Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


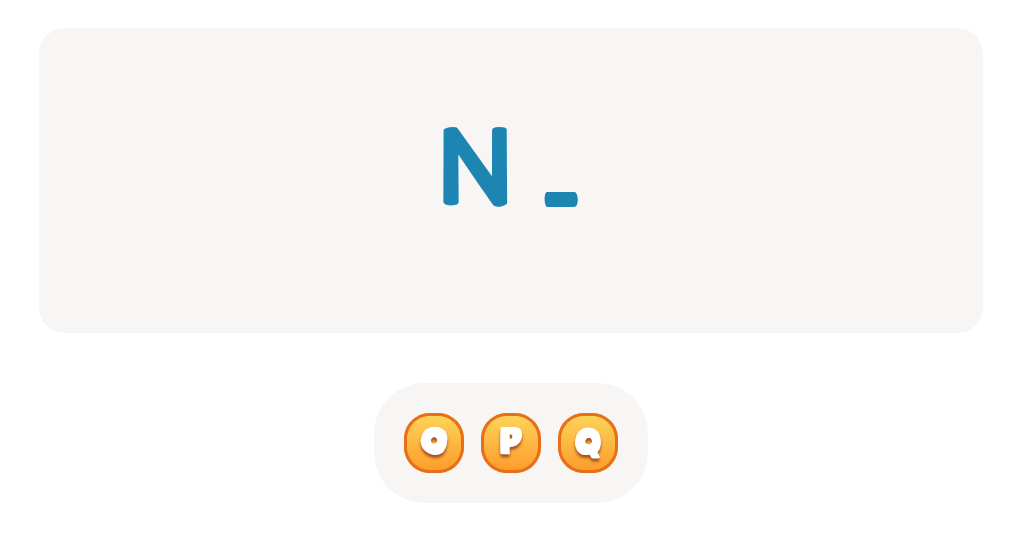
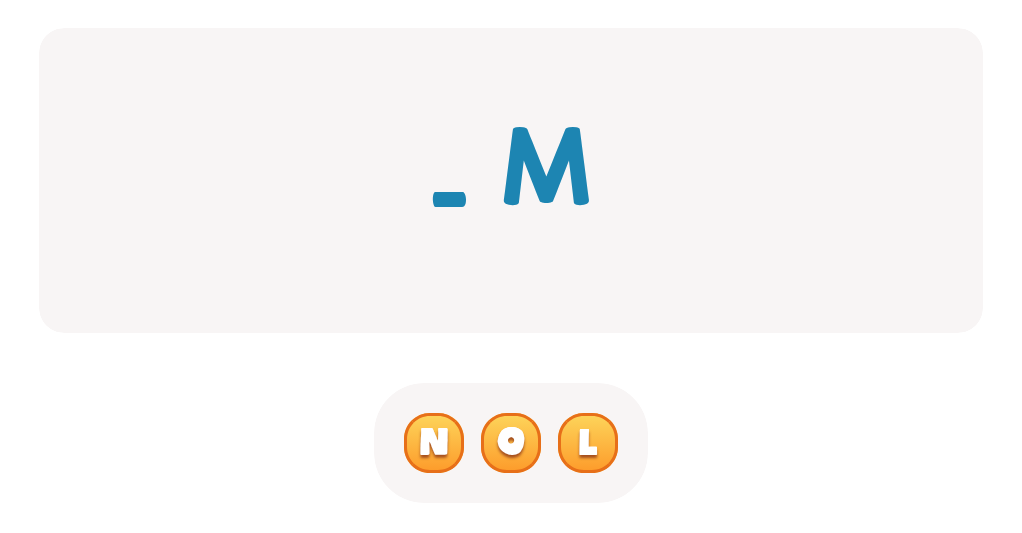
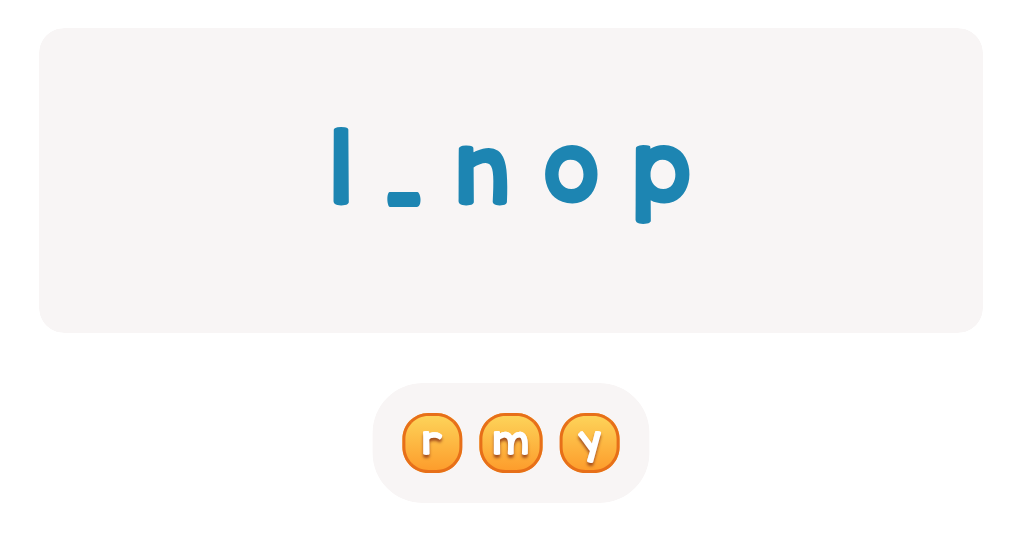
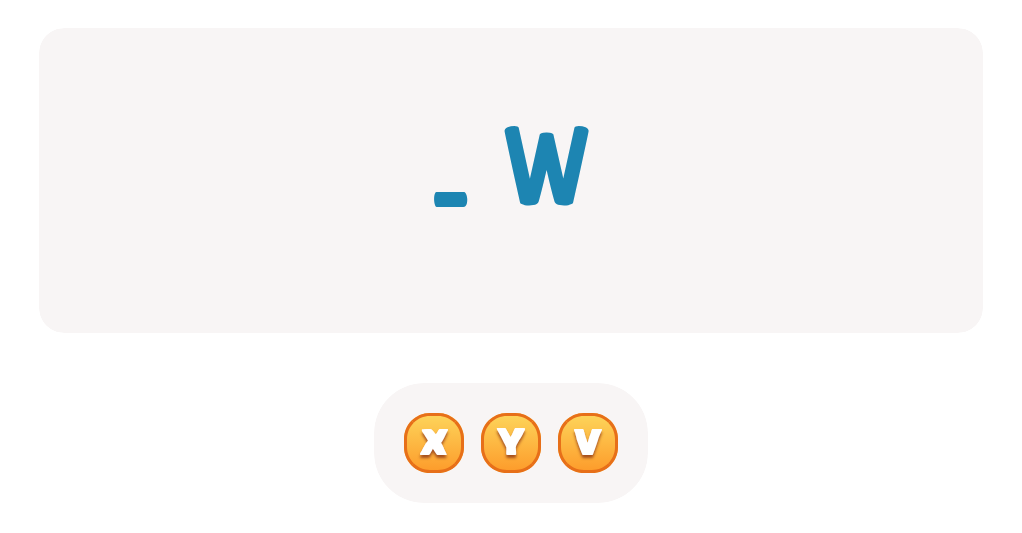
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice for letters is crucial for children aged 3-7, as it lays the foundation for effective communication skills. During these formative years, children are developing fine motor skills, hand-eye coordination, and cognitive abilities. Engaging in handwriting practice helps strengthen their muscles in the hand, leading to better control and dexterity—the building blocks for writing and other daily activities.
Moreover, handwriting supports literacy development. As children learn to form letters, they are also honing their phonetic awareness and vocabulary. Writing letters reinforces the connection between sounds and symbols, aiding in reading comprehension later on.
Additionally, handwriting offers an emotional and creative outlet for young learners. It allows them a sense of accomplishment as they see their skills improve over time. This boosts their self-esteem and encourages a love for learning.
Finally, practicing handwriting fosters focus and discipline. It requires attentiveness and practice, helping children develop patience and perseverance—essential qualities for future academic success.
In summary, handwriting practice is not just about the physical ability to write; it encompasses motor skills, cognitive development, emotional growth, and foundational literacy. Parents and teachers play a vital role in facilitating this important skill for their students.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students