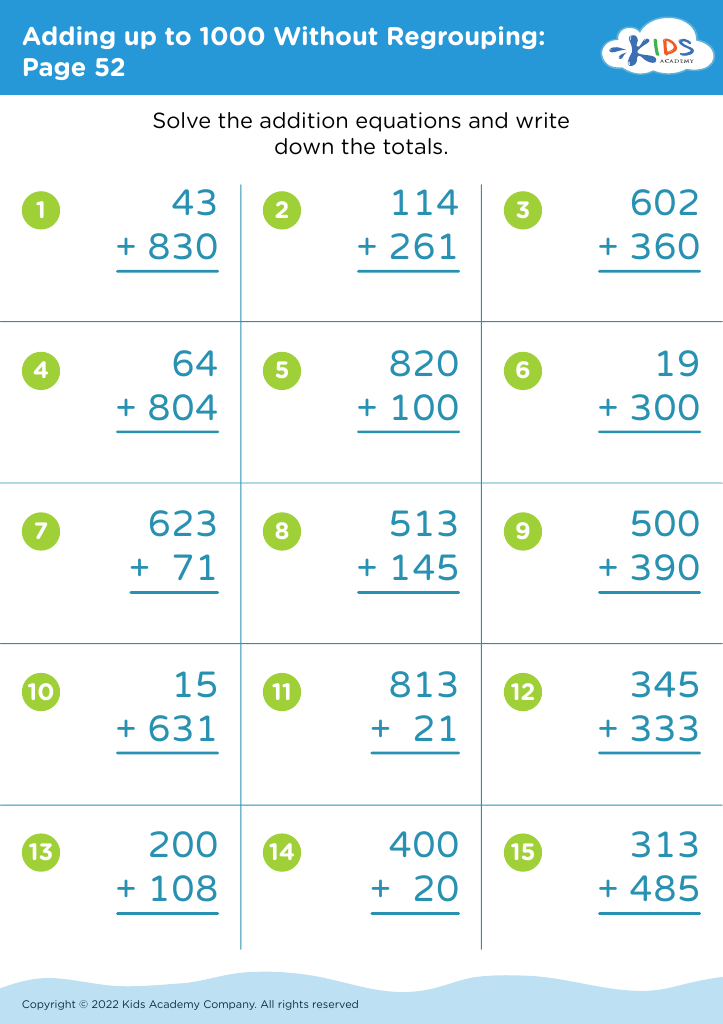
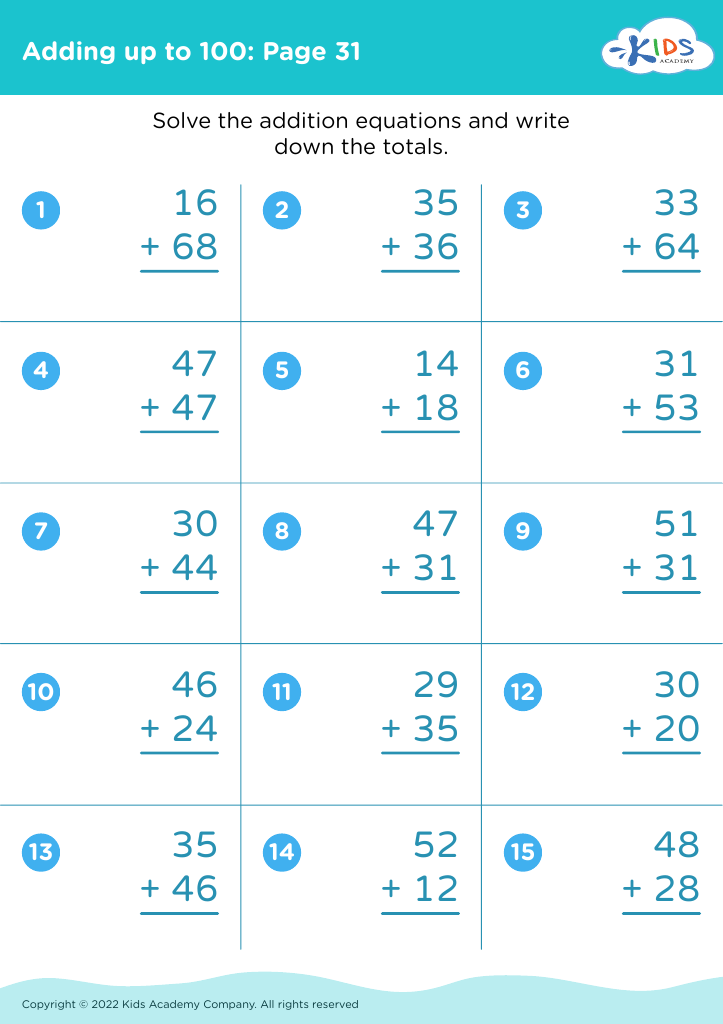
Improve fine motor skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child's potential with our "Improve Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets" designed for ages 3-7! These engaging, interactive worksheets seamlessly combine essential early math concepts with fine motor skill development. Young learners can practice addition while enhancing their hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and control through fun activities like tracing, coloring, and connecting dots. These worksheets not only foster critical math skills but also support essential physical development, making learning enjoyable and effective. Ideal for home or classroom use, our resources encourage creativity and confidence in young mathematicians. Start your child’s journey to mastery in addition today!
Enhancing fine motor skills in children aged 3-7 is crucial for their overall development, and it's an area where both parents and teachers should focus their attention. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for daily activities like writing, dressing, and even feeding. As children refine these skills, they gain confidence in their abilities, contributing to improved self-esteem and motivation in learning environments.
Engaging in activities that promote fine motor development, such as cutting with scissors, threading beads, or drawing, encourages hand-eye coordination and dexterity. These skills are foundational for later academic tasks, such as handwriting and using tools or instruments. Moreover, fine motor skills are closely linked to cognitive development and problem-solving abilities, as children learn to manipulate objects and explore their environments.
By nurturing fine motor skills, parents and teachers can help ensure that children are not only prepared for future educational challenges but also develop independence and self-care abilities. This investment in early skill-building can significantly influence a child’s readiness for school and overall success in various learning experiences throughout their formative years. Ultimately, caring about fine motor skill development is about fostering a well-rounded, capable, and confident child.