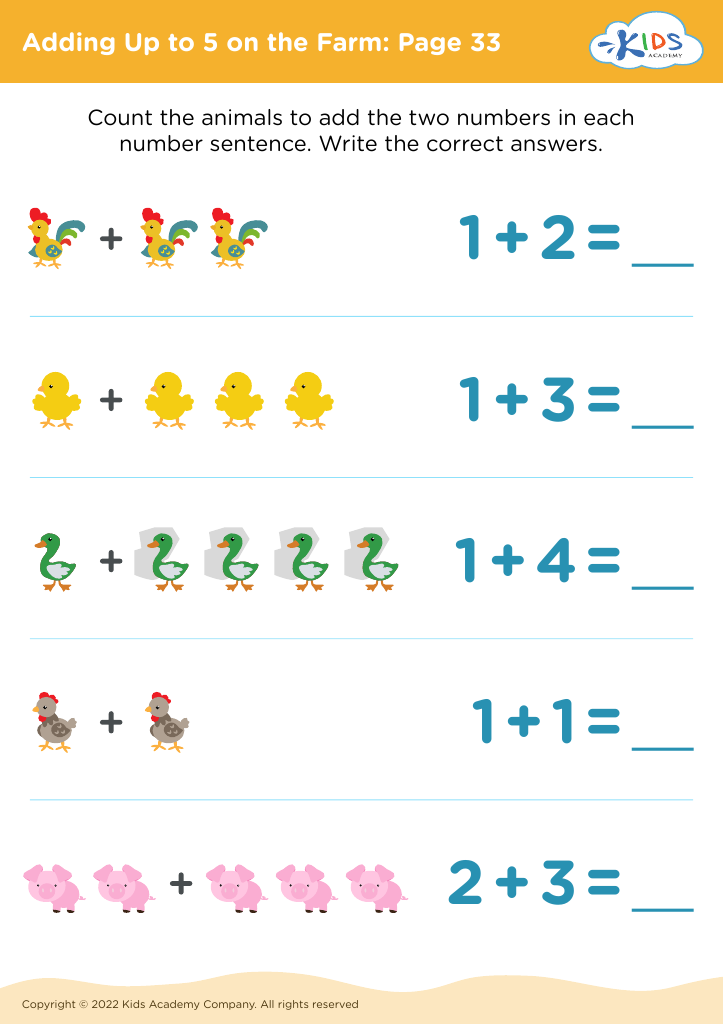Developing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-5
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Nurture your child's growth with our Developing Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-5. Designed to blend foundational math concepts with fun, engaging activities, these worksheets help children practice crucial skills like tracing, drawing, and cutting. Perfectly tailored for preschoolers, each worksheet emphasizes the development of dexterity and hand-eye coordination while introducing basic math principles. Our expertly crafted activities build confidence and support school readiness. Explore our diverse collection to strengthen your child’s fine motor skills and ignite a lifelong love for learning. Set the stage for early academic success with Kids Academy's trusted resources!
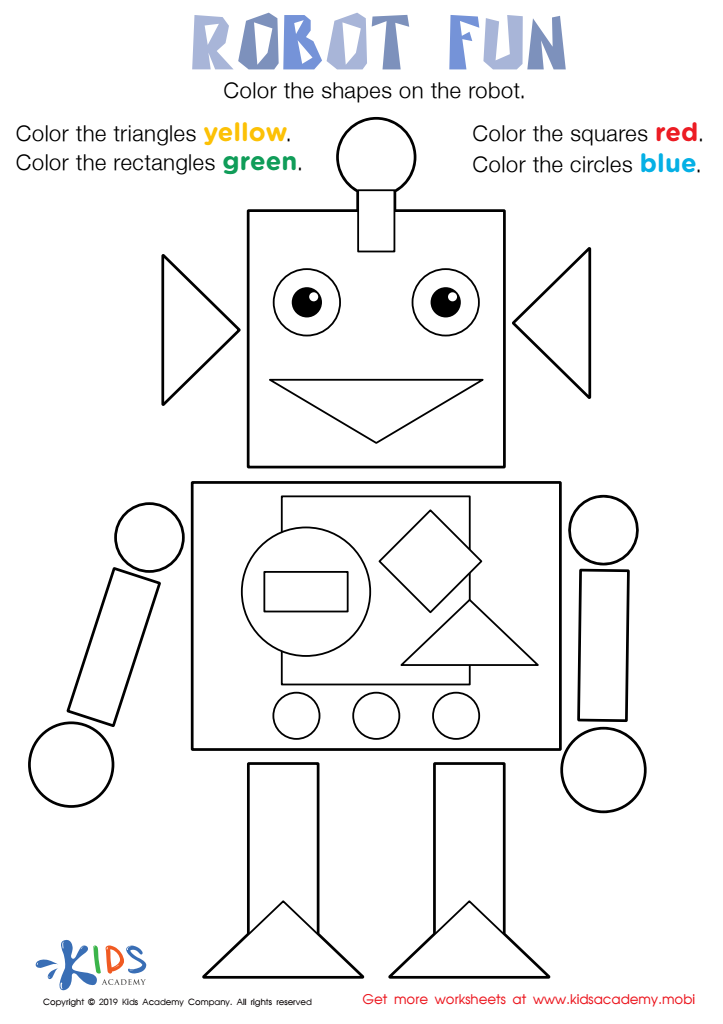

Robot Fun Worksheet
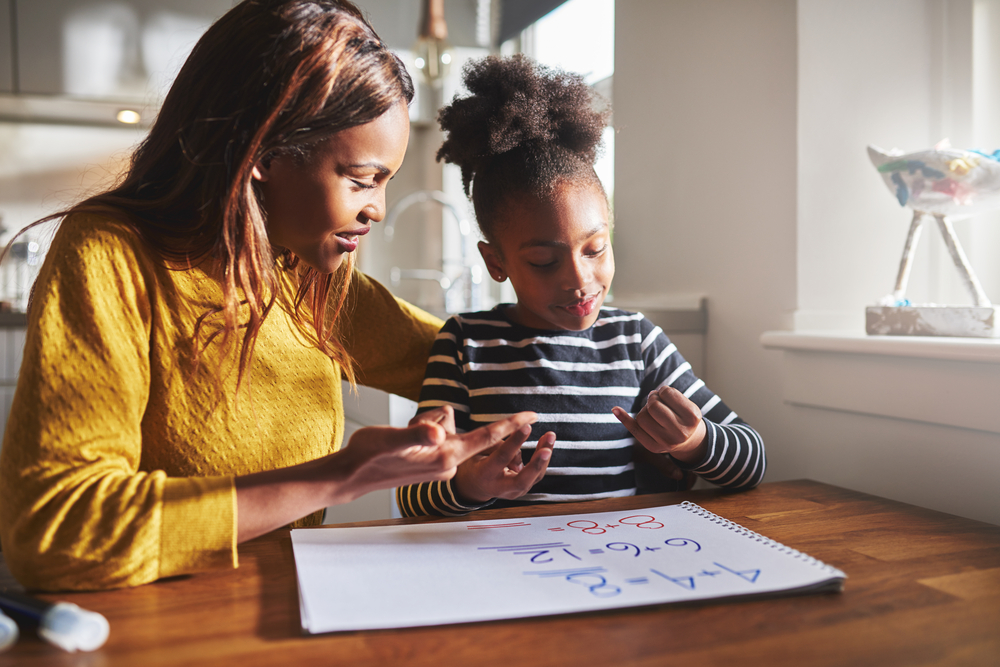
Developing fine motor skills in children aged 4-5 is essential because these skills form the foundation for many everyday activities and academic tasks. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which is crucial for tasks like writing, cutting with scissors, and buttoning clothes. These abilities are not only important for daily life but also for succeeding in school.
