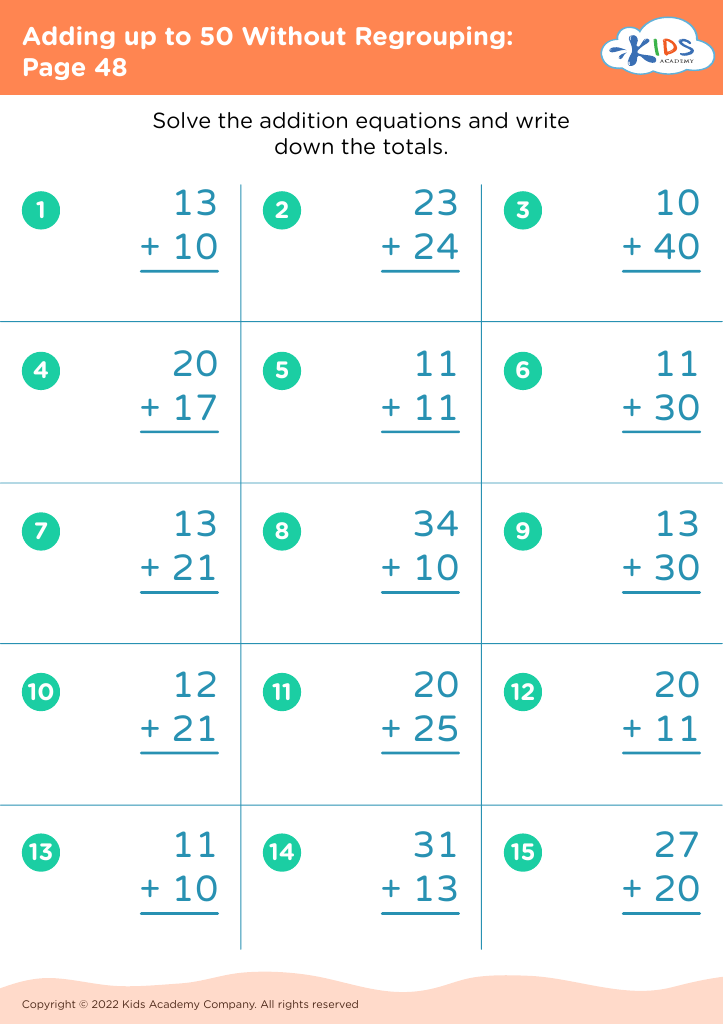
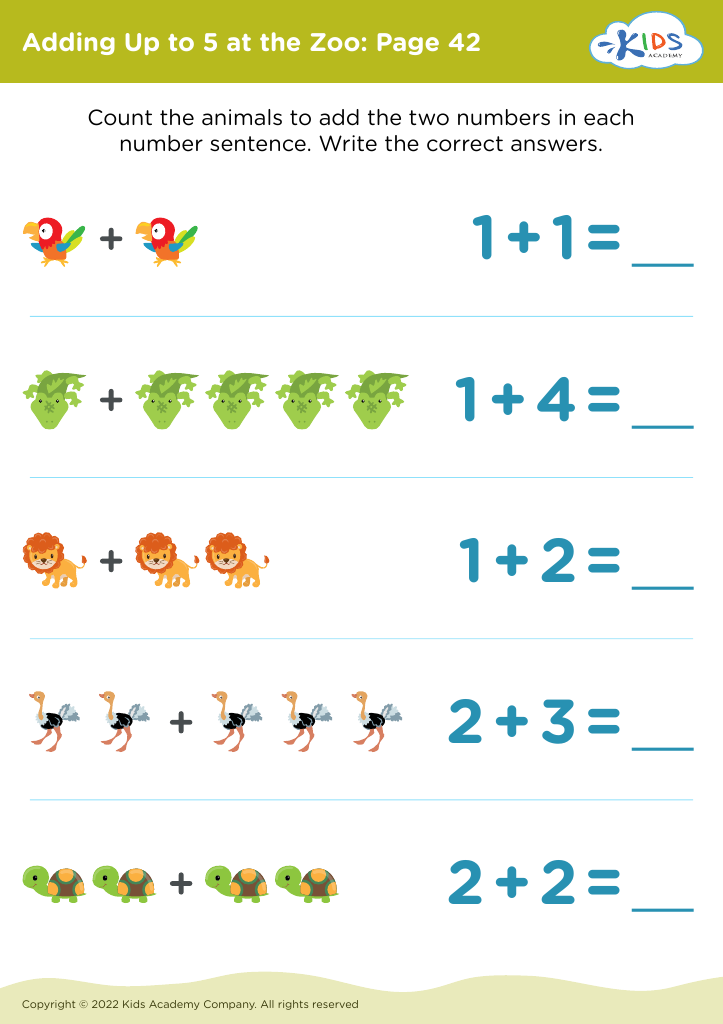Fine motor skills (writing) Math Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
43 filtered results
-
From - To


