Fine Motor Skills Reading Worksheets for Ages 4-6 - Page 2
42 filtered results
-
From - To

Red and Green Worksheet
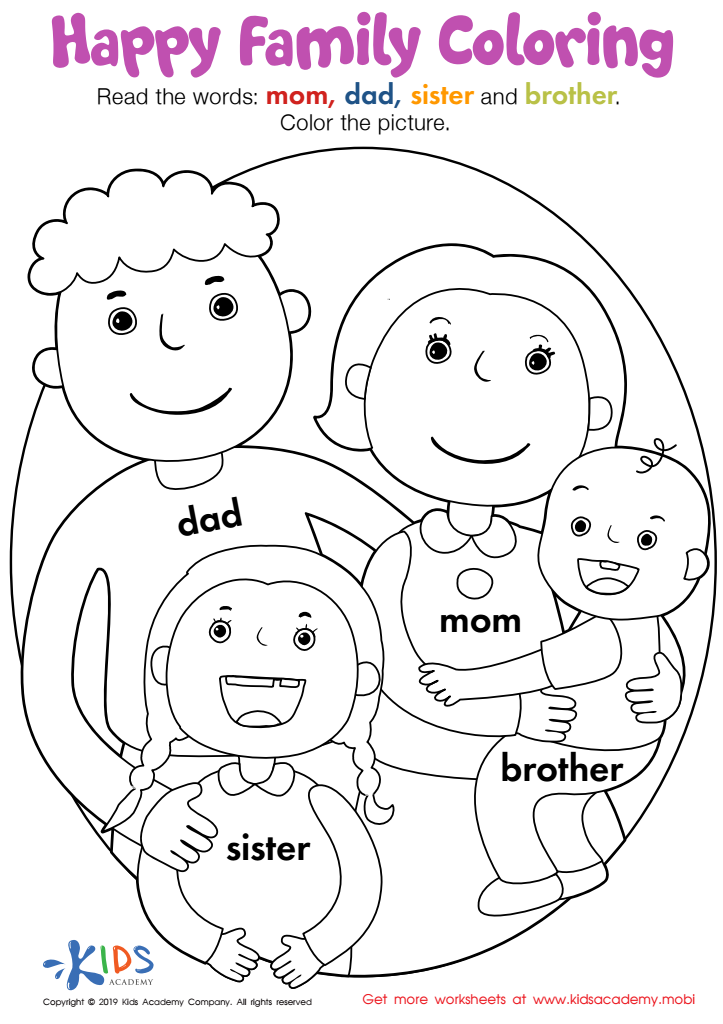


Happy Family Coloring Worksheet


Bee Rhyming Words Worksheet


Baby, Boat, Bird Worksheet Sight Words Worksheet


White and Pink Coloring Fun Worksheet

Pair Pears Worksheet

Big Bad Wolf Printable Coloring Page


The Bingo Song: Coloring The Dog Worksheet


Pen Rhyming Words Worksheet


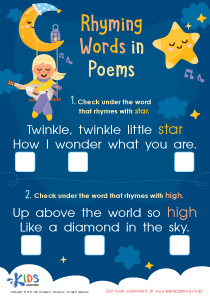
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills play a crucial role in a child's overall development, particularly in the realm of reading and literacy for ages 4-6. During these foundational years, children's ability to grasp, manipulate, and control small objects directly correlates with their reading progress. Skills such as grasping a pencil for writing, turning the pages of a book, or using scissors are all fine motor activities that support their engagement with print and drawings.
Parents and teachers should be particularly invested in fostering fine motor skills because these capabilities not only contribute to improved reading abilities but also enhance children's confidence and independence during learning activities. Developing these skills helps children recognize letters through activities like tracing, facilitates writing their names, and enables them to participate actively during reading group sessions.
Furthermore, these skills are integral to their transition into more complex tasks, such as spelling and handwriting, as they progress in education. Engaging in fine motor activities—like crafts, puzzles, and playful writing exercises—not only builds these skills but also makes learning enjoyable. Therefore, emphasizing fine motor skill development is essential for nurturing early literacy and helping young learners thrive academically.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students