Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
26 filtered results
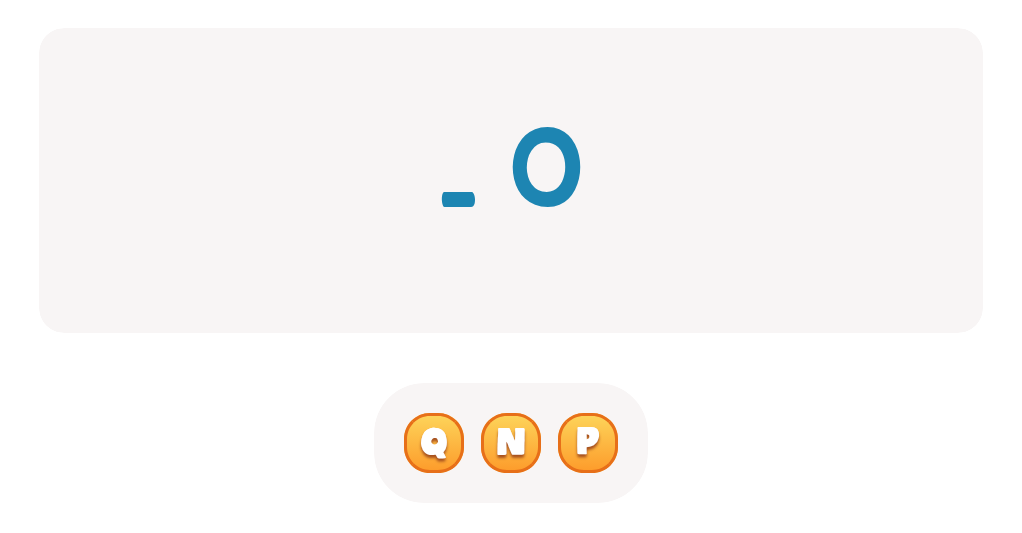
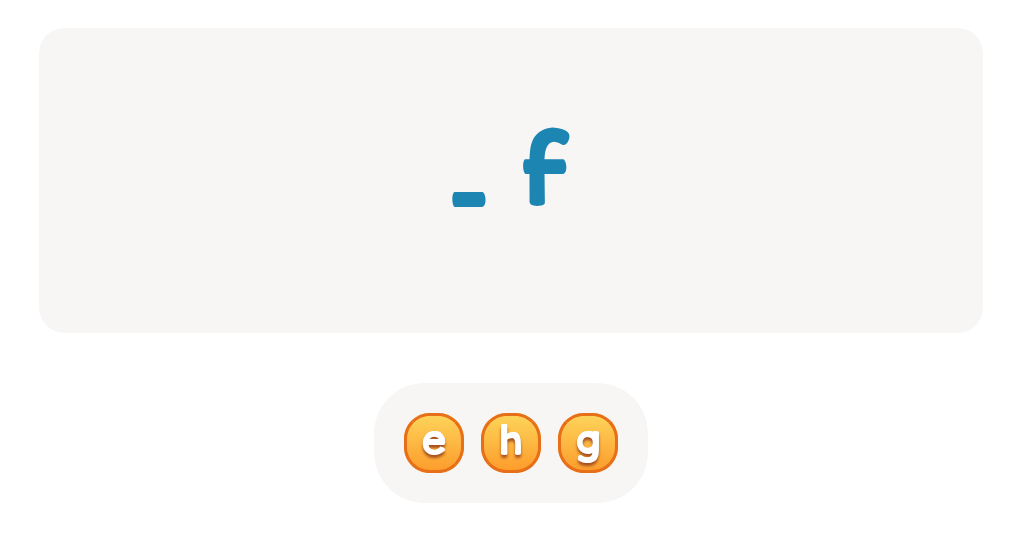
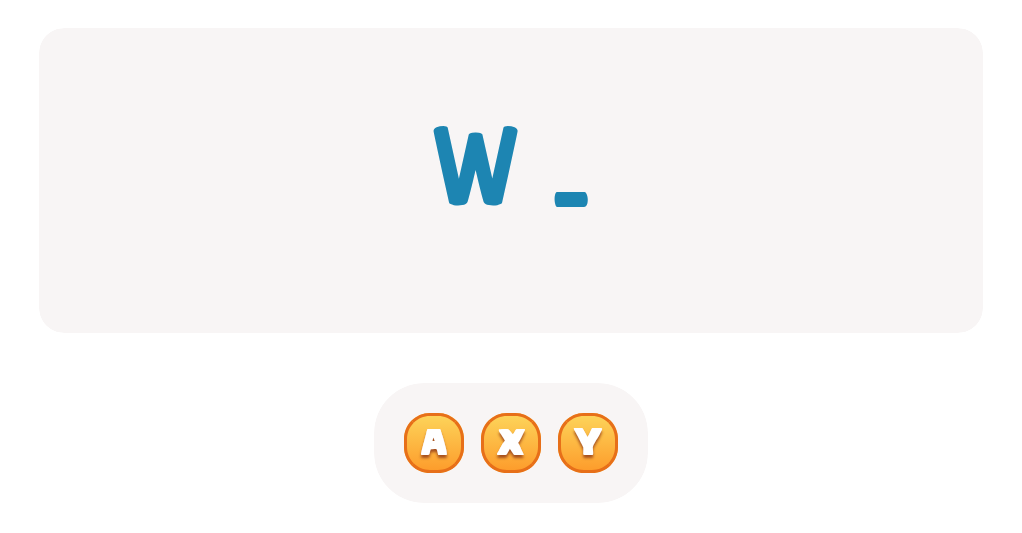
-
From - To


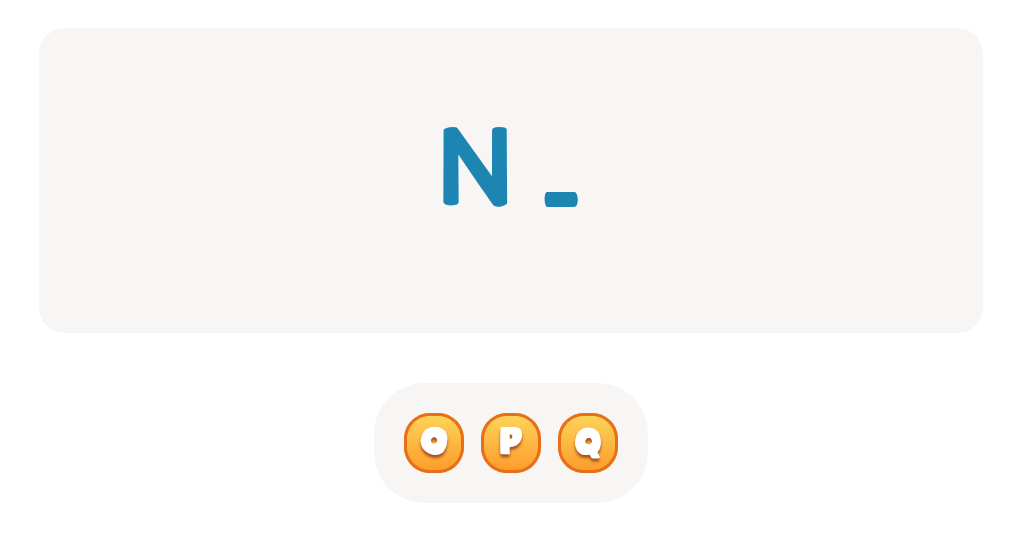
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice in early childhood, particularly focusing on ABC letters for children ages 4-5, is an essential aspect of both cognitive and motor development. At this formative stage, handwriting practice aids in refining fine motor skills crucial for more complex tasks such as tying shoelaces, using scissors, and later writing legibly. Developing these skills early can significantly enhance a child's dexterity and hand-eye coordination.
Moreover, learning to write letters forms the bedrock of literacy. As children practice writing, they become more familiar with the alphabet, which helps in letter recognition and, subsequently, in learning to read. This early mastery of letters promotes language development, enriches vocabulary, and fosters a love for reading and writing.
Beyond motor skills and literacy, consistent handwriting practice instills discipline and patience. The repetitive nature of forming letters enhances a child's attention to detail and concentration. These sessions also offer an opportunity for parents and teachers to engage positively with children, providing encouragement and support.
Investing in handwriting practice thus not only supports academic success but also contributes to a child's overall developmental health, enabling better performance in various areas of life. It's a fundamental step that blends skill-building with emotional and educational growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students