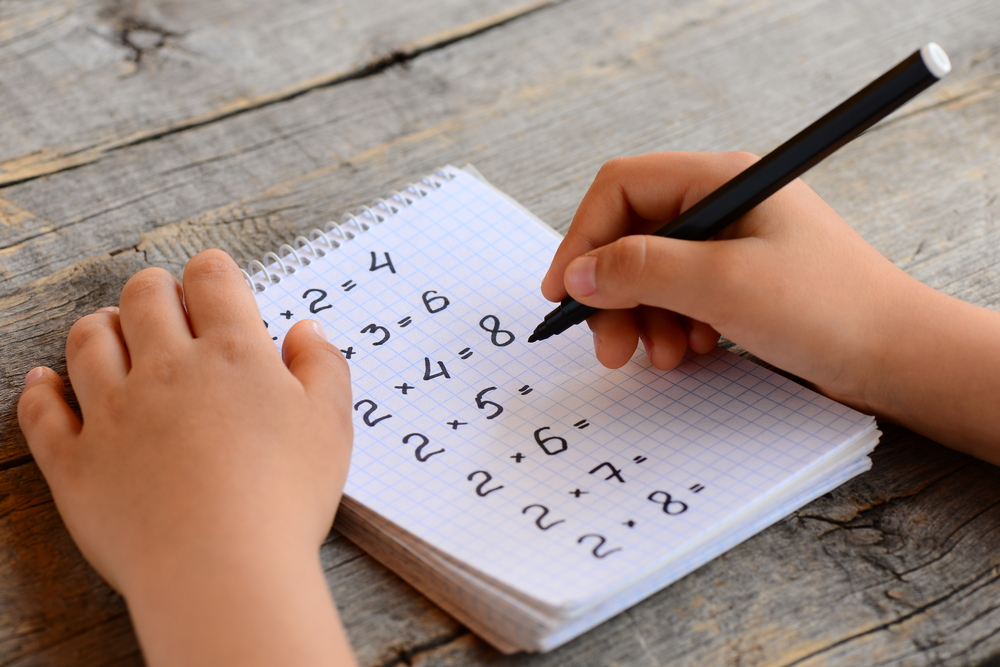
When it comes to math, fine motor skills play a significant role too. Young children often use their fingers and hands to count objects, manipulate shapes, and place puzzle pieces. Activities like these help them understand mathematical concepts in a tangible way. For instance, sorting small items or assembling block structures enhances their spatial awareness and ability to recognize patterns—key components of early mathematical learning.
Moreover, fine motor skills indirectly support cognitive development. As children practice these skills, they are also improving their concentration, problem-solving abilities, and hand-eye coordination. This well-rounded development is fundamental for their academic growth and confidence.
Parents and teachers should therefore emphasize fine motor activities such as drawing, playing with building blocks, and engaging in crafts. By doing so, they are not just preparing children to write but also laying a solid foundation for mathematical understanding and overall educational success.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students