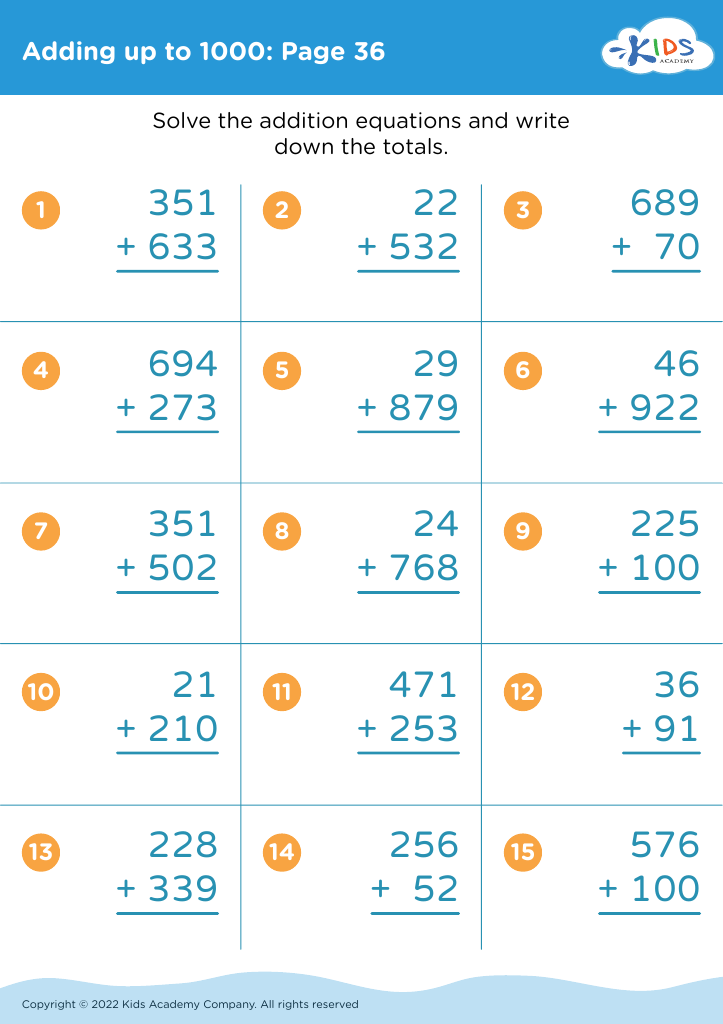
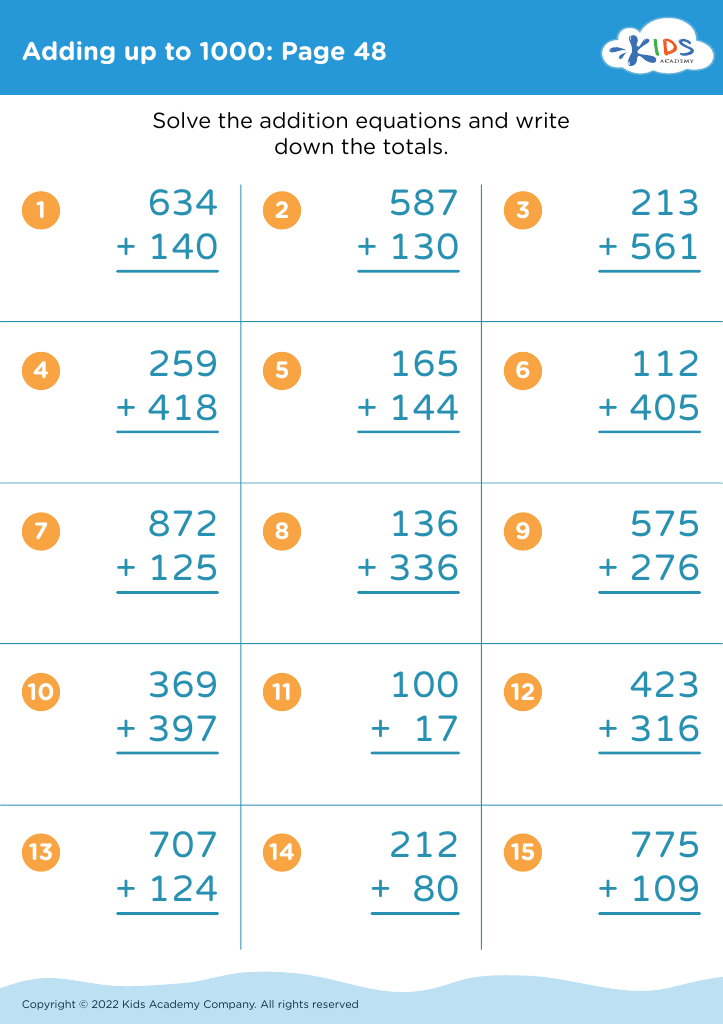
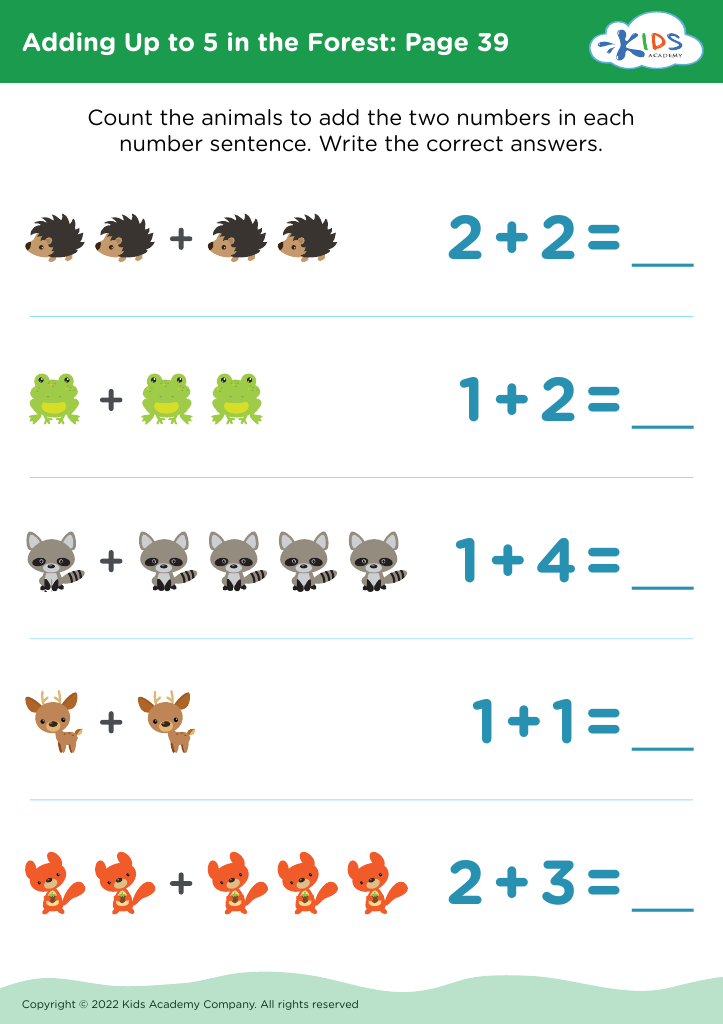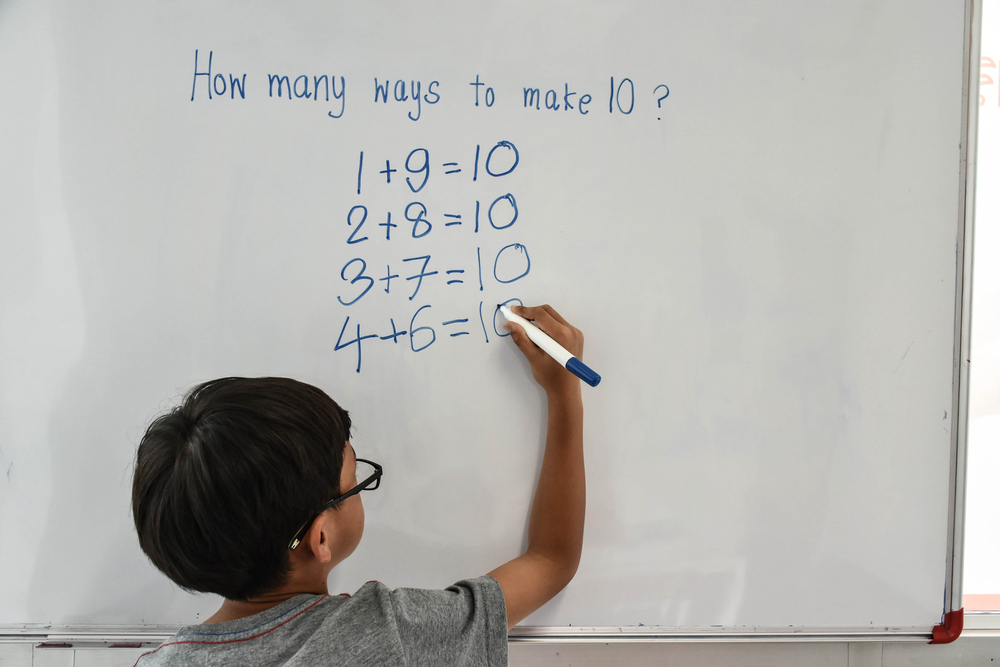Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 5-7 - Page 4
82 filtered results
-
From - To


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet


Math Matching Pairs Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 5-7 as they form the foundation for various academic and everyday tasks, including addition and subtraction. At this age, children are not only learning basic math concepts but also developing the dexterity required to manipulate objects, which supports their numeracy skills.
Engaging children in activities that enhance fine motor skills—such as cutting with scissors, threading beads, or building with blocks—invites opportunities for counting, grouping, and organizing numbers. This not only makes math tangible but also encourages problem-solving and critical thinking. For instance, using small objects like coins or buttons allows children to physically represent addition and subtraction, reinforcing their understanding of these concepts through manipulation.
Moreover, with well-developed fine motor skills, children gain greater confidence and independence in their learning. As they master tasks like writing numbers or drawing calculations, they are more likely to engage positively with mathematical practices, fostering a love for learning.
Parents and teachers play an integral role in deliberately incorporating fine motor skill activities into everyday routines. By doing so, they support a child’s overall development, paving the way for successful mathematical understanding and real-world application. Thus, nurturing fine motor skills is essential for enhancing both academic and life skills in young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students