Fine Motor Skills Reading Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 2
42 filtered results
-
From - To
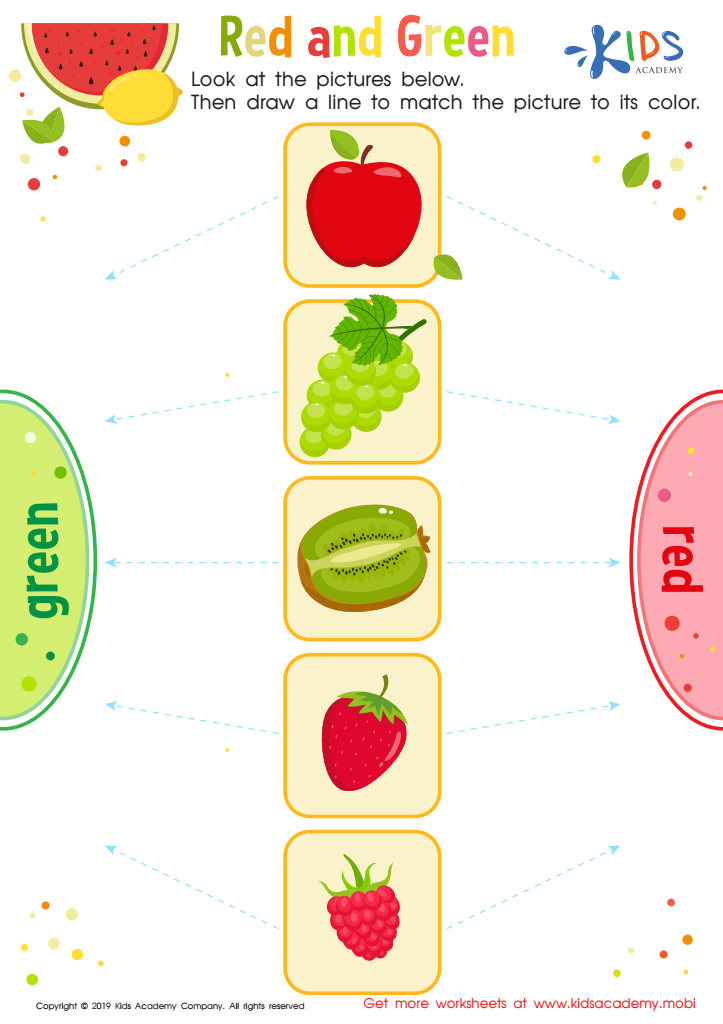

