Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 4
96 filtered results
-
From - To


Uppercase Letters D, E, and F Worksheet
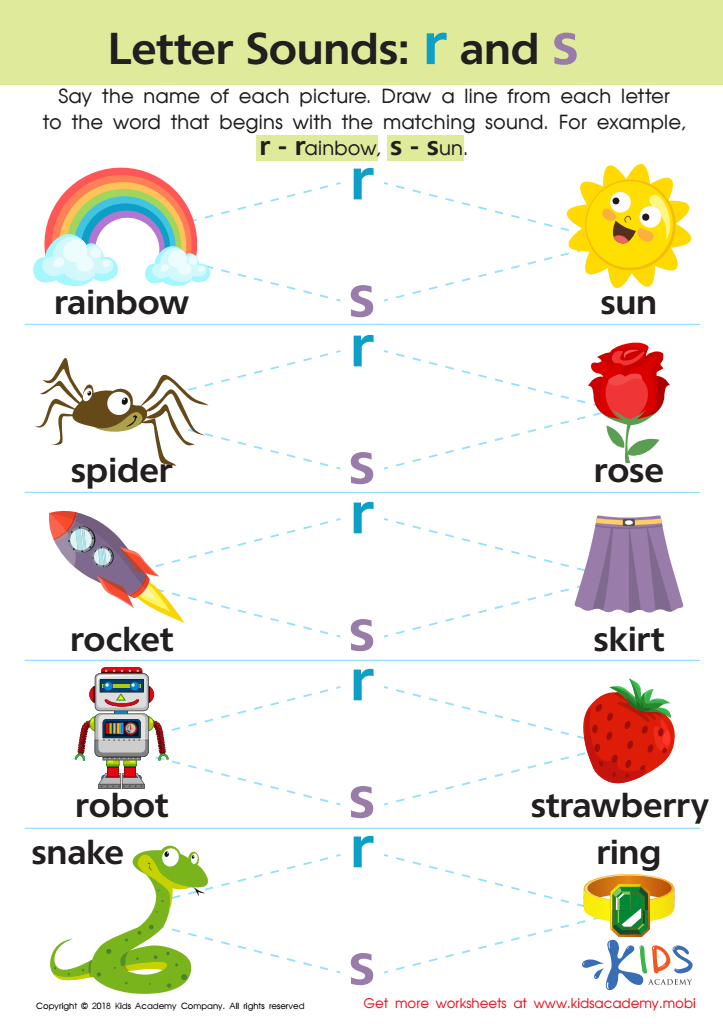

Letter R and S Sounds Worksheet


Brown Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Number 6 Worksheet


Upon, Around, Off Sight Words Worksheet


Numbers and Number Words 6–1 Worksheet


Letter K Coloring Sheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet
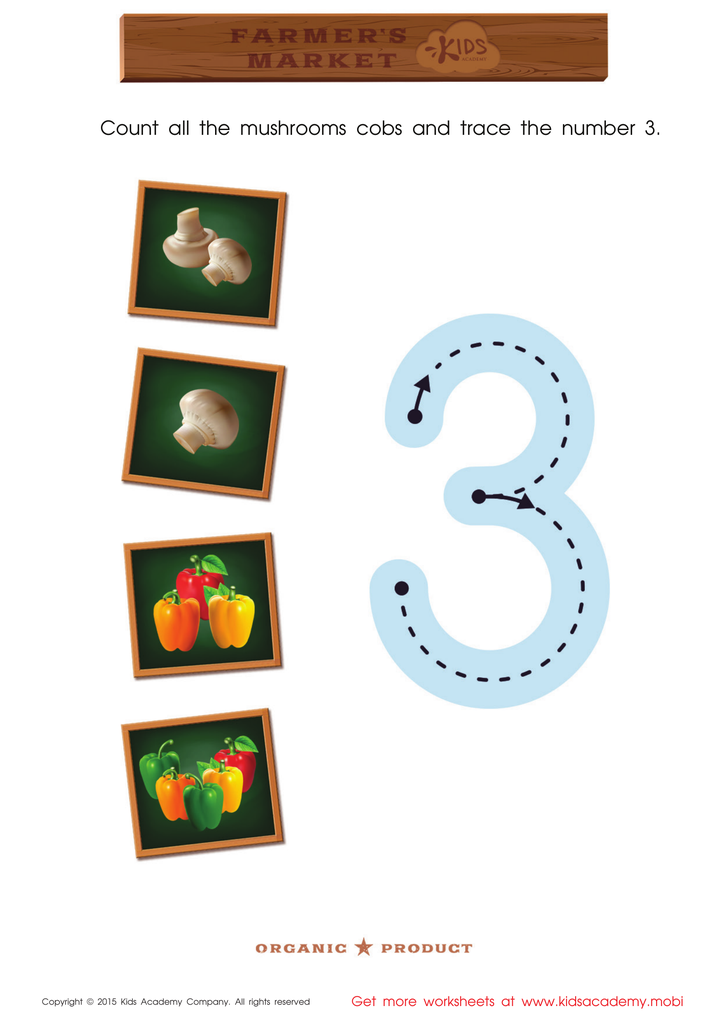


