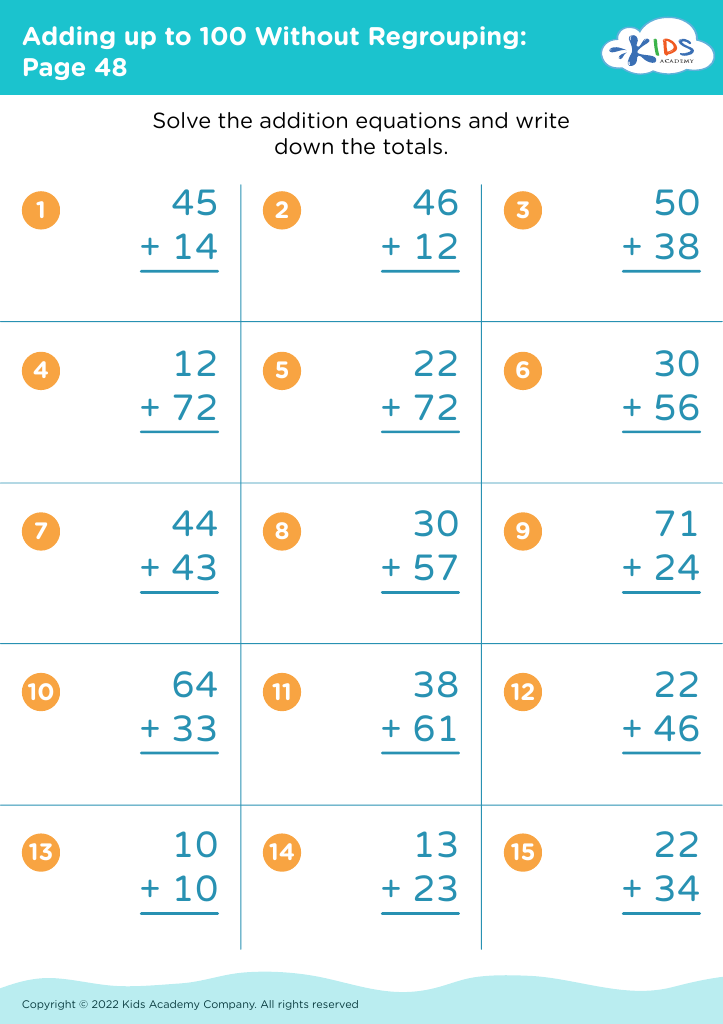
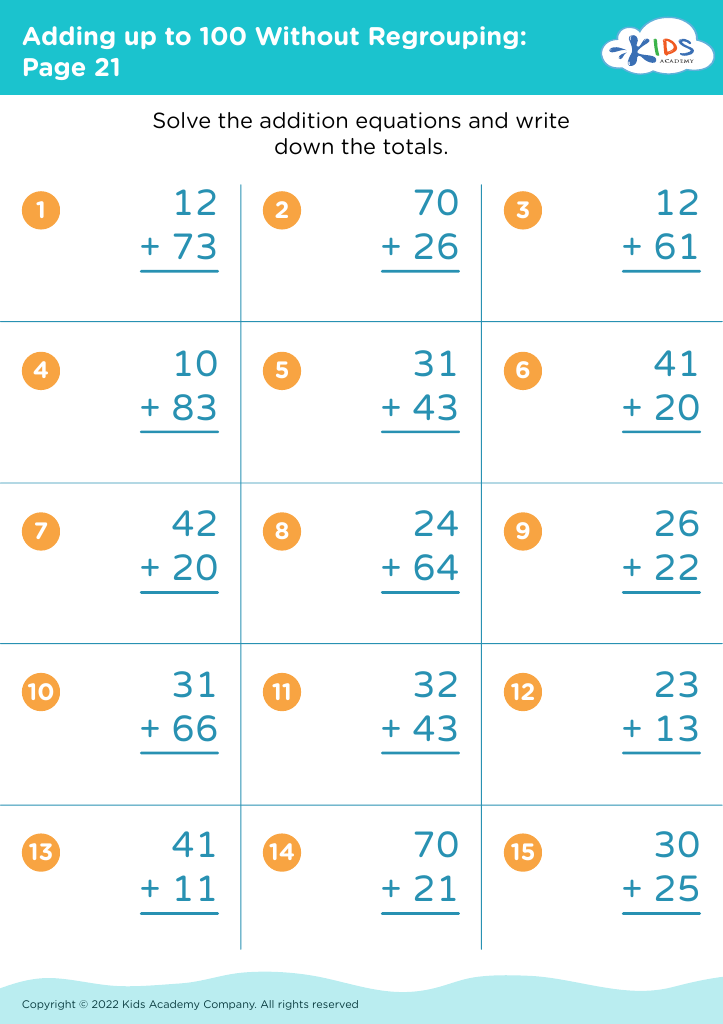
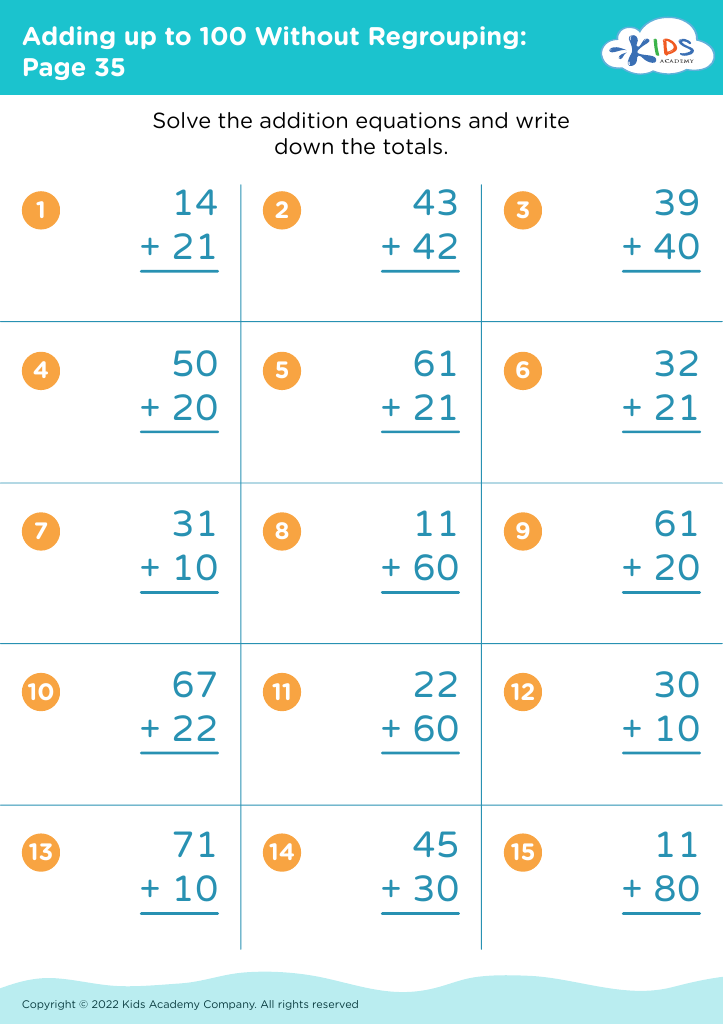
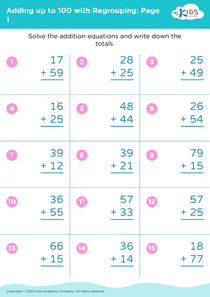
Improve reading comprehension Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 5-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's reading comprehension and math skills with our "Improve Reading Comprehension Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets." Perfect for ages 5-7, these worksheets combine engaging reading passages with math exercises, helping young learners understand and solve addition problems without the need for regrouping. Kids will enhance their ability to add numbers up to 100 while also improving reading comprehension and critical thinking skills. Our fun and interactive worksheets are designed to make learning enjoyable and effective, laying a strong foundation for future academic success. Explore these invaluable resources to enrich your child's educational journey today!
Improving reading comprehension and mastering addition up to 100 without regrouping are foundational skills for children ages 5-7 and should be a priority for both parents and teachers. Reading comprehension is crucial because it allows children to understand and engage with text, which is essential for all other areas of learning. When children comprehend what they read, they can follow instructions, grasp concepts in other subject areas, and improve their overall communication skills. Strong reading comprehension at an early age sets the stage for academic success and instills a lifelong love of learning.
Similarly, basic arithmetic skills such as adding up to 100 without regrouping serve as the building blocks for future mathematical learning. Mastering these early math skills promotes problem-solving abilities, logical thinking, and numeracy. These competencies are essential not only for advanced math topics that children will encounter later in their education but also for everyday life skills. Ensuring that children grasp these concepts early on helps to build a strong academic foundation, eases future learning, and boosts their confidence in their abilities. In summary, prioritizing reading comprehension and basic arithmetic for young learners equips them with the critical skills needed for future academic endeavors and practical decision-making in their daily lives.