Hand-eye Coordination Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-9 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
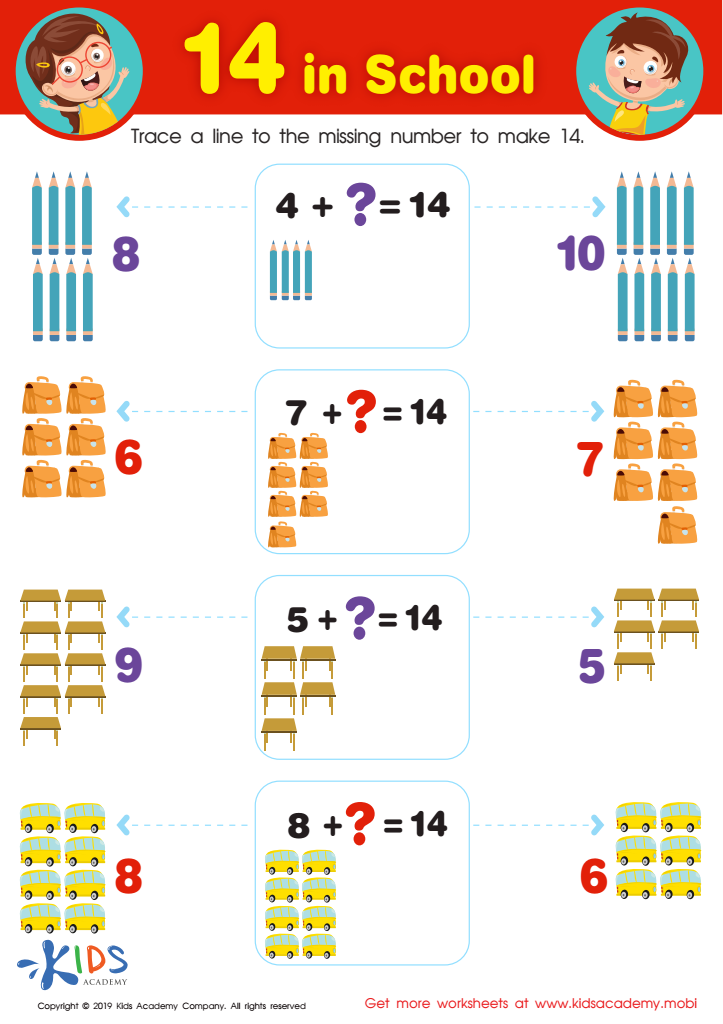

14 in School Worksheet
Hand-eye coordination is a fundamental developmental skill essential for children aged 3-9, and integrating it with addition and subtraction exercises is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, this skill helps enhance fine motor abilities, which are vital for various everyday tasks, such as writing, drawing, and personal grooming. Hands-on activities like counting physical objects or using interactive math games encourage children to associate numerical concepts with physical actions, thereby making abstract arithmetic operations more concrete and relatable.
Secondly, good hand-eye coordination can improve a child's ability to focus and follow instructions, which are crucial attributes for academic success. When children manipulate objects or use educational tools that require both sight and touch, they gradually build the capacity to concentrate and solve problems more effectively.
Moreover, activities that combine physical movement with cognitive tasks stimulate different areas of the brain simultaneously. This dual engagement bolsters brain development, fostering both mental agility and physical dexterity. Encouraging this form of learning primes children not just for mathematical proficiency, but for a range of activities that require coordinated effort between their mental processing and physical actions.
Therefore, prioritizing hand-eye coordination through addition and subtraction practices is an invaluable strategy for parents and teachers aiming to promote comprehensive developmental growth in young learners.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students