Understanding sequencing Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8
7 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's math skills with our "Understanding Sequencing Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8" at Kids Academy. Tailored specifically for young learners, these printable worksheets simplify the concept of addition through engaging, step-by-step exercises. Focused on building a strong foundation in sequencing, our activities help kids understand the order of operations. Each worksheet is designed to boost confidence, develop critical thinking, and lay the groundwork for future math success. Ideal for classroom or at-home learning, explore how our sequenced addition worksheets make mastering math fun and accessible for children from 4 to 8 years old.
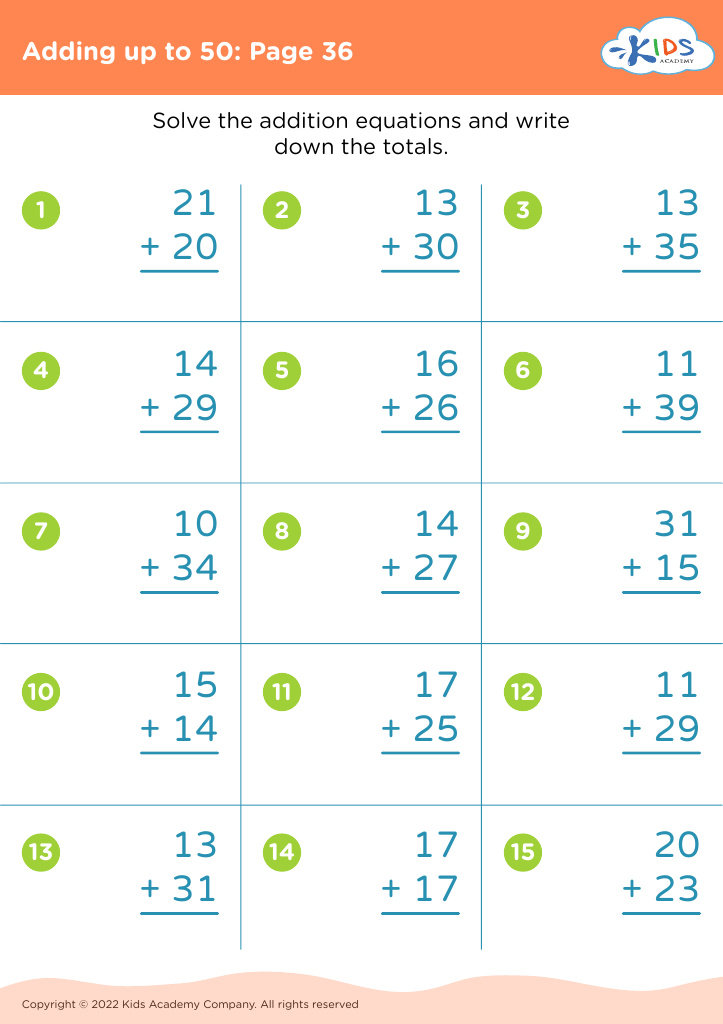
