Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
44 filtered results
-
From - To
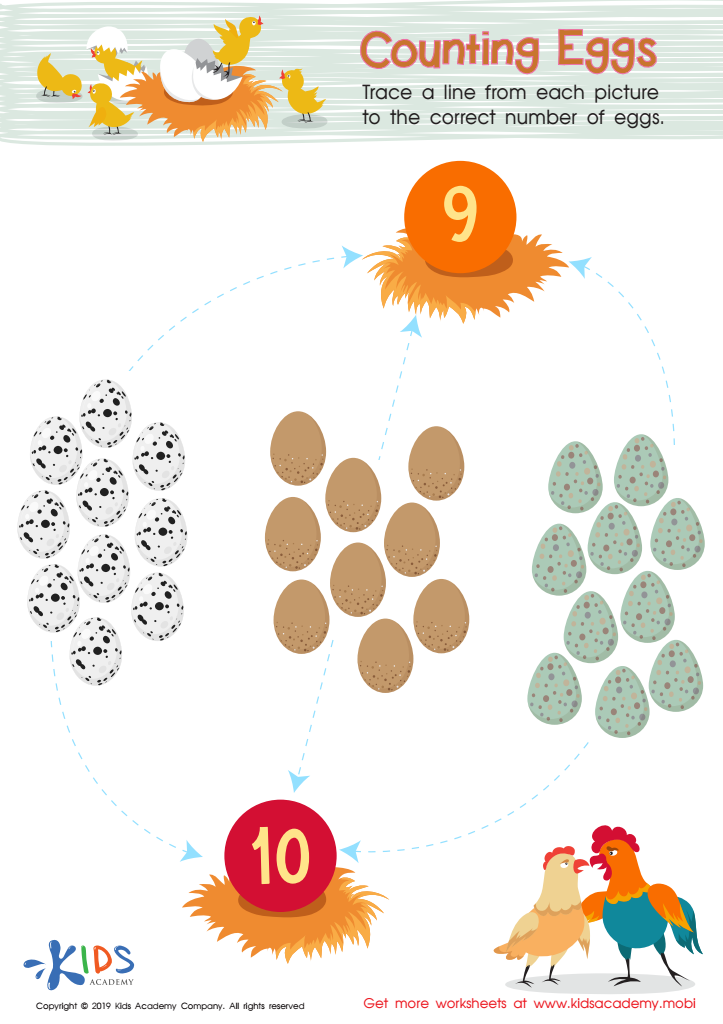

