Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Misc Worksheets for Ages 5-7
5 filtered results
-
From - To
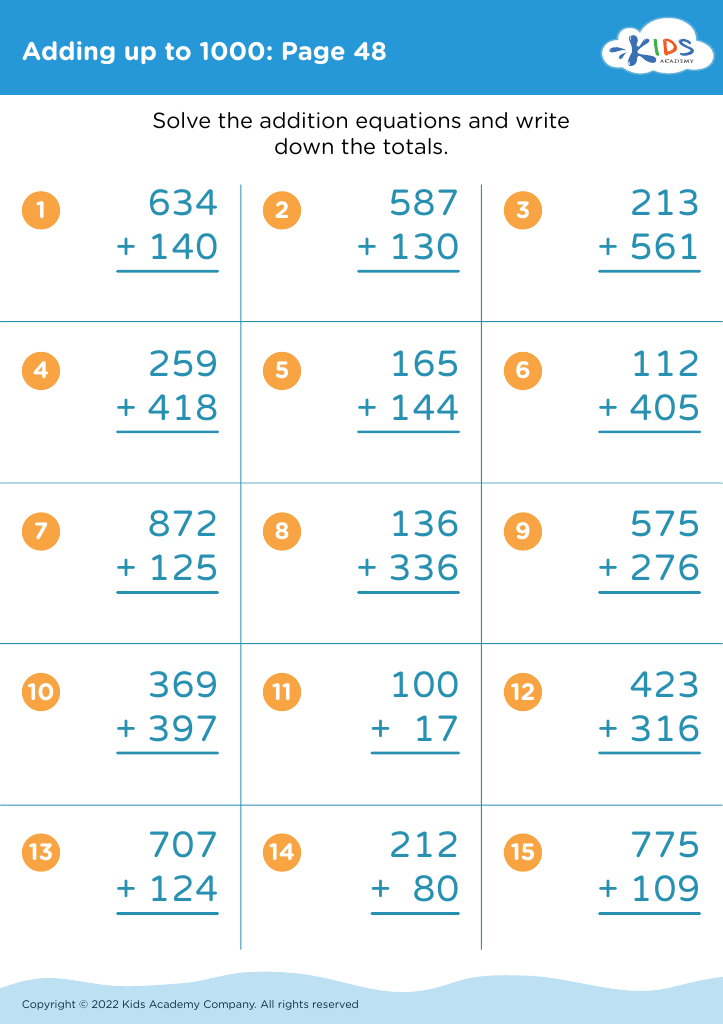
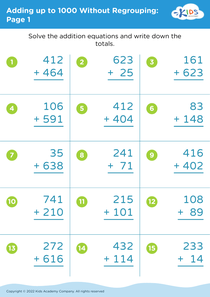
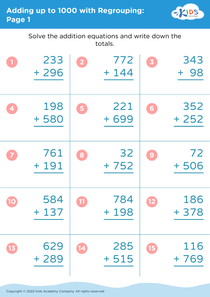
Boost your child's fine motor skills with our engaging collection of worksheets designed for ages 5-7. Featuring a variety of activities that incorporate essential math concepts while promoting hand-eye coordination and dexterity, these printable resources are perfect for early learners. Each worksheet encourages children to trace, cut, and manipulate objects, seamlessly blending foundational math skills with fun fine motor exercises. From counting to addition and number recognition, our Fine Motor Skills worksheets make learning interactive and enjoyable. Prepare your little ones for academic success while enhancing their creativity and precision. Dive into a world of educational activity with our Adding Up to 1000 worksheets!
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 5-7 as they form the foundation for various everyday tasks and academic activities. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling children to perform tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. By refining these skills, children develop greater hand-eye coordination and dexterity, which enhances their ability to engage in schoolwork, art projects, and self-care tasks like buttoning shirts.
Teachers and parents should prioritize the development of fine motor skills because they directly impact a child's confidence and independence. Children who struggle with these skills may find it challenging to keep up with peers academically or socially, leading to frustration. Activities that promote fine motor skills, such as using scissors, completing puzzles, or engaging in craft projects, can foster a willingness to learn and explore.
Moreover, fine motor skills contribute to cognitive development—tasks requiring precision can significantly influence learning processes, including problem-solving and critical thinking. By supporting this growth, adults help set a strong pathway for future success, ensuring that children are well-prepared for the more complex skills they will encounter as they progress in education and life. Investing in fine motor skills is an investment in a child's overall development.