Hand-eye Coordination Math Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 3
66 filtered results
-
From - To
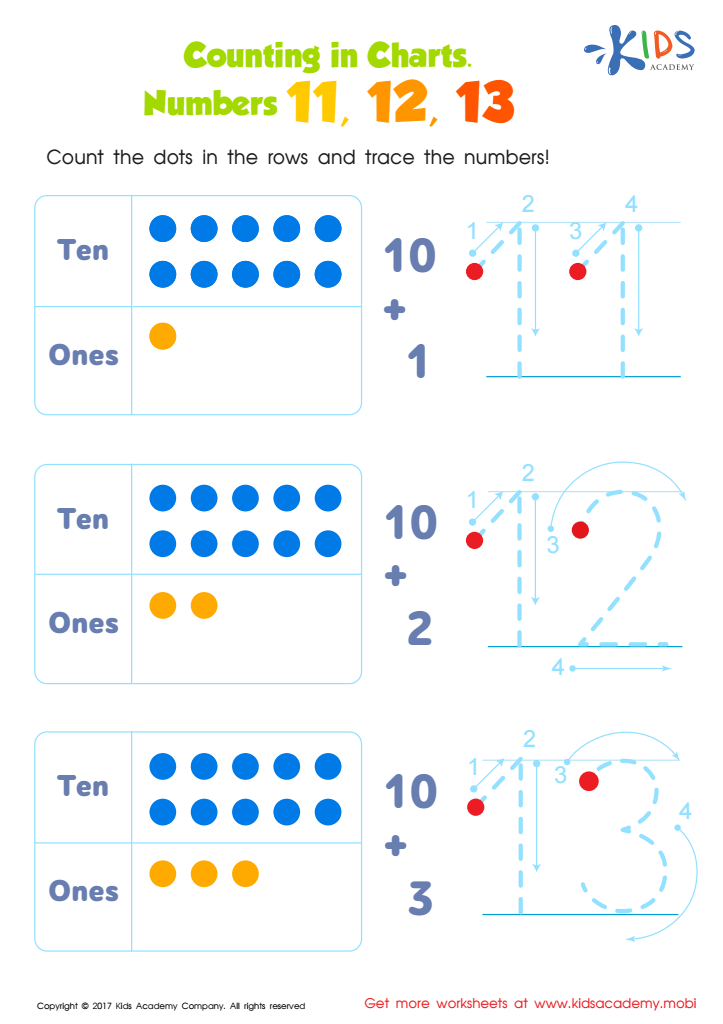

Number Tracing Worksheet For Kindergarten
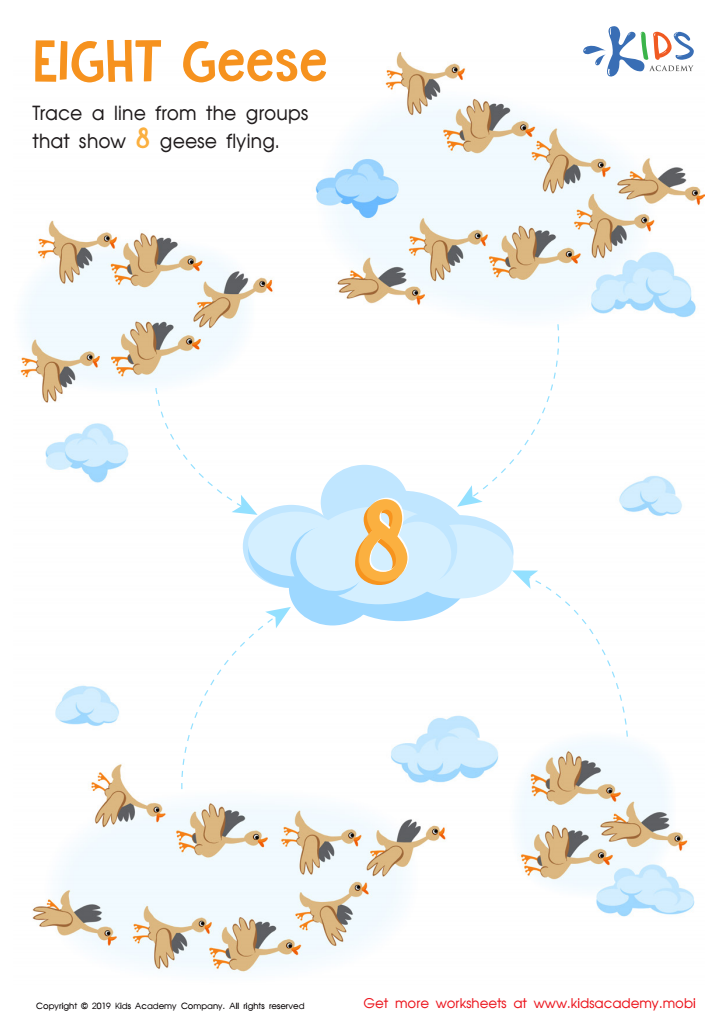

