Improve fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 5-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our fun and engaging Math Worksheets for ages 5-7! Designed to blend math learning with essential motor skill development, these worksheets help young learners strengthen their hands, fingers, and coordination. Each activity, from tracing numbers to solving puzzles, promises to captivate and challenge. Ideal for at-home practice or in the classroom, our worksheets support academic growth and physical dexterity. Explore a wide range of topics, including counting, addition, and more, ensuring a well-rounded approach to math learning. Boost your child's confidence and skills today with our expertly crafted resources!
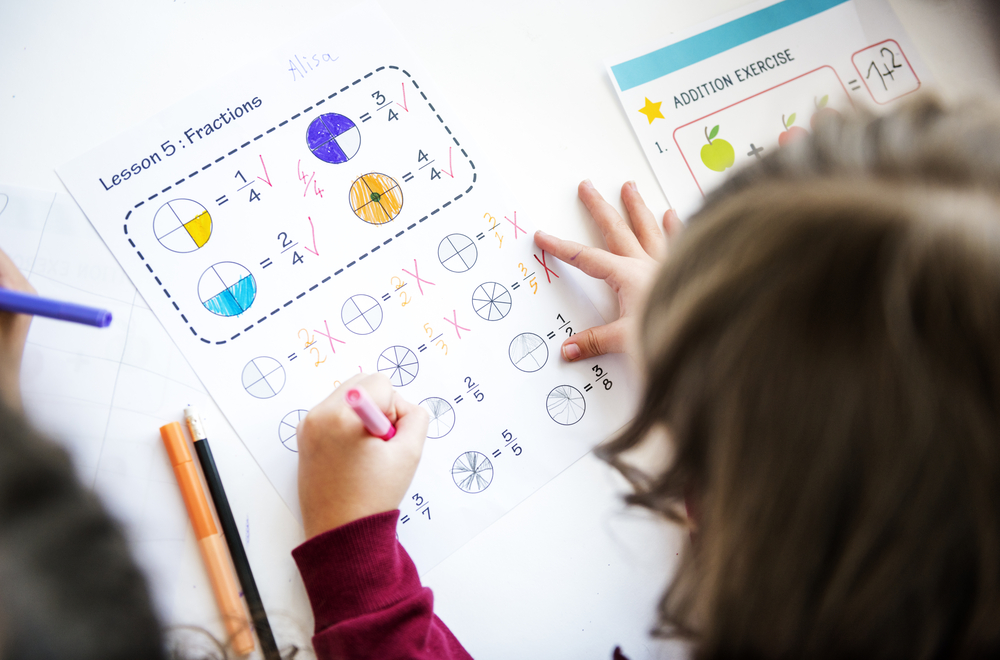
Developing fine motor skills, coupled with early math education, is crucial for children aged 5-7 as these foundations impact both academic and everyday life skills. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscle movements, particularly those in the hands and fingers. For young children, these skills are vital for tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using scissors. Strengthening fine motor skills can enhance hand-eye coordination, boost independence, and foster greater self-esteem.
Integrating math into activities that develop fine motor skills offers dual benefits. Hands-on math activities like sorting small objects, building block towers, or threading beads not only enhance numerical understanding but also refine dexterity and precision. These engaging tasks help children grasp foundational math concepts such as counting, pattern recognition, and basic arithmetic in an enjoyable manner. Opportunities to manipulate objects physically can make abstract math ideas more concrete and relatable.
Additionally, mastering these skills early on sets a critical groundwork for more complex tasks in the future. Children who are proficient in fine motor skills and early math are better prepared for more intricate handwriting, problem-solving, and spatial reasoning tasks. Consequently, nurturing these abilities can foster a smoother transition to higher-level academic challenges and everyday practical tasks, laying the groundwork for lifelong learning and success.