Visual discrimination Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets for Ages 4-5
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's literacy skills with our engaging Visual Discrimination Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets, designed specifically for ages 4-5. These interactive worksheets help preschoolers distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters, fostering essential early reading and writing abilities. Through colorful illustrations and playful activities, young learners can easily identify and match letters, strengthening their visual perception and cognitive skills. Our carefully crafted exercises keep children motivated and excited to learn the alphabet, laying a solid foundation for future literacy success. Explore our comprehensive collection of worksheets and watch your child bloom in their learning journey today!


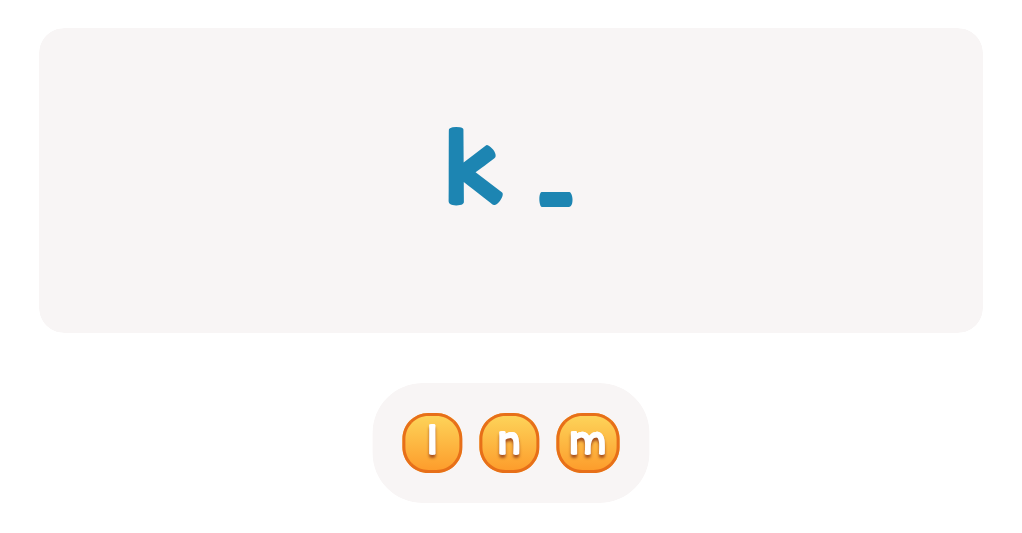
Find Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


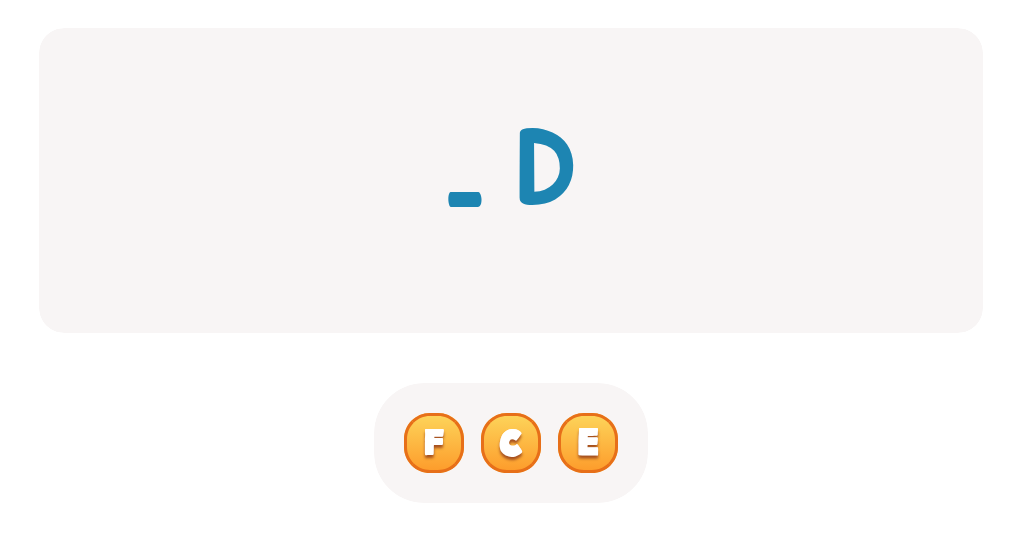
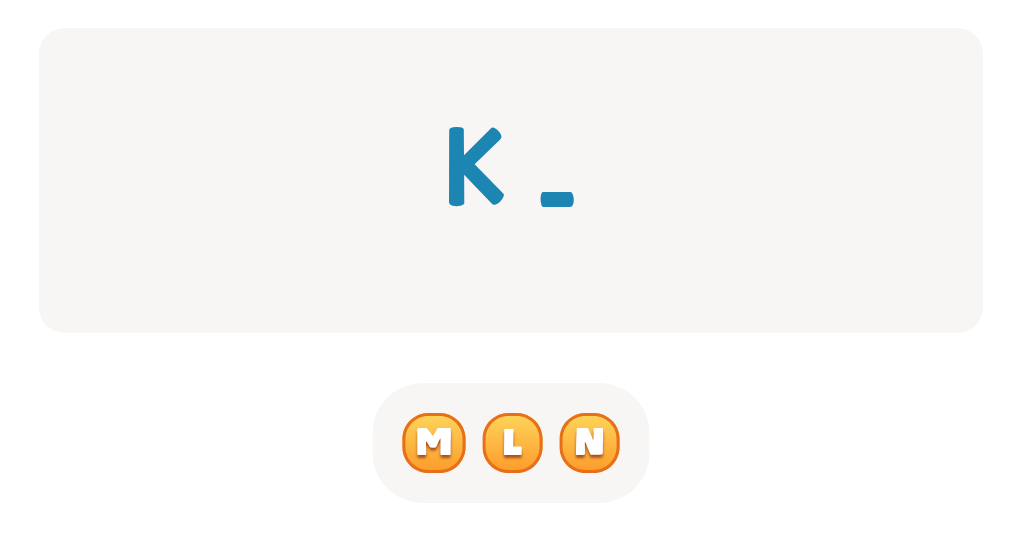
Find Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet


