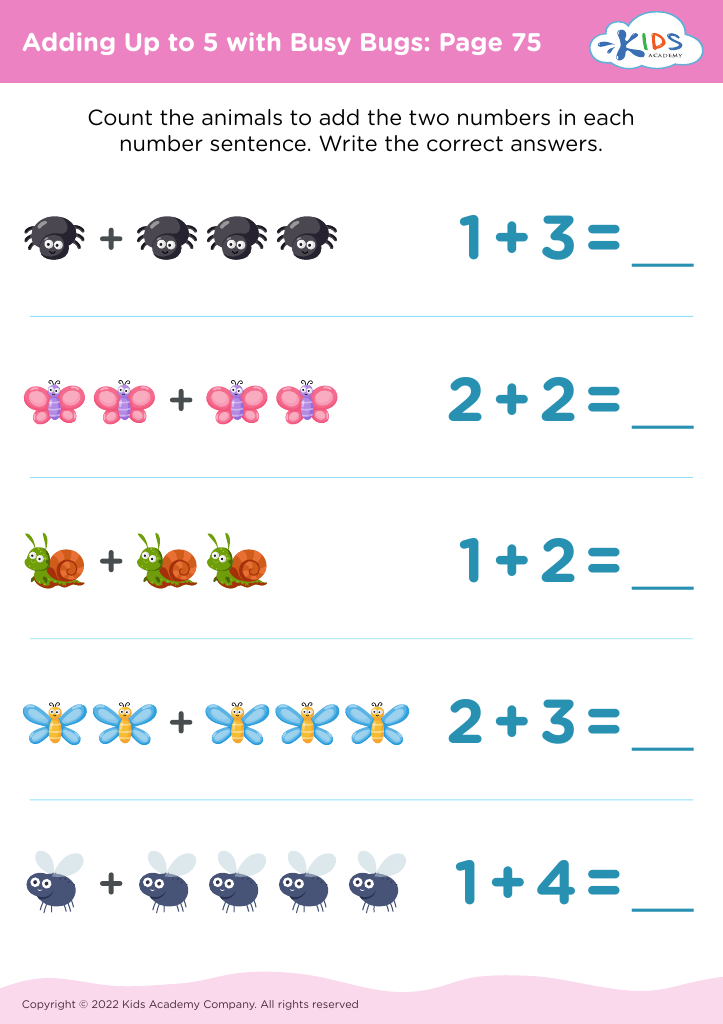
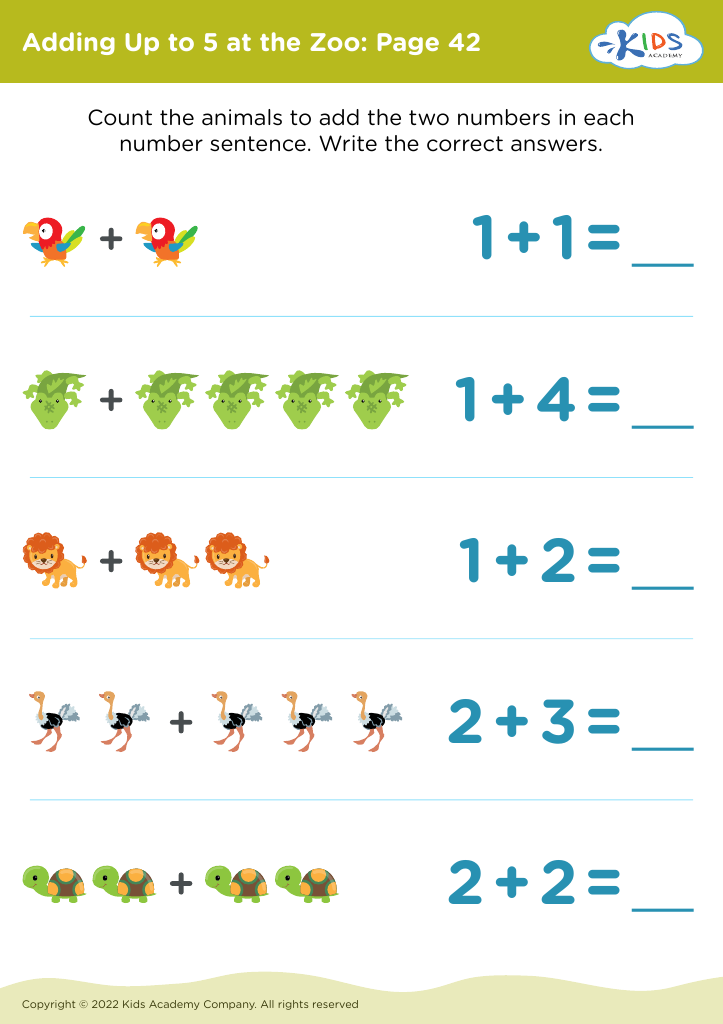Fine motor skills (writing) Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-5 - Page 2
32 filtered results
-
From - To
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children, especially those aged 3-5, as they serve as the foundation for various everyday tasks, including writing, buttoning shirts, and using utensils. Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills development because they play a significant role in a child's overall cognitive, social, and emotional growth.
At this age, children are eager to explore the world around them, and engaging in activities that promote fine motor skills fosters independence and confidence. Writing, in particular, isn't just about putting pencil to paper; it's a complex task that requires coordination, control, and concentration. By encouraging children to practice writing, parents and teachers help them develop concentration and perseverance.
Additionally, strong fine motor skills lay the groundwork for literacy. Children who can manipulate writing tools will have better handwriting and be more willing to express themselves through writing, supporting their communication skills.
Moreover, these skills are intertwined with other areas of learning, such as numeracy, as children learn to draw shapes, count, and conduct other mathematical explorations. Overall, promoting fine motor skills during early childhood is essential for a child's successful academic journey and life skills development.