Red and Green Worksheet


Happy Family Coloring Worksheet


Bee Rhyming Words Worksheet


Baby, Boat, Bird Worksheet Sight Words Worksheet


White and Pink Coloring Fun Worksheet
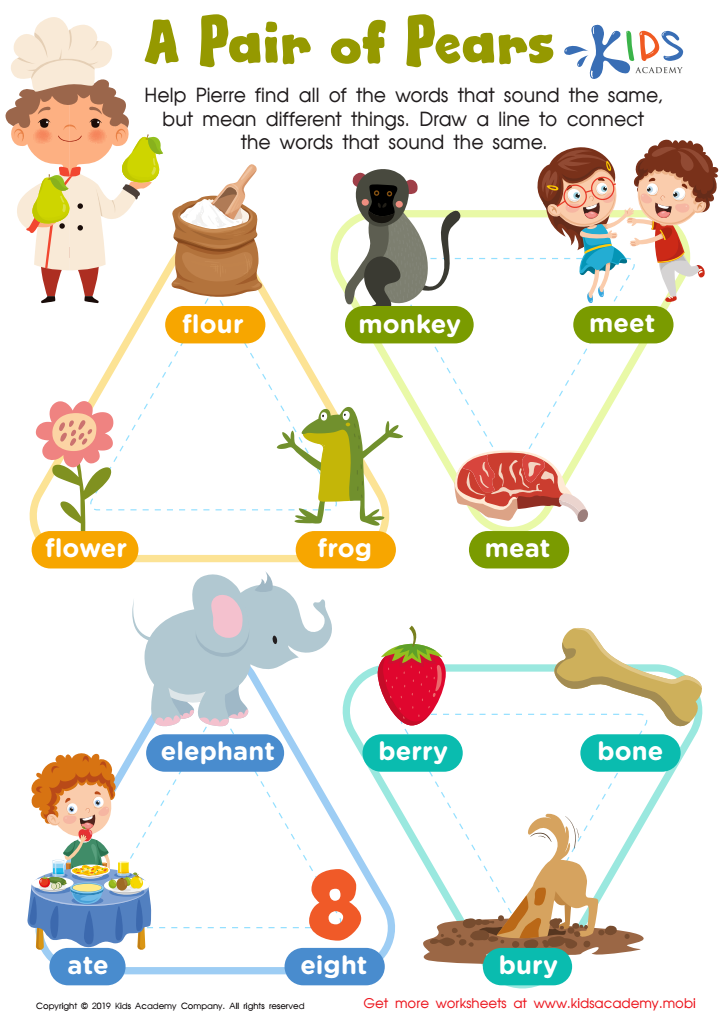

Pair Pears Worksheet
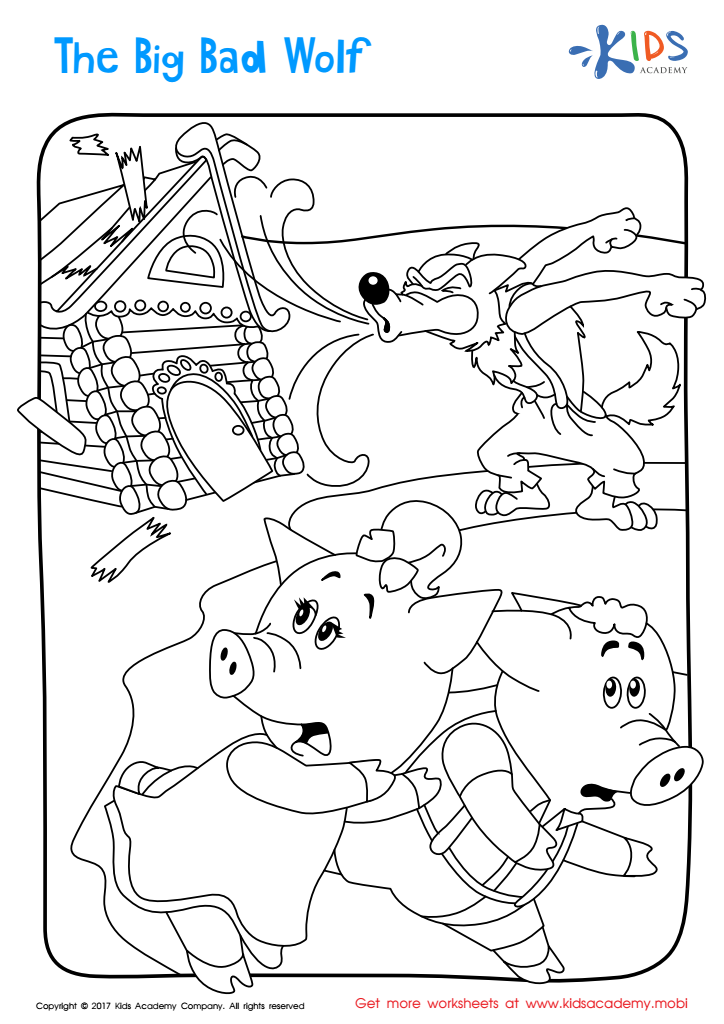

Big Bad Wolf Printable Coloring Page


The Bingo Song: Coloring The Dog Worksheet


Pen Rhyming Words Worksheet


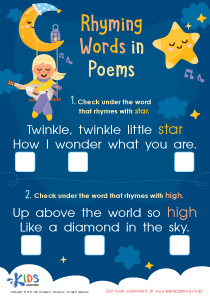
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills are critical for children aged 5-6 as they form the foundation for various academic and everyday activities. For young learners, developing these skills enhances their ability to grasp pencils, write letters, and turn pages in books, which are essential actions in learning to read. When children improve their fine motor skills, they gain better control over small hand muscles, making tasks such as manipulating book pages smoother and more efficient. This not only helps in reading but also fosters independence and confidence.
Furthermore, refined motor skills support cognitive development. For instance, coordination and precision in tasks like cutting, drawing, or playing with small objects encourage brain development and establish neuronal connections critical for learning processes. Kids at this age are in a crucial period of brain growth, and engaging in activities that develop fine motor skills reinforces pathways that enhance their overall cognitive and academic abilities.
As reading becomes more integral to children’s learning curriculum, adequately developed fine motor skills prepare them to face challenges associated with it confidently. This readiness not only boosts their initial academic success but also influences their long-term educational trajectory. By prioritizing fine motor skill development, teachers and parents are investing in a foundational element that promotes multitiered growth—academically, cognitively, and socio-emotionally.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students











.jpg)