Counting Flowers Worksheet
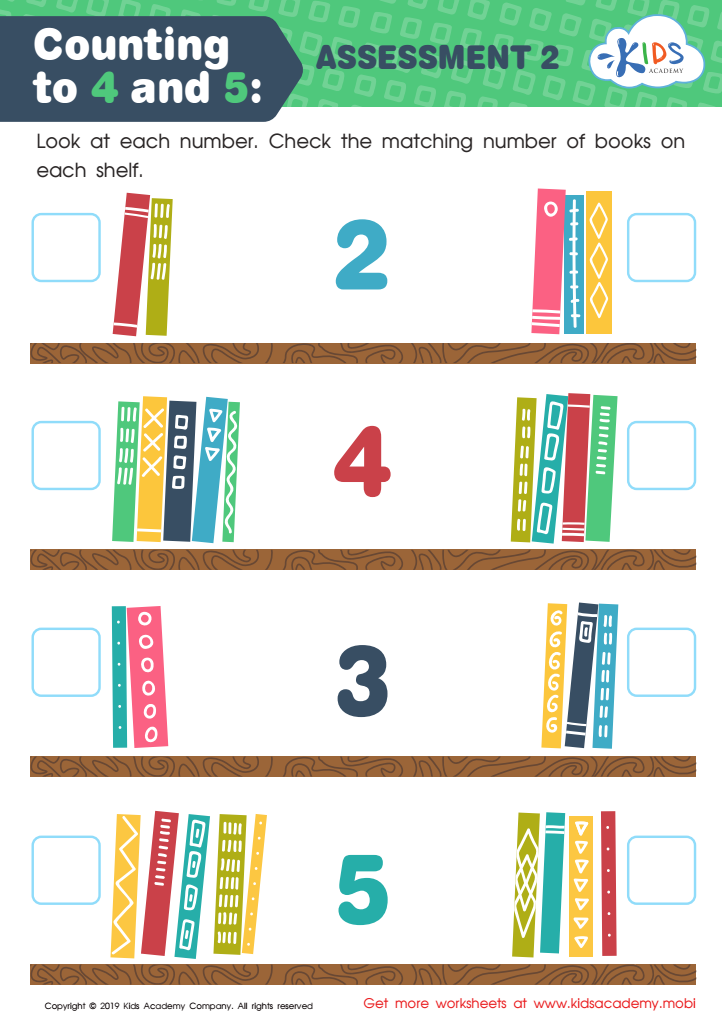

Counting to 4 and 5: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Parents and teachers should place significant importance on developing fine motor skills in children ages 4-8, particularly because these skills are foundational for success in writing and math. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, especially those in the hands and fingers, and are essential for tasks like gripping a pencil, forming letters, and manipulating small objects.
In the context of writing, the ability to grasp and control a pencil accurately allows children to express their thoughts, complete assignments, and communicate effectively. Early proficiency in writing can bolster a child's confidence, facilitating a more engaging and fruitful learning experience across all subjects.
In math, fine motor skills play a key role in activities such as organizing objects, counting, drawing shapes, and using math tools like rulers and manipulatives. Manipulating small items such as counting beads enhances children's understanding of quantities and spatial relationships. When children develop these skills early, they are better able to focus on cognitive tasks rather than struggling with the physical demands of writing or handling objects, thereby enhancing their overall academic performance.
Moreover, early mastery of fine motor skills lays the groundwork for future educational tasks that require even more complex motor coordination. Therefore, fostering these skills at a young age is crucial for holistic academic development and lifelong learning.

