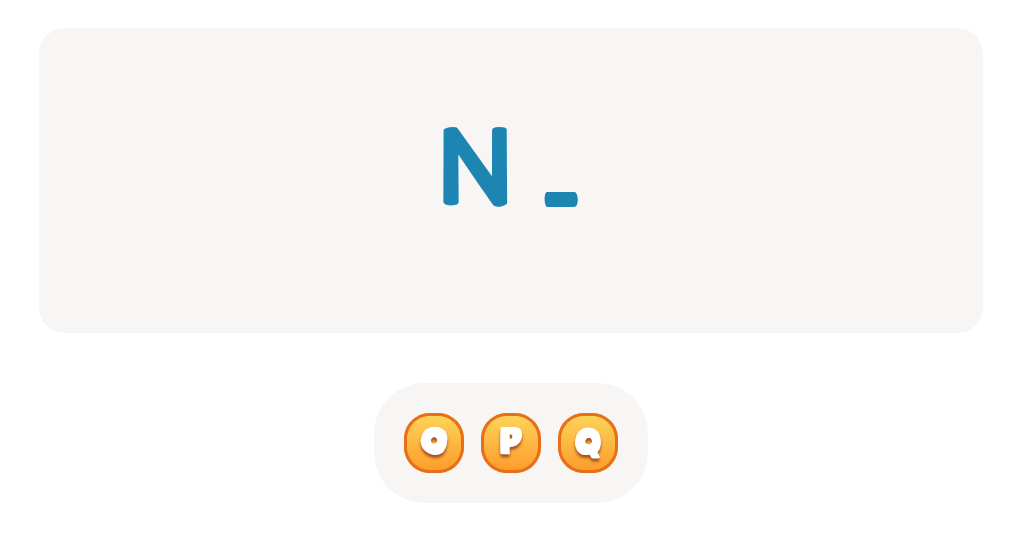
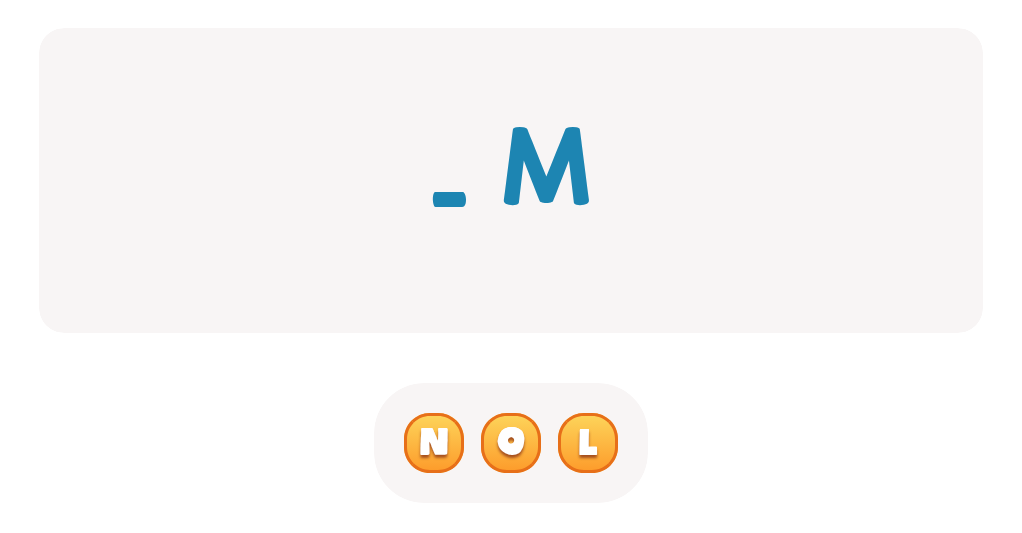
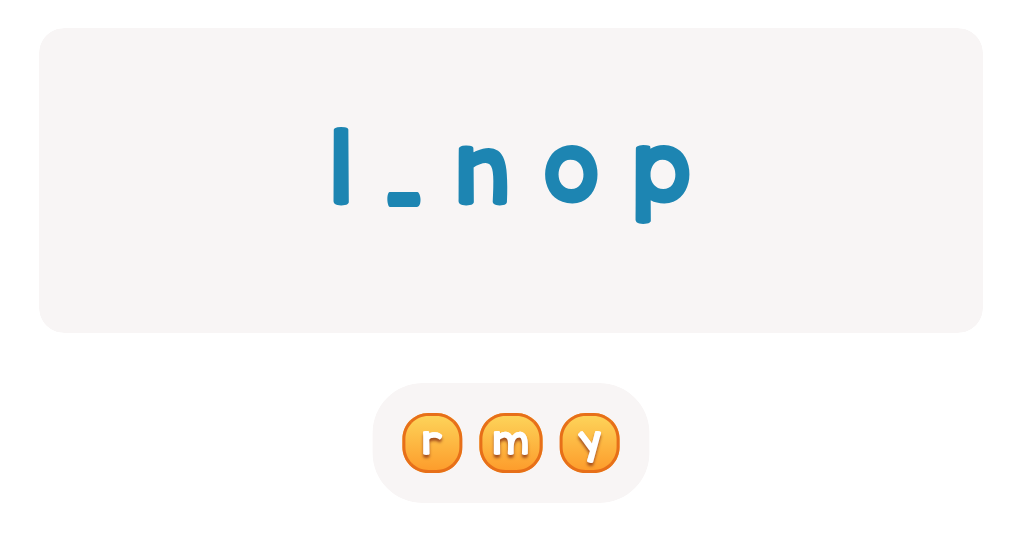
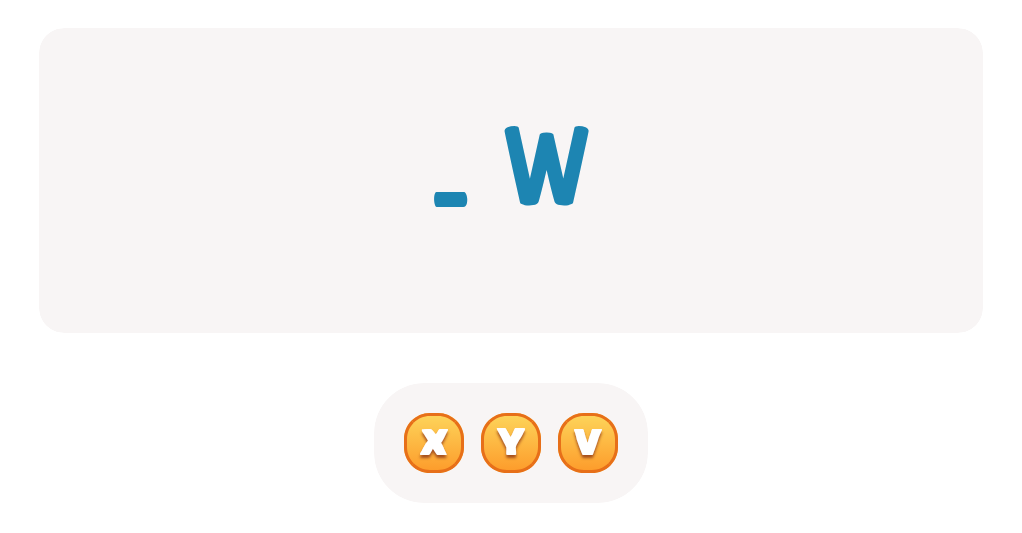
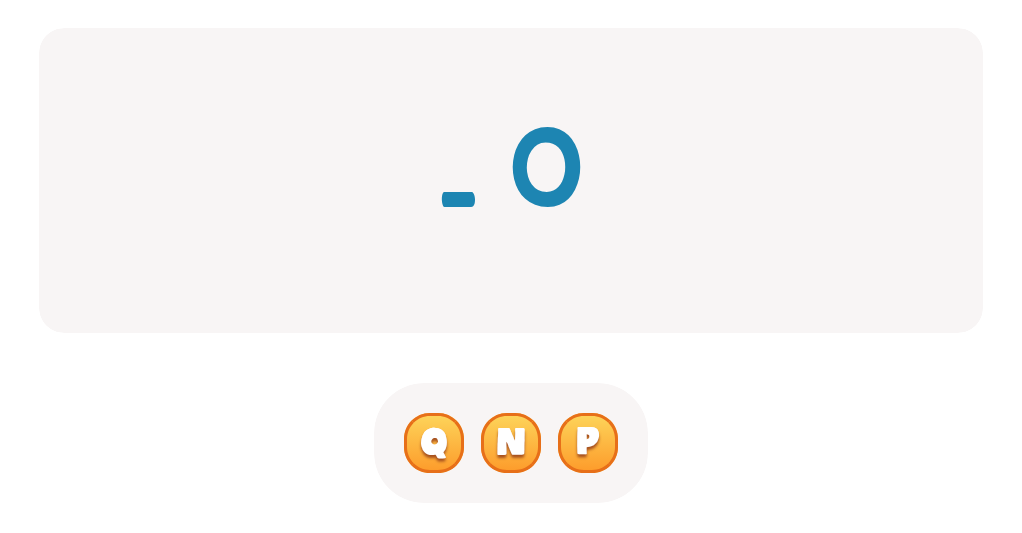
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice, particularly focusing on ABC letters for ages 3-5, serves as a crucial foundation for early childhood education, impacting cognitive and motor skills development. For young learners, practicing ABC letters enhances fine motor skills by refining hand-eye coordination, grip strength, and dexterity. These are essential competencies that will support their ability to perform tasks requiring precise hand movements, such as using utensils or tying shoelaces.
Moreover, learning to write ABC letters encourages phonemic awareness and early reading skills. As children form letters, they begin to associate specific shapes with sounds, paving the way for more advanced literacy skills. This process can also improve their concentration and attention span, fostering a beneficial routine centered around focused learning.
From a psychological perspective, achieving proficiency in handwriting boosts self-esteem and confidence. Children get a sense of accomplishment as they progress, which in turn fosters a love for learning and curiosity. Teachers and parents play a vital role in making this practice enjoyable and effective, setting a positive tone for lifelong educational experiences.
In essence, dedicating time and resources to handwriting practice for young children aids in their holistic development, blending cognitive, motor, and emotional growth, thus laying the groundwork for future academic and life success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students