Hand-eye Coordination Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 4-7 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To
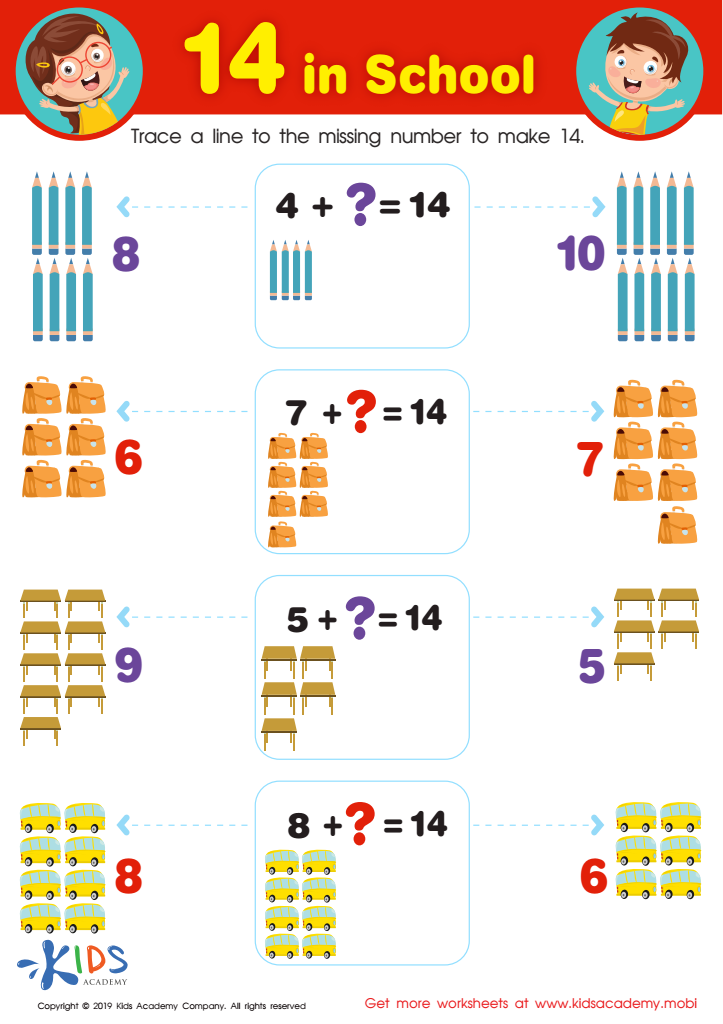

14 in School Worksheet
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial developmental skill that involves the integration of visual input with appropriate motor responses. For children ages 4-7, developing this coordination is fundamental not just for physical activities, but also for essential cognitive skills including addition and subtraction.
At this young age, children are in a critical period of growth in which their brains are particularly plastic and ready to form important neural connections. Engaging in activities that build hand-eye coordination while also incorporating arithmetic fosters these neural pathways more effectively. For example, physical actives such as sorting objects or using manipulatives like beads or blocks for counting and calculations help blend physical coordination with cognitive functions. This dual engagement can make abstract concepts more concrete and understandable for young minds.
Teachers and parents should care about strengthening hand-eye coordination in tandem with arithmetic skills as it promotes multi-sensory learning. This method helps improve spatial awareness, precision, and motor planning, which are all essential for writing skills and general physical development. Moreover, children who develop strong hand-eye coordination are often more confident in tackling both physical and cognitive challenges, setting a positive foundation for lifelong learning and problem-solving abilities.
Therefore, integrating hand-eye coordination development with basic arithmetic prepares children for future academic and life success by catering to the holistic development of mind and body.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students