Count the Mushrooms and Trace the Number 3 Printable


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet


Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


Lowercase Letters a b c Worksheet


Lowercase Letters v w x Worksheet


"B" Words Printable Sight Words Worksheet


Letter N Coloring Sheet
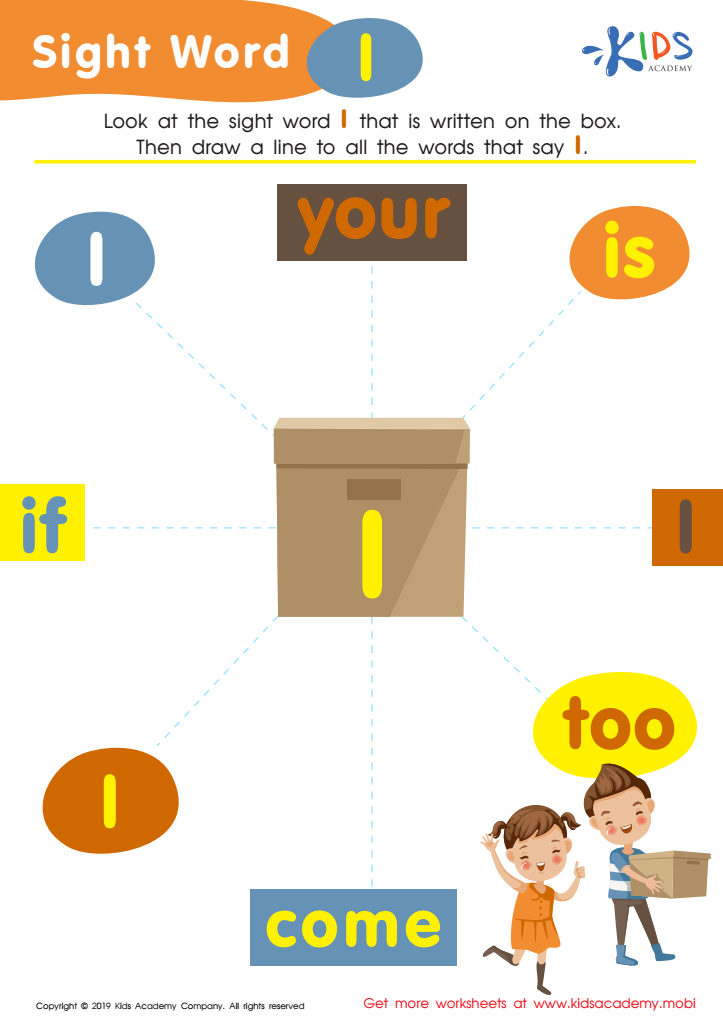

Sight Word I Worksheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet


Count and Write 6 Worksheet


Letter D and E Sounds Worksheet


Uppercase Letters V, W, and X Worksheet


Finish Rhyming Poem Worksheet


Trace Read You Like Worksheet


Finish the Word Worksheet
Handwriting practice is crucial for children aged 4-9 because it significantly impacts their academic and personal development. Firstly, learning to write legibly enhances a child's ability to communicate ideas clearly. Good handwriting skills contribute to better reading comprehension, as forming letters by hand helps children recognize them. This creates a strong literacy foundation. Additionally, handwriting practice improves fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination, essential for tasks like using scissors or tying shoelaces.