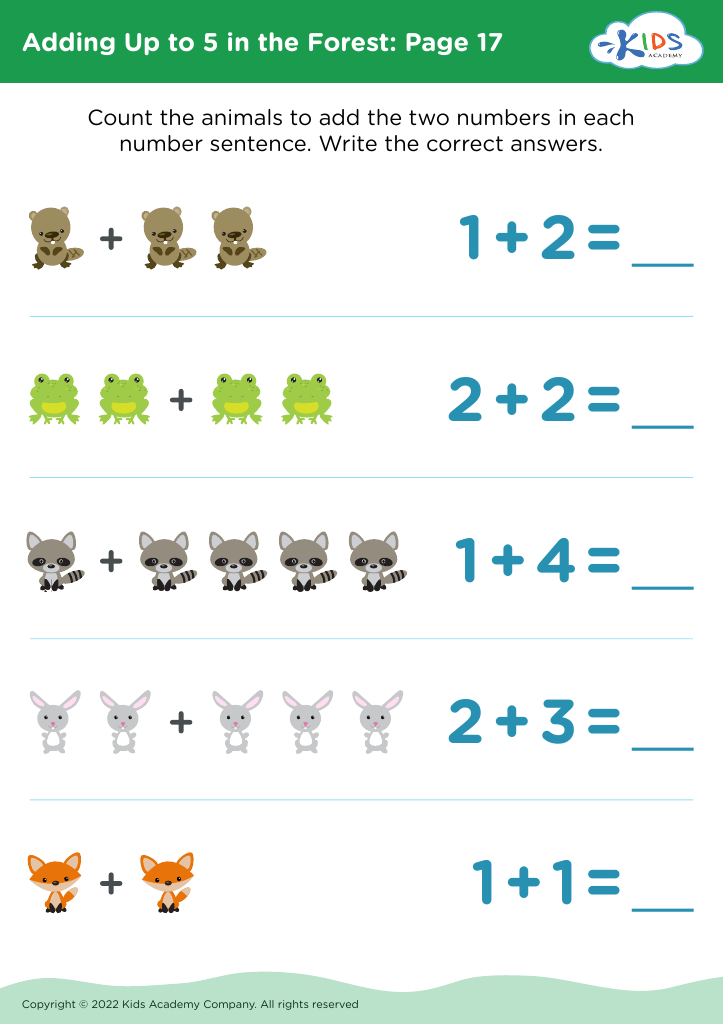



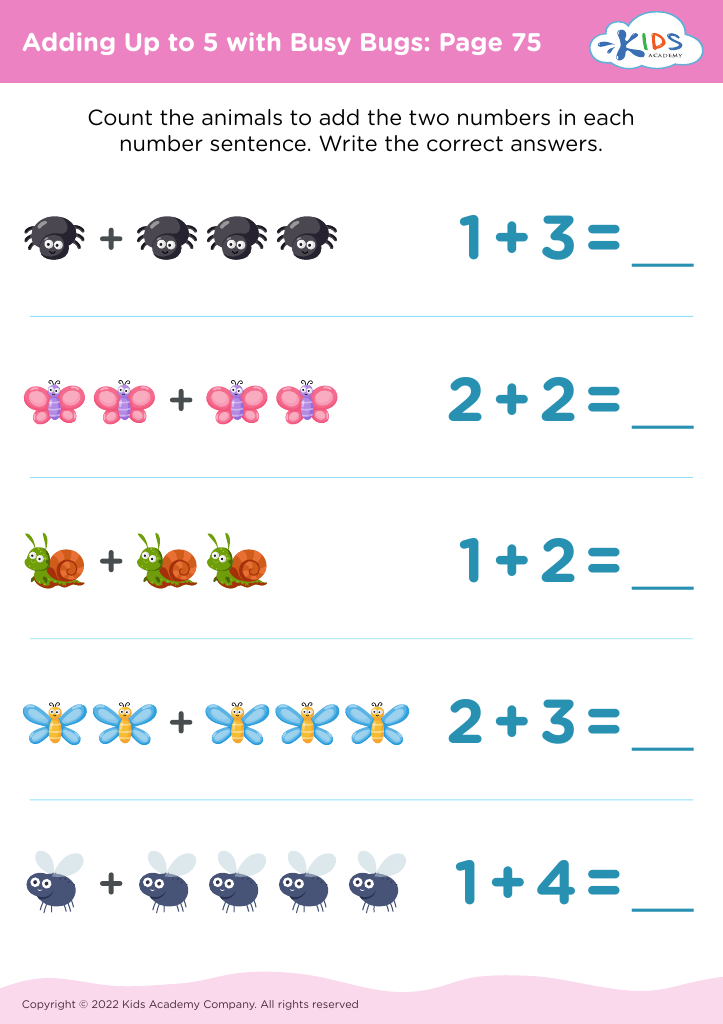

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students