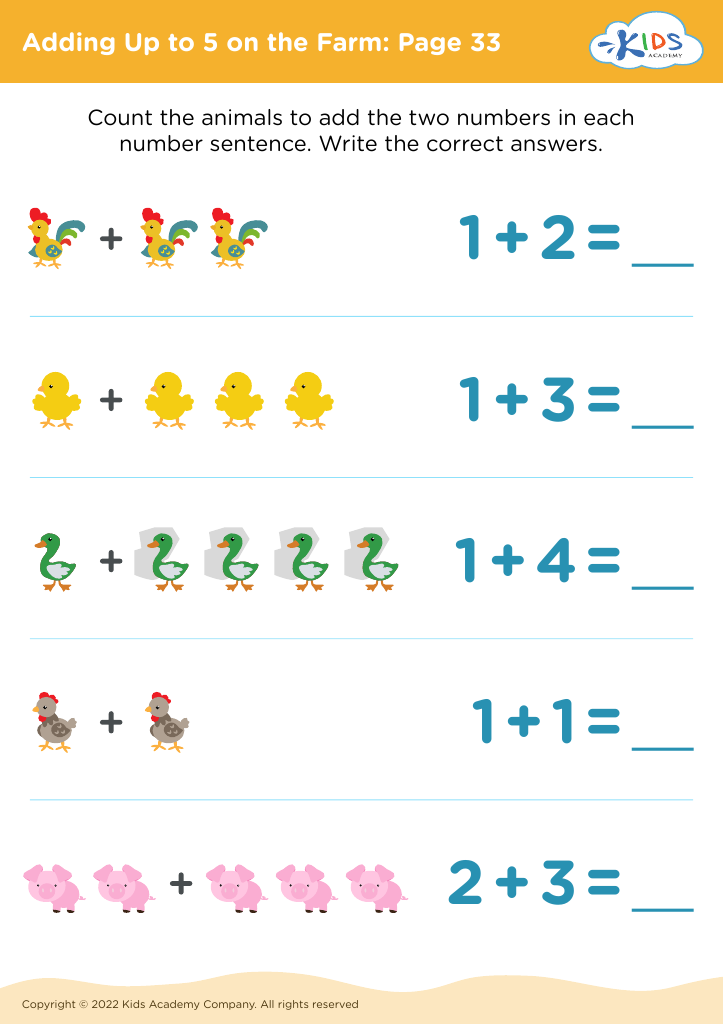Developing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for 3-Year-Olds
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Developing fine motor skills is essential for young learners, and our specialized math worksheets for 3-year-olds serve this critical need. Designed thoughtfully to enhance hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and precision, these engaging activities integrate fundamental math concepts with fun-filled tasks. From tracing numbers to solving simple puzzles, each worksheet provides a combination of cognitive and motor skills practice, fostering an interactive learning experience. Perfect for parents and teachers aiming to bolster early math proficiency while nurturing vital motor skill development, these resources support budding minds in a playful and educational environment. Explore endless learning possibilities with our expertly crafted worksheets!
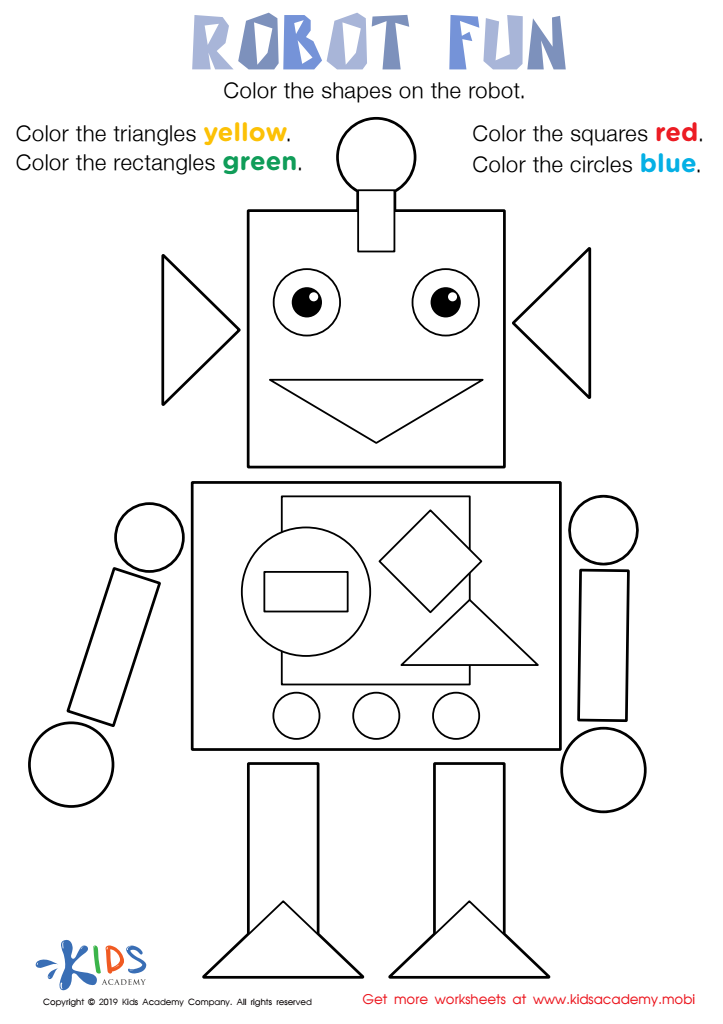

Robot Fun Worksheet
Developing fine motor skills in three-year-olds is crucial for holistic growth and has a significant impact on math readiness. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling children to perform essential tasks such as grasping objects, drawing, and writing. For three-year-olds, engaging in activities that enhance these skills lays a strong foundation for future academic success, particularly in math.
Fine motor development directly influences a child's ability to manipulate objects and use writing tools, which are fundamental in learning math concepts like counting, sorting, and patterning. For instance, when children use their fingers to count or manipulate small objects, they strengthen their number sense and spatial awareness, key components of early math. These activities help them understand one-to-one correspondence, quantities, and basic mathematical operations.
Moreover, developing fine motor skills fosters concentration, patience, and hand-eye coordination, which are important in all learning areas. When children draw shapes or color within lines, they are not just engaging in art but are also honing the precision needed for future math tasks. Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize activities that enhance fine motor skills, such as playing with building blocks, threading beads, and using child-safe scissors. These experiences build confidence, readiness for more complex math concepts, and overall cognitive development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students