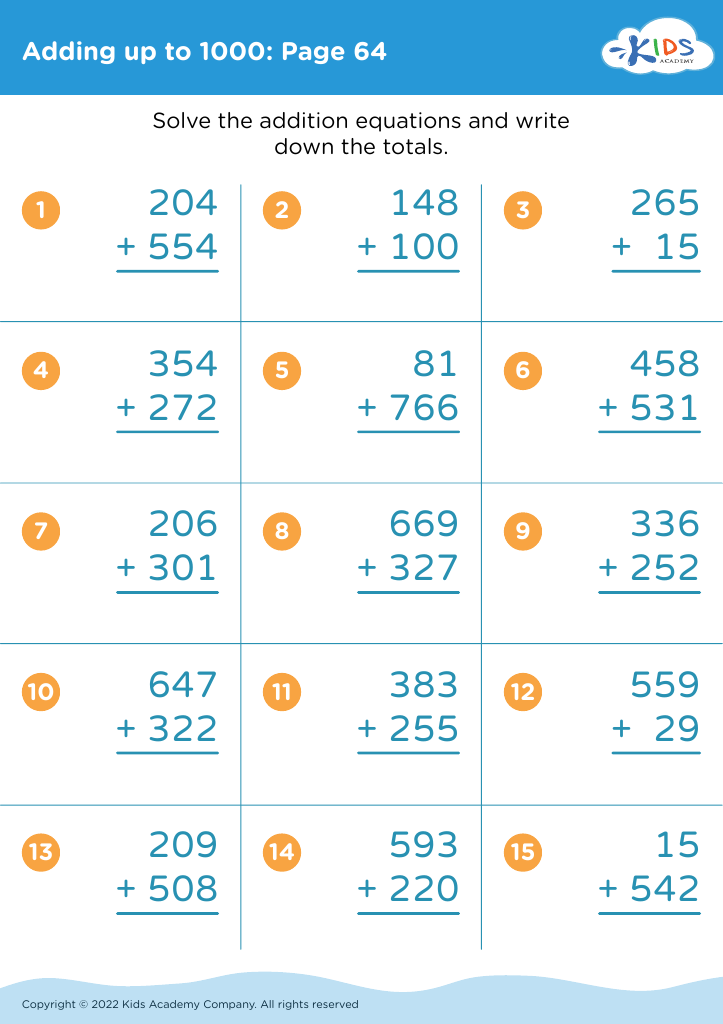
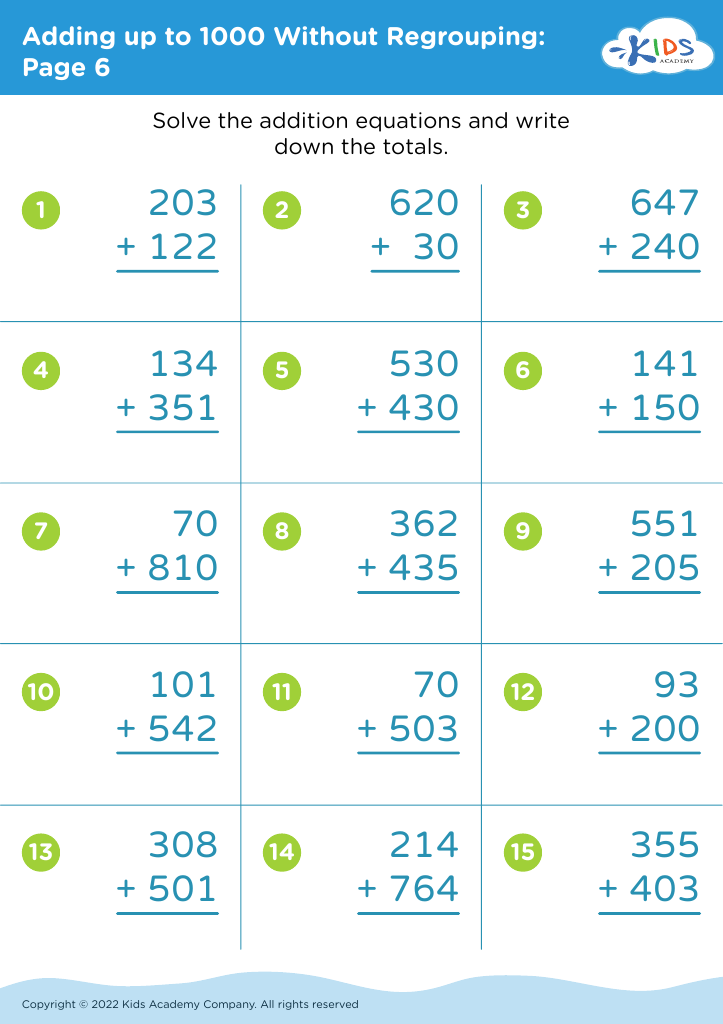
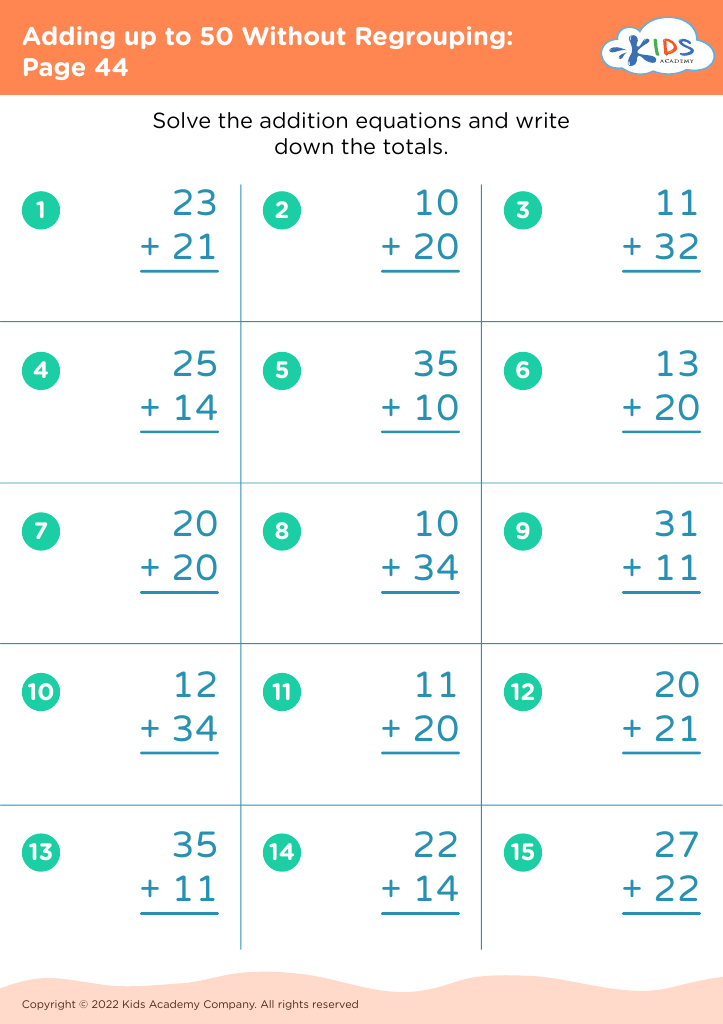
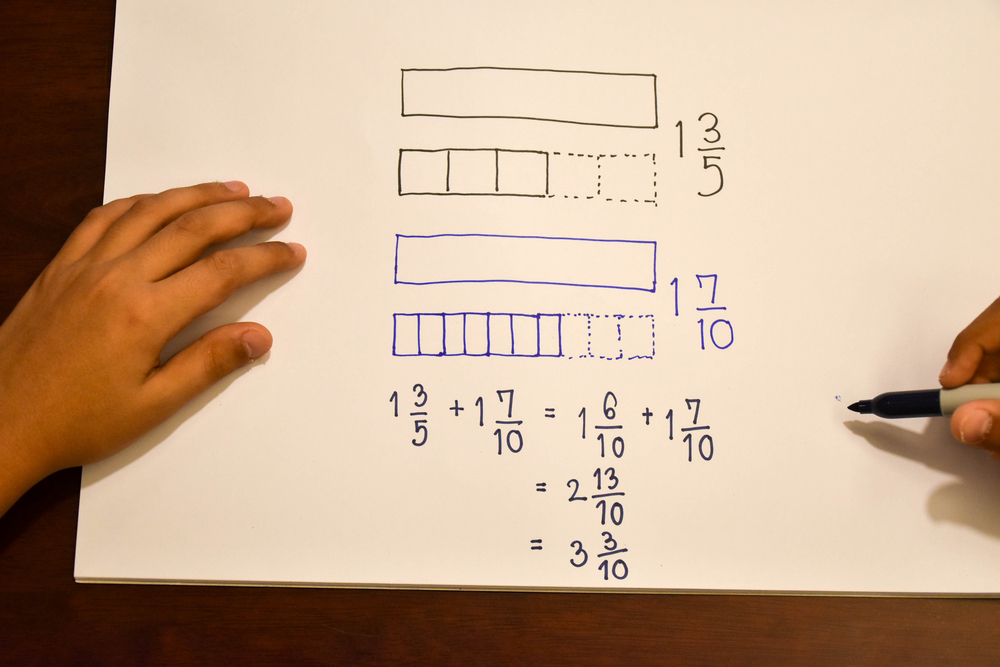
Understanding sequencing in addition is crucial for young children (ages 4-8) as it lays the foundation for future mathematical learning and cognitive development. Sequencing—the ability to understand and arrange elements in a logical order—is essential in grasping the steps involved in any mathematical process, especially addition.
When children comprehend the sequence of numbers and how they fit together to create sums, they are not just memorizing facts, but learning the 'why' and 'how' behind the process. This deep understanding encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills. For example, when a child can arrange the numbers 1 to 5 and understand that adding 2+3 equals 5, they can apply this knowledge to larger and more complex problems later on.
Moreover, understanding sequencing aids in the development of strong computational skills. Students who recognize that numbers are part of a continuing progression (e.g., 2 comes before 3 and adding 2+1 makes 3) can perform addition more intuitively and accurately.
Lastly, fostering these skills early builds confidence in young learners, making them more likely to engage with math positively. This balanced developmental foundation can prompt academic success not only in math but in other subjects requiring logical thinking and organized thought processes. Therefore, both parents and teachers should prioritize sequencing in addition to set children on a successful academic path.