Eight Geese Worksheet


Leprechaun Maze Printable


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet
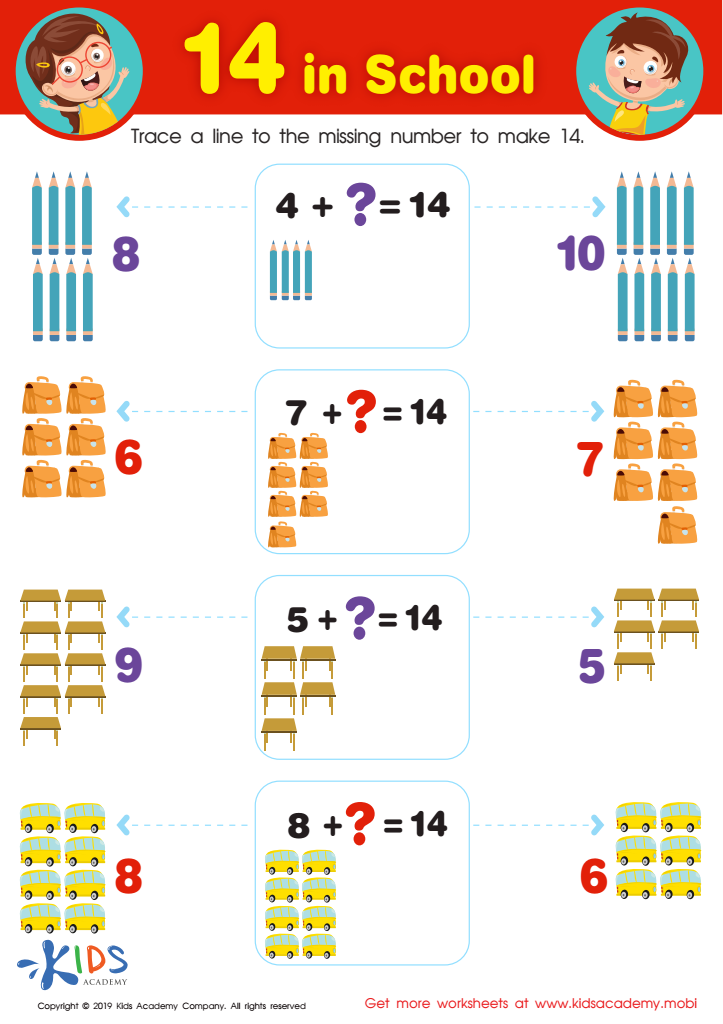

