Understanding prepositions Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-5
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Understanding Prepositions Geometry Worksheets" for ages 3-5 offer an exciting and engaging way for young learners to develop essential geometry skills. Through colorful and interactive activities, children will learn to recognize and use prepositions like above, below, next to, and more, all while enhancing their spatial awareness. Perfect for early educational settings or home practice, these worksheets will keep kids captivated and motivated. Start building a strong foundation in geometry and language skills today with our specially designed resources that support Cognitive Development and align with early learning standards. Embark on a fun-filled learning adventure with us!
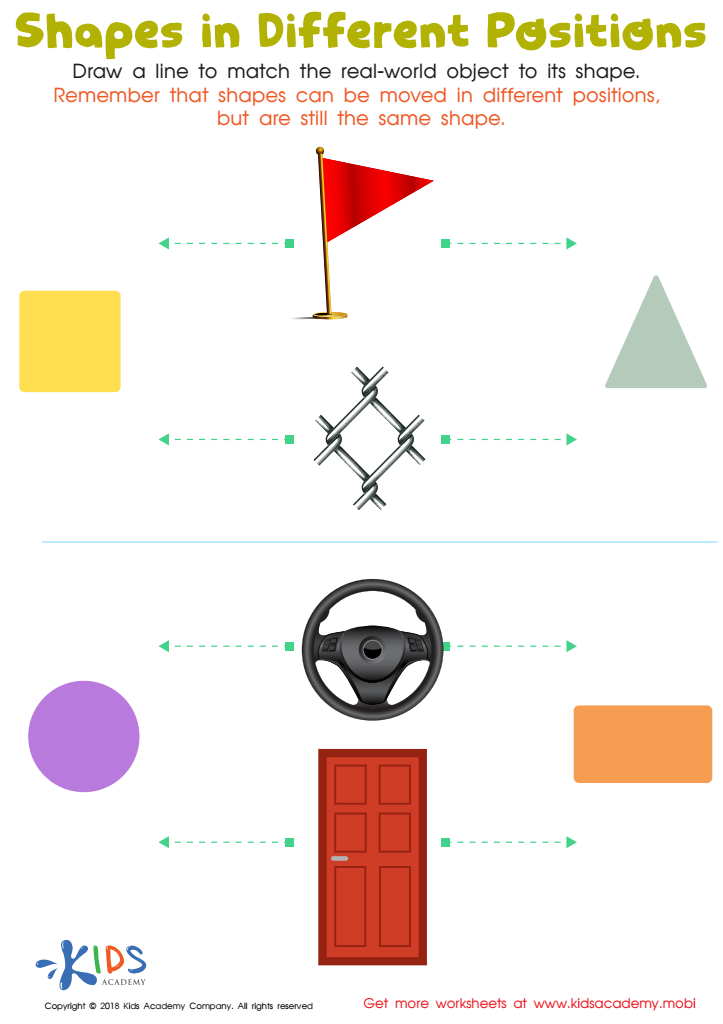

Shapes in Different Positions Worksheet
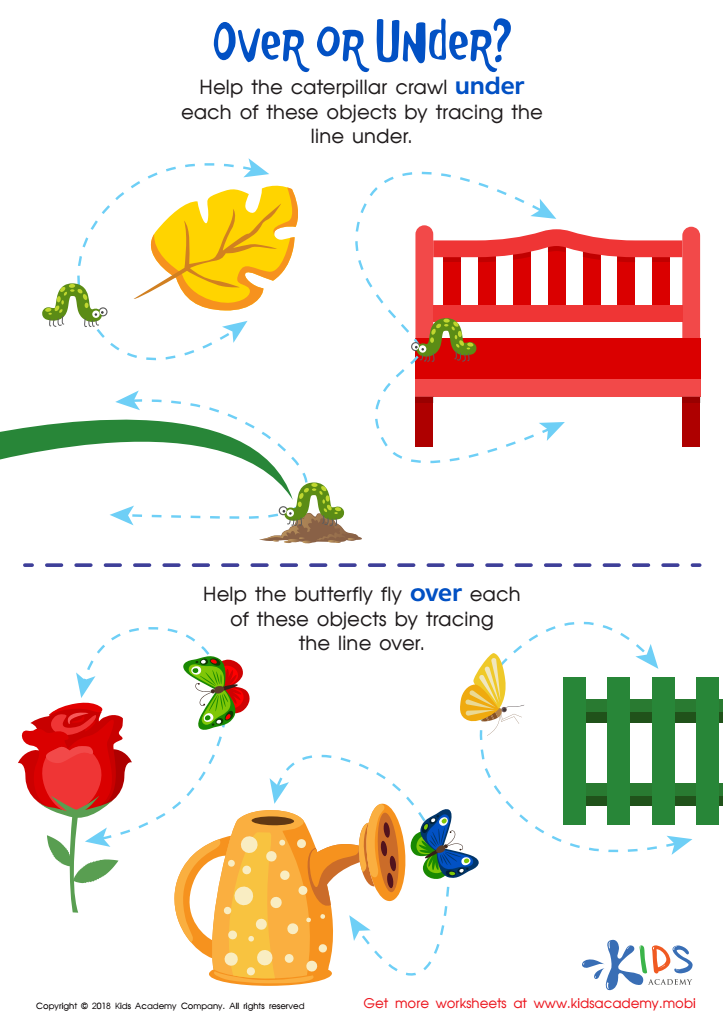

Over or Under? Worksheet


Over or Under Worksheet

In Front or Behind Worksheet
Understanding prepositions in the context of geometry is crucial for children between the ages of 3 to 5 because it forms the foundation for both language and spatial awareness. Prepositions like "above," "below," "beside," "behind," and "in front" are fundamental in describing the relationships between objects in space. Mastering these concepts can significantly aid in vocabulary expansion and enhance communication skills.
In terms of cognitive development, grasping spatial relationships is essential. It helps young children make sense of the world around them and aids in everyday problem-solving tasks, such as navigating spaces or even understanding location-based instructions. For instance, knowing the difference between “under the table” and "on the table" is essential for following directions in daily activities.
Moreover, early exposure to spatial language can boost mathematical thinking. Prepositional geometry helps lay the groundwork for more advanced mathematics and sciences. Recognizing shapes and their positions improves a child's ability to engage with more complex geometric concepts later in school.
Parents and teachers play a crucial role by incorporating simple activities like story-telling using spatial terms, interactive play, and guided explorations of surroundings. Such enriching experiences foster both linguistic and cognitive growth, ensuring a smoother transition to formal education. Understanding these basics invites children into a world of learning that extends far beyond the early years.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students