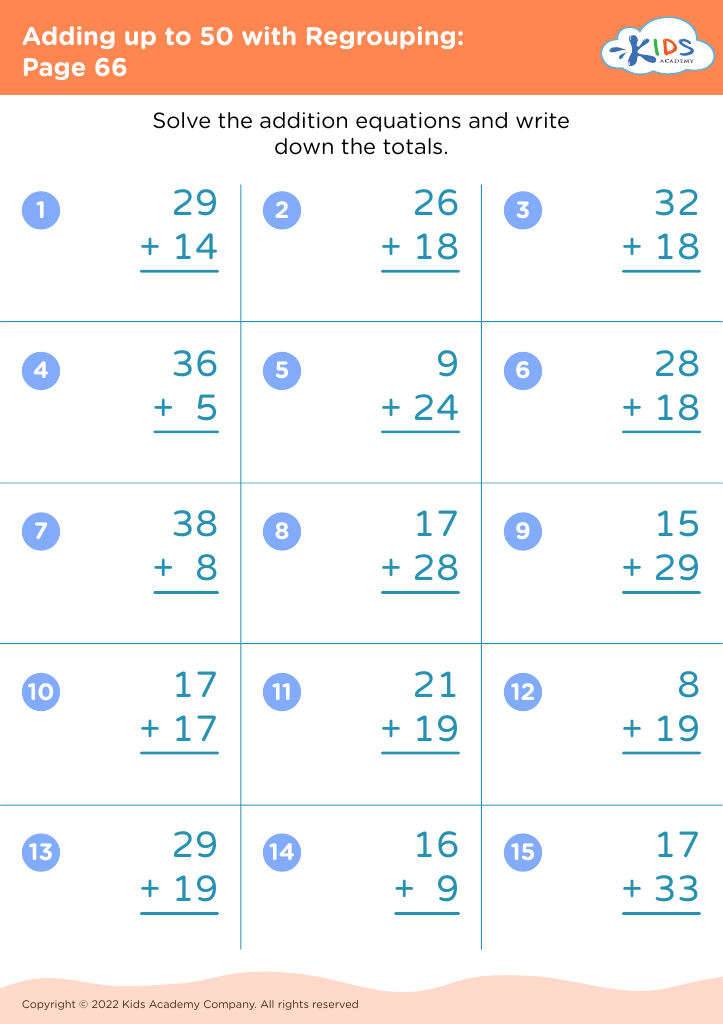
Observation skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's observational skills with our engaging "Observation Skills Addition Worksheets" designed for ages 3-7! These worksheets offer a fun and interactive approach to learning basic addition concepts while enhancing critical thinking and attention to detail. Your little learners will enjoy colorful illustrations that seamlessly combine observation tasks with simple math exercises. Through activities that require them to observe, compare, and deduce, children will develop both their addition skills and their analytical thinking. Perfect for homeschooling or classroom activities, these worksheets provide an enriching experience that lays a strong foundation for future learning. Get started today for a fun math adventure!
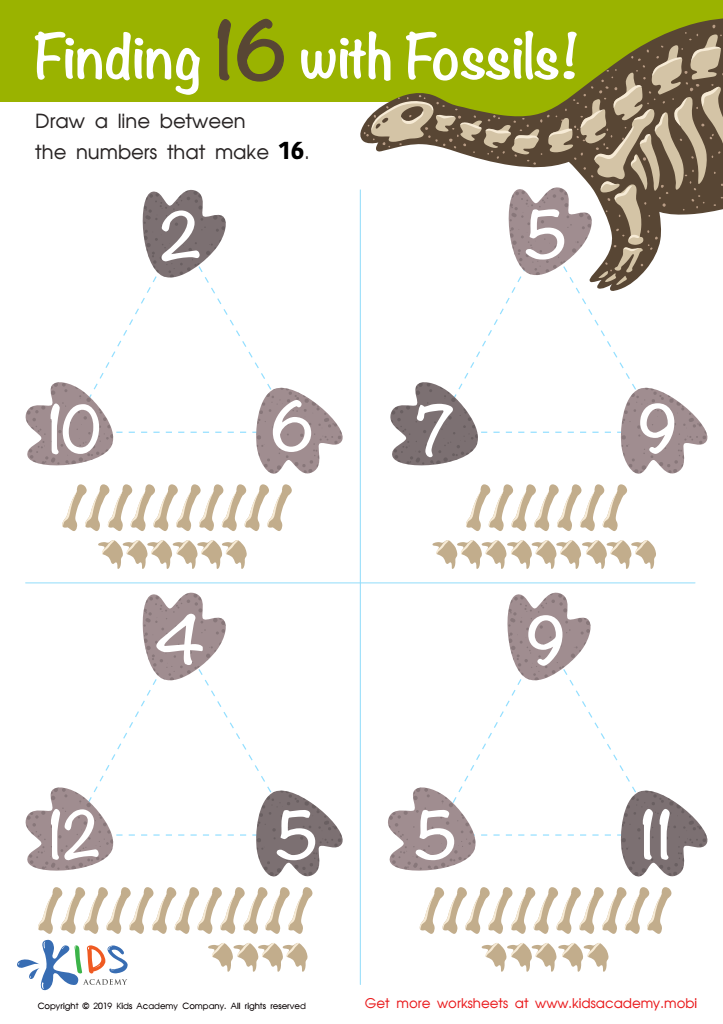

Finding 16 With Fossils Worksheet
Observation skills in early childhood play a crucial role in the development of children aged 3-7. For parents and teachers, cultivating these skills is essential for several reasons.
Firstly, children with strong observation skills demonstrate enhanced problem-solving abilities. These skills help them notice patterns, recognize shapes, and understand relationships in their environment, laying the groundwork for later math concepts, such as addition.
Secondly, when adults focus on developing children's observation skills, they engage in active, meaningful learning experiences. This not only makes learning enjoyable but also encourages critical thinking. By observing how children approach addition through counting objects, identifying groups, or comparing quantities, adults can adapt their teaching strategies to better meet individual needs.
Moreover, fostering observation skills helps in social interactions. Children learn to read nonverbal cues and respond appropriately, essential for cooperation in group settings while learning addition in collaborative contexts, like games or activities.
Lastly, this focus strengthens the bond between children and adults. Engaging in shared observation activities fosters communication, allowing adults to support children's learning and growth effectively. Therefore, promoting observation skills is vital for parents and teachers to nurture confident, thoughtful, and mathematically literate young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students