Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 4
88 filtered results
-
From - To


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet
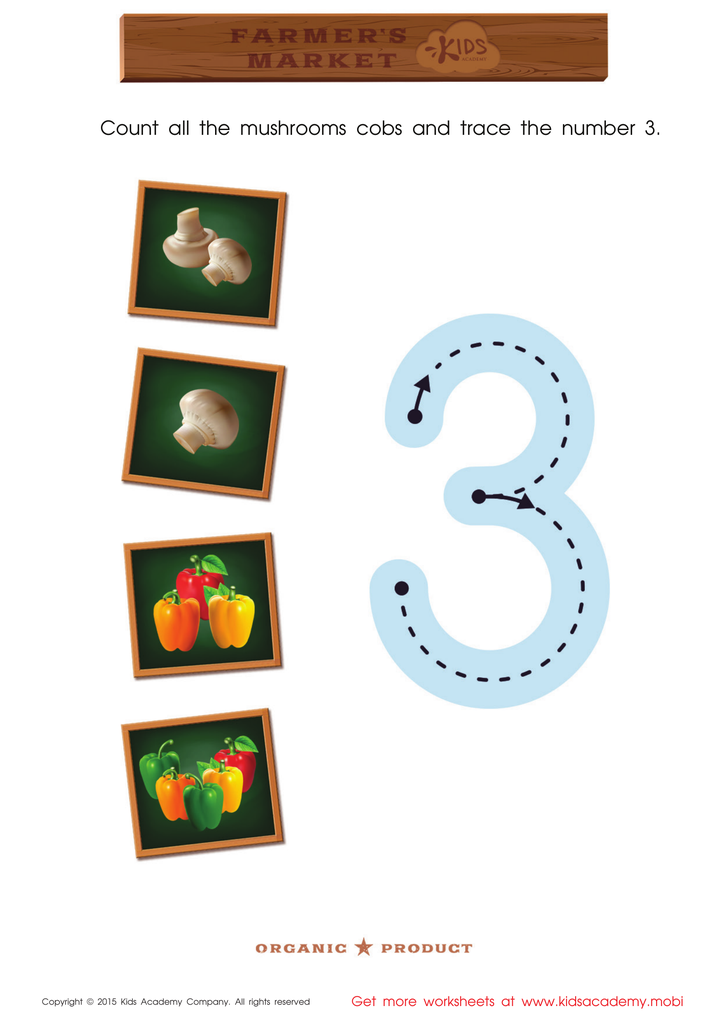


Count the Mushrooms and Trace the Number 3 Printable


Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


Lowercase Letters a b c Worksheet


Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet


"B" Words Printable Sight Words Worksheet


Letter N Coloring Sheet

Sight Word I Worksheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet


Count and Write 6 Worksheet


Letter D and E Sounds Worksheet


Uppercase Letters V, W, and X Worksheet


Finish Rhyming Poem Worksheet


Trace Read You Like Worksheet


Finish the Word Worksheet
Handwriting practice is essential for children aged 3-6, as it significantly contributes to their overall development. During this critical period, children are developing fine motor skills that are crucial for various tasks, including self-care and playing. Practicing handwriting enhances their hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and control, laying a foundation for future writing skills.
Furthermore, learning to write at a young age helps foster cognitive development. Children begin to understand letter formation, recognition, and sounds associated with letters, contributing to early literacy skills. This understanding boosts their confidence in language expression and aids in reading development later on.
Socially and emotionally, handwriting practice encourages patience and perseverance. Children learn the importance of practice and effort, which are vital attributes for life. Additionally, producing written work offers a sense of accomplishment, thereby building self-esteem.
For parents and teachers, facilitating handwriting practice creates opportunities for bonding and engagement. Through shared activities, they can promote a supportive environment that nurtures learning. Ultimately, refining handwriting skills in early childhood benefits not just academic performance, but also essential life skills that lay the groundwork for a successful future. Prioritizing this practice is investing in a child's holistic growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