14 in School Worksheet
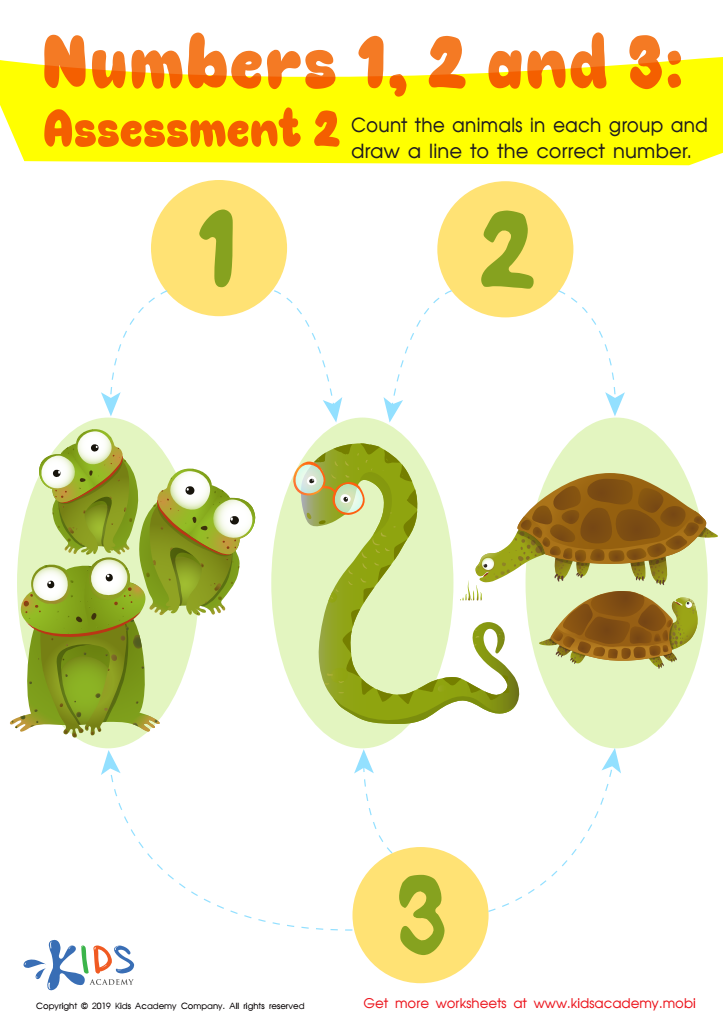

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet

Cutting Rectangles with Little Sunshine Worksheet

Scottish Sewing Part 2 Worksheet


Patchwork Math Worksheet
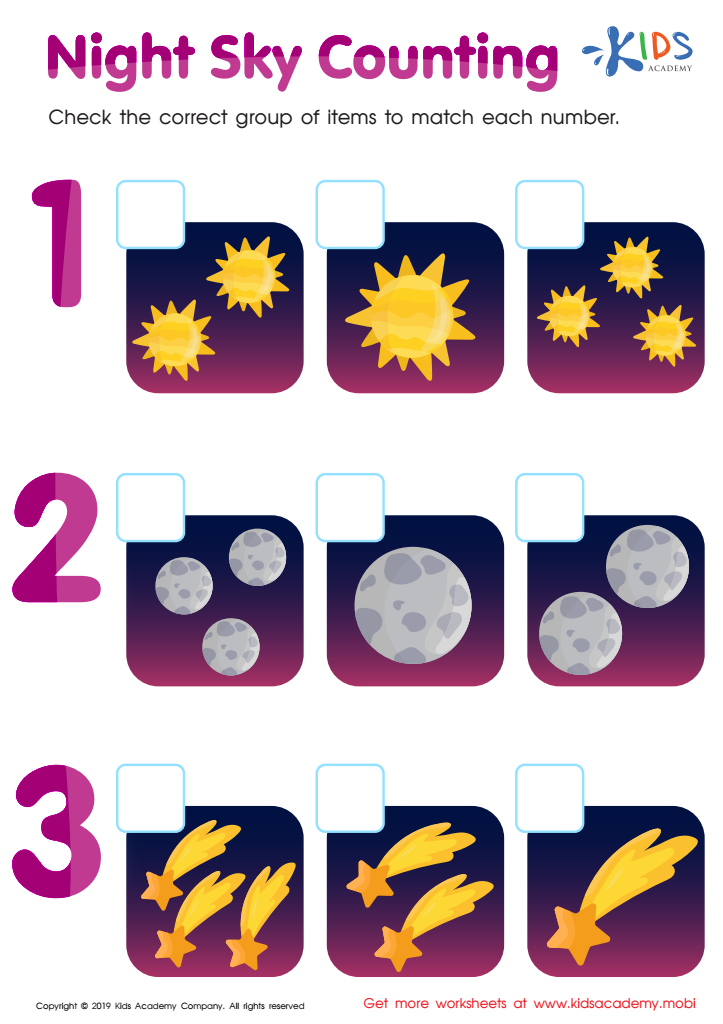


Night Sky Counting Worksheet

Number Tracing Worksheet


Hand-eye coordination is crucial for young children as it lays the foundation for essential life skills. Fostering this ability through math activities for ages 3-8 accomplishes multiple developmental goals simultaneously. Firstly, hand-eye coordination strengthens motor skills and dexterity, enabling children to perform everyday tasks such as writing, cutting with scissors, tying shoelaces, and even playing sports. Maintaining a focus on integrating hand and eye movements ensures these tasks become almost automatic with practice, boosting confidence and independence.
Integrating hand-eye coordination with math offers additional cognitive benefits. Activities like sorting shapes, counting objects, or tracing numbers help solidify mathematical concepts. By leveraging manipulatives—physical items like blocks or counters—children actively engage both their visual and motor systems, making abstract concepts more concrete and understandable. This dual engagement nurtures cognitive development, enhancing memory, problem-solving skills, and spatial awareness.
Moreover, combining these skills fosters a child's ability to pay attention and follow instructions, setting a precedent for structured learning and academic success. Early intervention in developing hand-eye coordination with math not only supports physical and cognitive growth but also cultivates a comprehensive, multi-faceted learning environment. Parents and teachers, therefore, play a pivotal role in shaping an engaging, effective educational experience that will benefit children beyond the classroom.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students






.jpg)













