Hand-eye Coordination Adding Up to 5 Worksheets for Ages 3-7
15 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's hand-eye coordination and early math skills with our engaging "Hand-eye Coordination Adding Up to 5 Worksheets" designed for ages 3-7. These interactive worksheets combine fun and learning as children practice addition with numbers up to 5 while developing fine motor skills. Each activity features colorful illustrations that captivate young learners, encouraging them to connect visual cues with mathematical concepts. Ideal for parents and educators, these worksheets promote cognitive growth through hands-on experiences. Equip your child with the essential skills they need while having fun! Download and explore our range of worksheets today to support your child’s learning journey.
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial skill for young children, especially for those aged 3-7, as it lays the foundation for more complex tasks in the future. For parents and teachers, fostering this skill through engaging activities helps enhance a child's ability to interact with their environment effectively. Activities such as throwing and catching a ball, using scissors or crayons, and assembling puzzles not only build hand-eye coordination but also contribute to cognitive development.
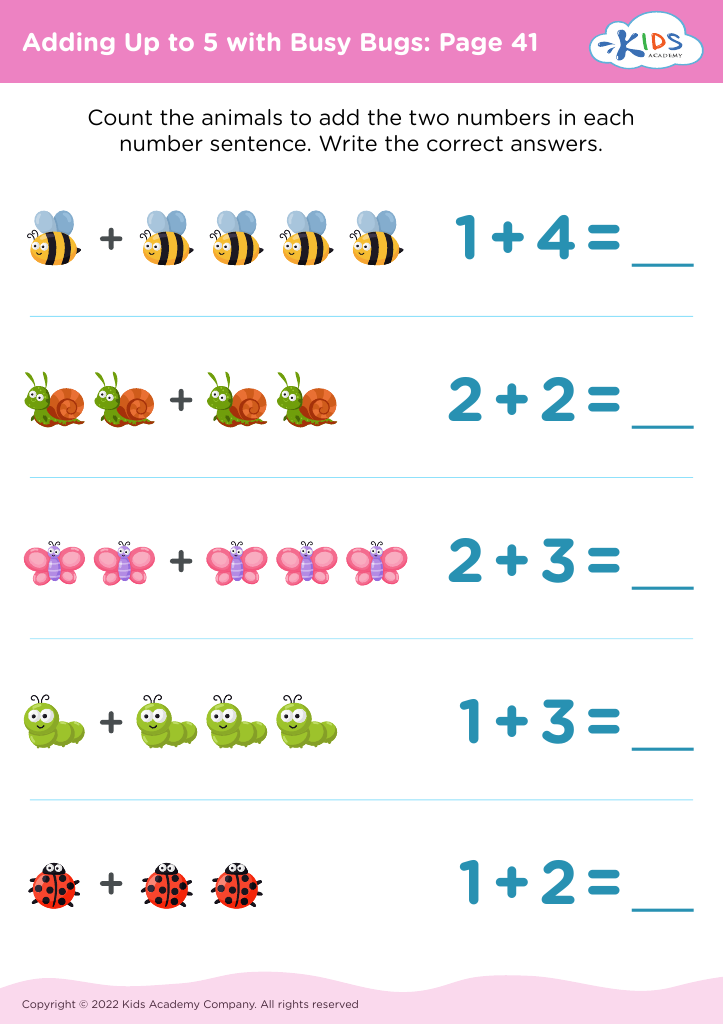
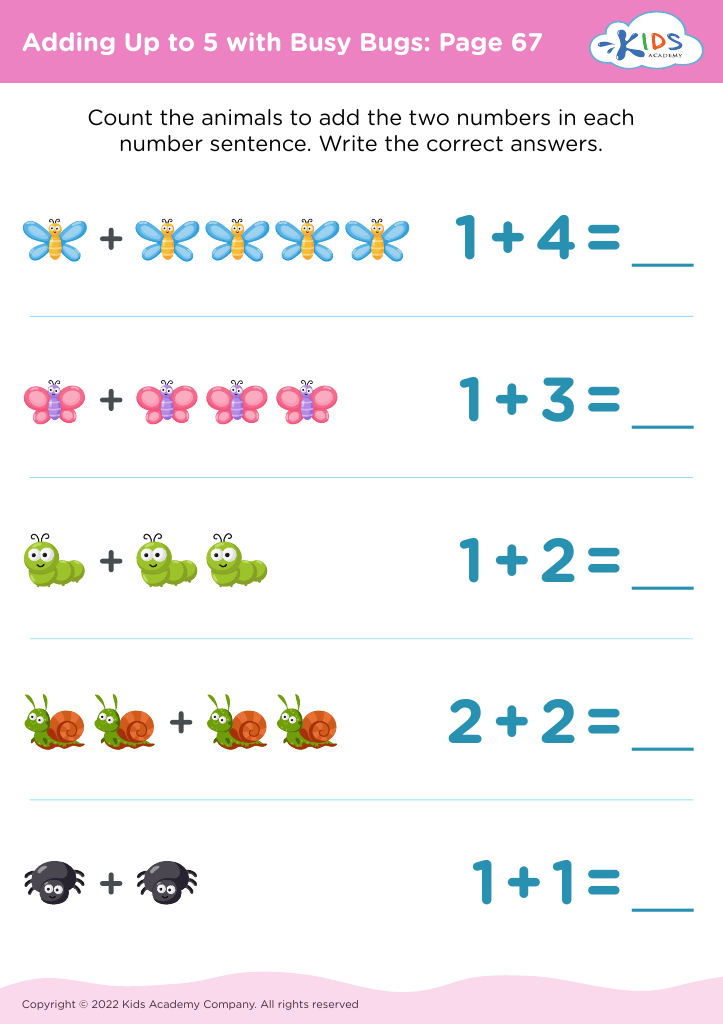
When children work on adding numbers up to 5, it offers an excellent opportunity to integrate movement and play into learning. This age group often learns best through interactive experiences; therefore, combining physical activities with basic math can make learning enjoyable and memorable. Engaging in these activities encourages focus, patience, and control, essential traits in both school and life.
Moreover, strong hand-eye coordination is linked to improved academic performance as children progress through their education. By emphasizing its importance early, parents and teachers help set a solid groundwork for future learning, including developing writing skills and participating in group sports and activities. Ultimately, encouraging hand-eye coordination alongside basic math paves the way for holistic development in young learners.





















.jpg)








