Problem-solving practice Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
28 filtered results
-
From - To


A Fox Family Worksheet
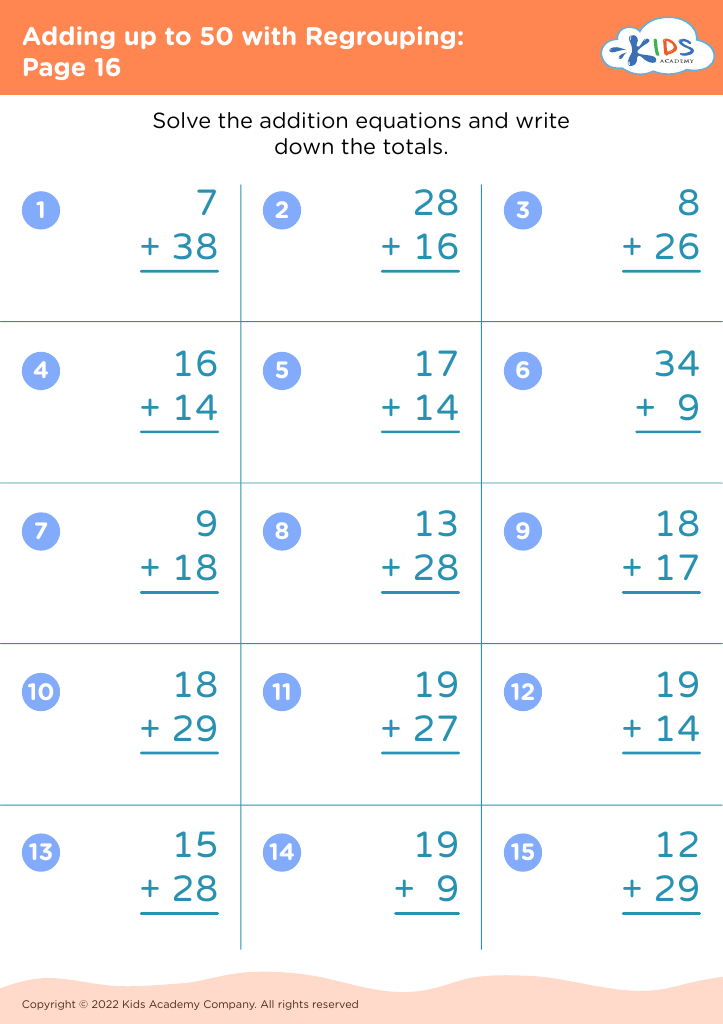
Parents and teachers should actively promote problem-solving skills in children ages 3-8 due to their critical role in cognitive development and lifelong success. This age is a formative period when children begin to explore the world and confront challenges, making it essential for them to learn how to think critically, analyze situations, and devise solutions.
Problem-solving practice encourages curiosity and creativity, enabling children to approach new situations with confidence. Engaging in problem-solving activities teaches persistence, as children learn to navigate setbacks and find alternative solutions. This resilience is fundamental for their emotional development, helping them cope with the complexities of life.
Additionally, fostering problem-solving skills cultivates collaboration and communication. Children often engage in group activities where they articulate their thought processes, share ideas, and learn from peers. These social skills are vital as they transition into more structured educational environments.
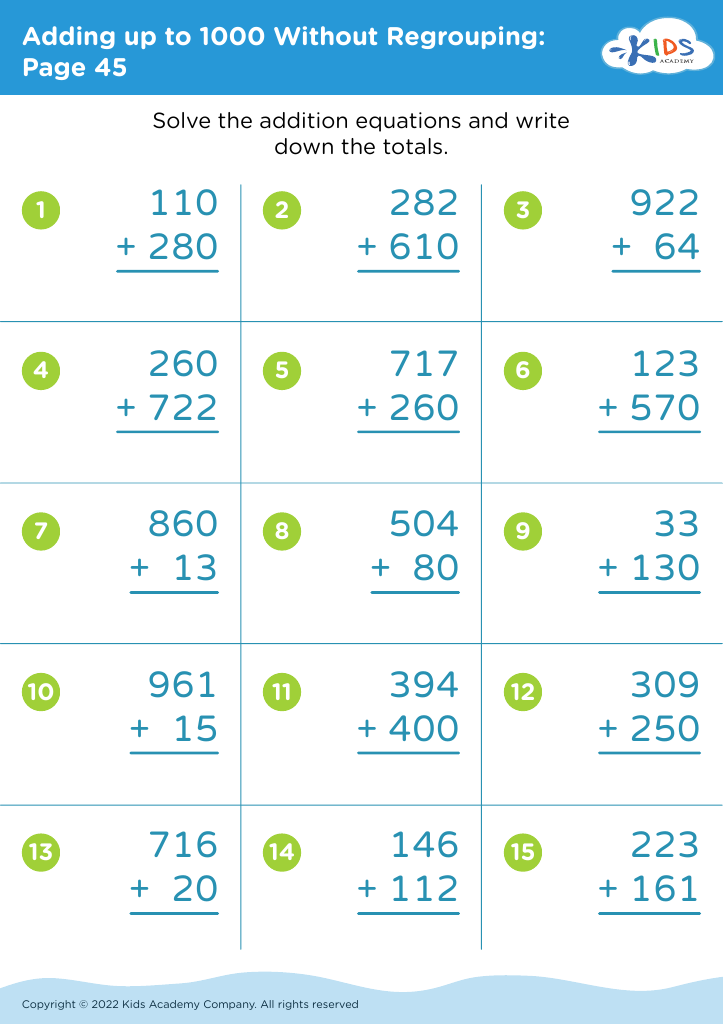
Moreover, early exposure to problem-solving enhances academic readiness, linking directly to future success in science, mathematics, literacy, and other subjects. Encouraging problem-solving not only enriches a child’s educational experience but also equips them with vital life skills—critical thinking, adaptability, and a growth mindset—that will serve them throughout their lives.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students

