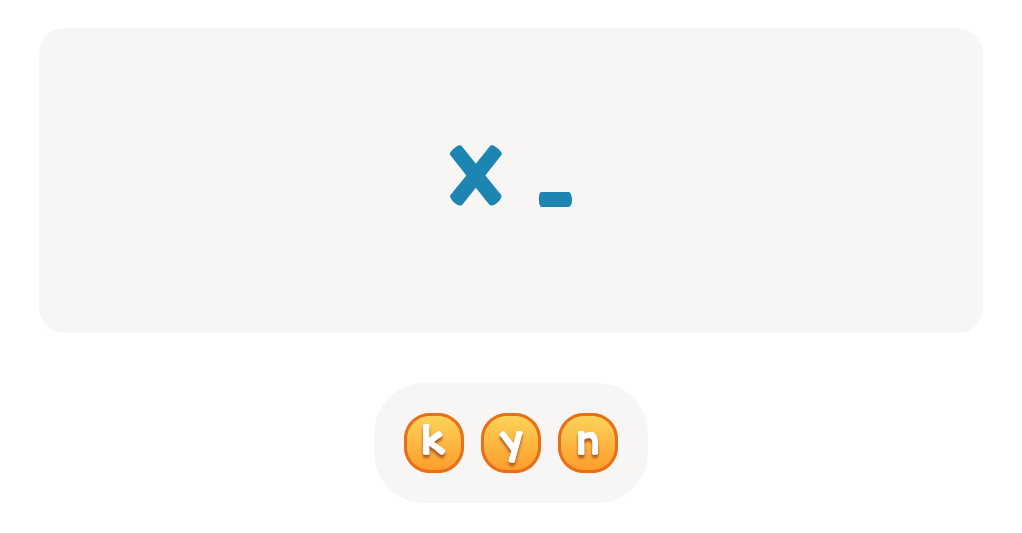
Find Uppercase Letters V, W, X Worksheet
Visual discrimination is a crucial skill for young children, particularly for those aged 4-5, as it forms the foundation for reading and writing. It involves the ability to differentiate between similar shapes, sizes, and patterns, which extends to recognizing upper and lowercase letters. For parents and teachers, fostering this skill is vital for several reasons.
Firstly, young learners often encounter uppercase and lowercase letters that appear similar, such as “b” and “d” or “p” and “q.” Developing visual discrimination helps children identify these letters accurately and avoid confusion, ultimately making the process of learning to read smoother and more enjoyable.
Secondly, strong visual discrimination skills are linked to language development, aiding children in recognizing and processing sight words and phonics. This advancement enhances their overall literacy, promoting confidence and motivation in their academic journey.
Moreover, promoting this skill can also improve children's fine motor skills, as they engage in letter writing and identification activities.
In summary, parents and teachers should prioritize visual discrimination of uppercase and lowercase letters, as it establishes a strong literacy foundation, boosts cognitive development, and cultivates critical thinking which is essential for the educational growth of young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students