Counting Eggs Worksheet
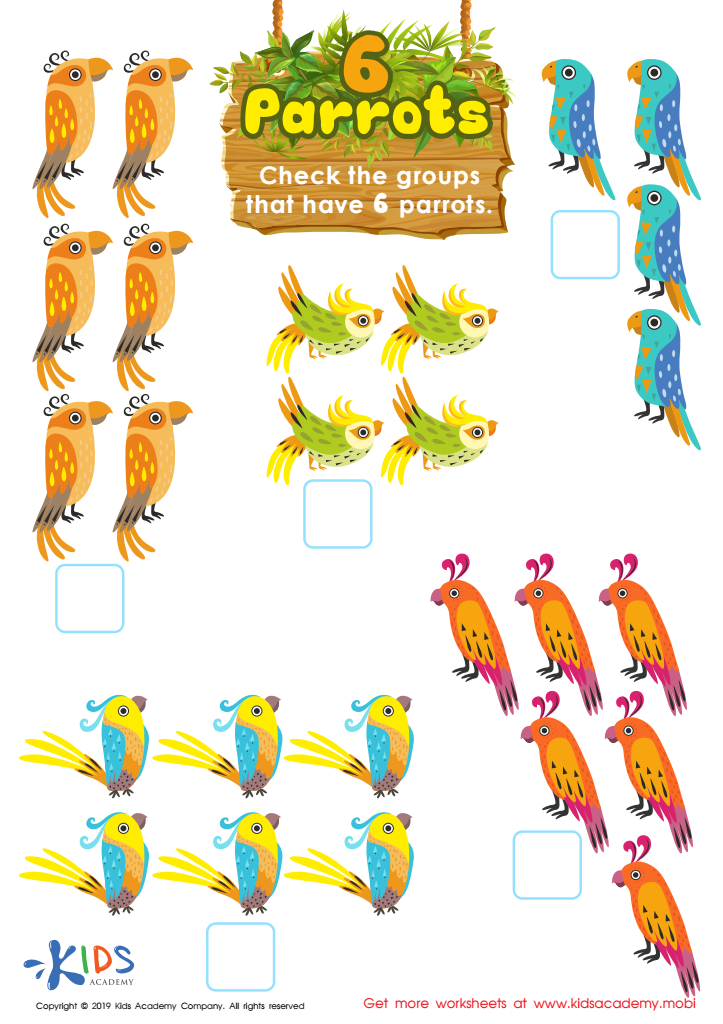

6 Parrots Worksheet
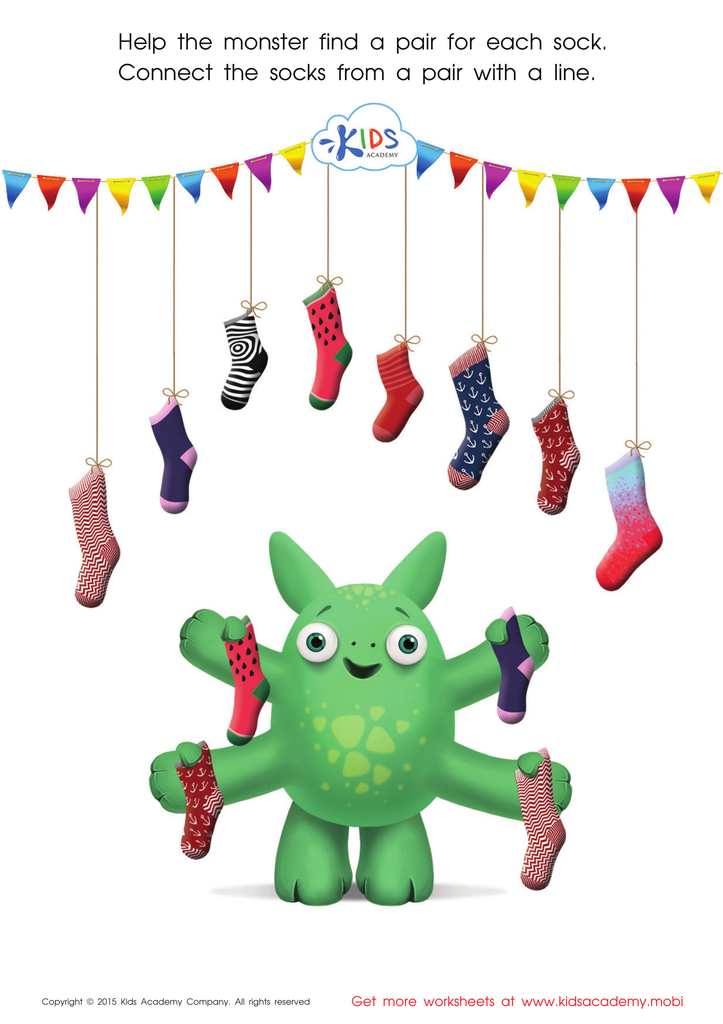


Math Matching Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet

Line up the Tigers Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet


Math Matching Pairs Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
Fine motor skills play a crucial role in the early development of children, especially in tasks involving addition and subtraction for ages 4-5. These foundational skills are essential for effective learning and interpersonal interaction. By refining fine motor skills, children enhance their ability to manipulate objects, which directly supports their understanding of mathematical concepts.
When children engage in hands-on activities like counting with beads or using fingers to represent numbers, they connect physical movements with mathematical ideas. Such activities foster cognitive development as it inspires problem-solving skills and an understanding of number relationships. Moreover, fine motor activities promote hand-eye coordination, which is vital for later tasks like writing and drawing.
By focusing on fine motor skills, parents and teachers can create a fun and interactive environment where young learners feel motivated to explore mathematics. It helps build confidence, encourages perseverance when facing challenges, and provides the groundwork for more complex math operations in the future. Comments and feedback from parents and teachers reinforce these activities as valuable tools for cognitive growth. Ultimately, reinforcing fine motor skills in addition and subtraction equips children with critical life skills and a positive attitude towards learning from an early age.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students