Neurodevelopmentally, writing by hand activates neural circuits associated with thinking, memory, and language. This deep engagement boosts cognitive skills, aiding overall learning. Moreover, the discipline of regular writing practice instills a sense of responsibility and perseverance, fostering essential habits for long-term academic success.
In today’s digital age, parents and teachers might overlook handwriting. However, research suggests that writing aids brain development differently than typing. For instance, the focused attention required for handwriting practice enhances concentration and patience, qualities less effectively developed through screen interaction.
Finally, neat handwriting engenders pride in a child's work, providing a boost to their self-esteem and academic confidence. By prioritizing handwriting in the early years, parents and teachers lay the groundwork for comprehensive educational and personal growth.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
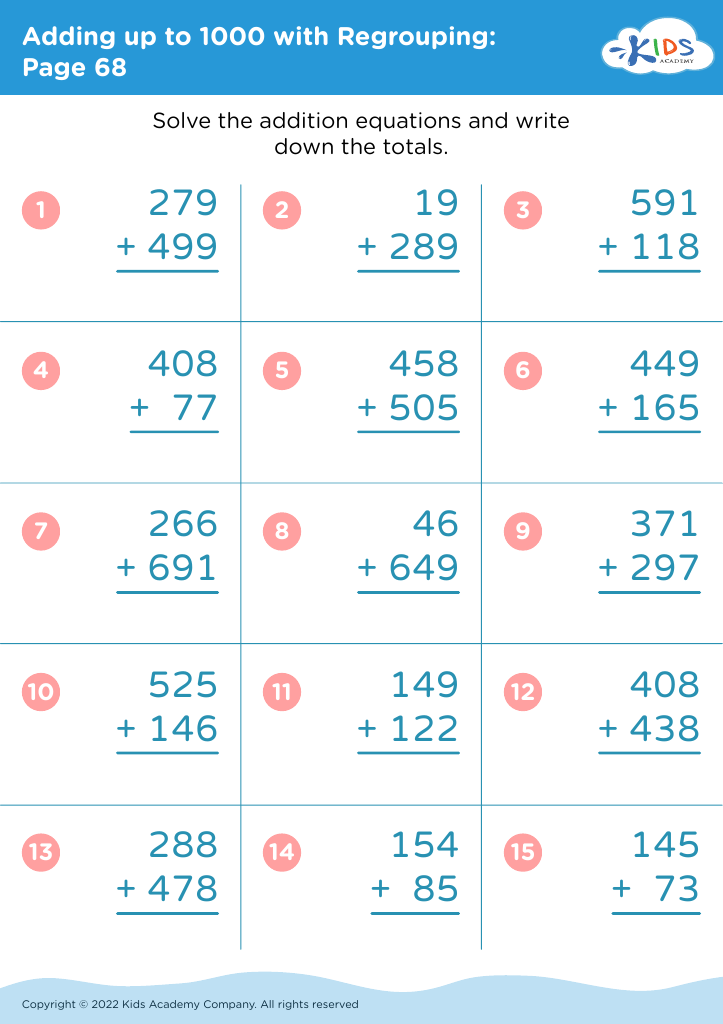





.jpg)










