Enhancing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for 3-Year-Olds
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child's potential with our "Enhancing Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for 3-Year-Olds." Designed specifically for toddlers, these engaging worksheets combine fun and learning, focusing on essential fine motor skills in conjunction with early math concepts. Through activities like tracing, cutting, and coloring, children improve their hand-eye coordination and dexterity while exploring numbers, shapes, and basic counting. Our worksheets encourage independence and creativity, making math exciting at this crucial developmental stage. Perfect for at-home learning or classroom use, these resources provide a dynamic way to foster essential skills that lay the foundation for future academic success. Get started today!
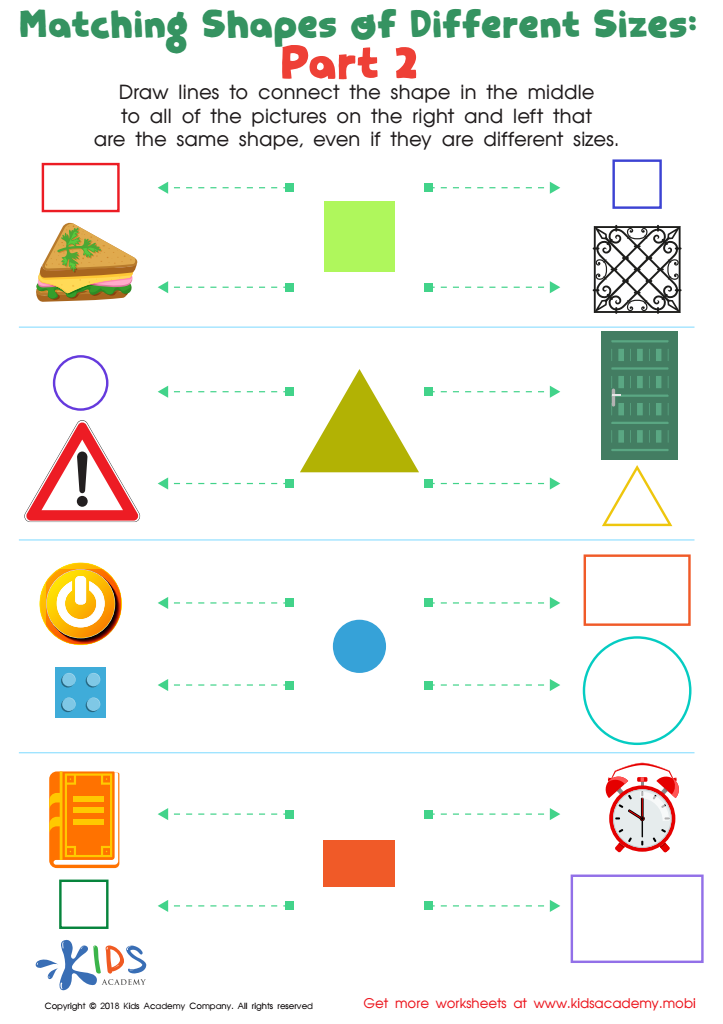

Geometry: Part 2 Worksheet
Enhancing fine motor skills in 3-year-olds is crucial not only for their overall physical development but also for laying the groundwork for mathematical skills. Fine motor skills involve the ability to control small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for tasks like writing, drawing, and manipulating objects. By focusing on these skills, parents and teachers can significantly improve children’s readiness for learning math concepts.
Developing fine motor skills allows young children to engage in activities that promote spatial awareness and problem-solving, both critical to math understanding. For example, activities like building with blocks, threading beads, or cutting with scissors not only enhance dexterity but also involve counting, shape recognition, and spatial reasoning. These experiences create a solid foundation for mathematical concepts as children learn to manipulate objects with precision.
Furthermore, strong fine motor skills boost confidence. When children can grasp tools, count, and create shapes effectively, they are more motivated to explore mathematical experiences. Involving parents and teachers in these activities fosters a supportive environment that encourages a love for learning.
Ultimately, enhancing fine motor skills provides a multifaceted approach to early math education, marrying physical development with cognitive growth and setting the stage for future success.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students

















