Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 100 Misc Worksheets for Ages 5-8
5 filtered results
-
From - To
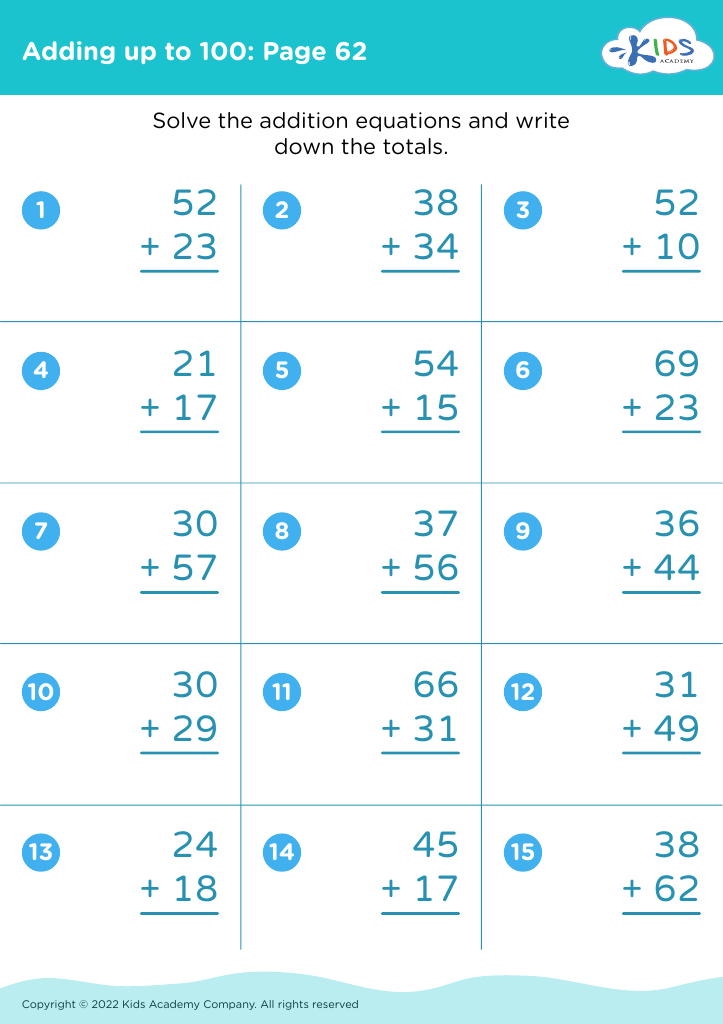
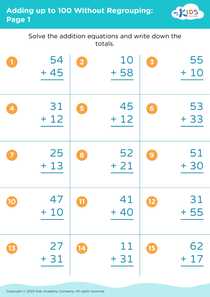
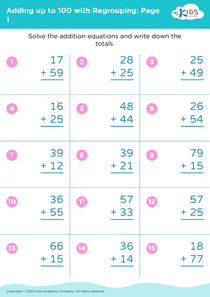
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our comprehensive collection of 100 worksheets designed for ages 5 to 8. These engaging activities blend fun and learning, helping young learners develop essential hand-eye coordination through various tasks, including tracing, cutting, and coloring. Each worksheet is crafted to support fine motor development while incorporating math skills, such as addition and number recognition, all focused on reaching the milestone of adding up to 100. Perfect for classrooms or at-home practice, these worksheets not only promote dexterity but also confidence in foundational math skills. Discover the joy of learning through play with Kids Academy!
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 5-8 as they are foundational for numerous everyday activities and lifelong learning. These skills involve the coordination of small muscle movements, particularly in the hands and fingers. Teachers and parents should prioritize these skills because they directly affect a child’s ability to perform tasks such as writing, drawing, cutting, and buttoning clothes. As students learn to engage their fine motor skills, they also enhance their academic performance and confidence, particularly in subjects like art and writing.
Furthermore, children who struggle with fine motor skills may experience frustration and a lack of motivation in school settings, potentially leading to learning delays. By providing activities that support the development of fine motor skills—such as playing with building blocks, using scissors, or engaging in arts and crafts—parents and educators can help children reach important developmental milestones.
Additionally, fine motor development is linked to cognitive skills, relaxation, and emotional expression, making it essential for holistic growth. By caring about fine motor skills, adults ensure children are equipped with the necessary tools to thrive both academically and socially. This foundational development sets the stage for future success in more complex tasks requiring dexterity and coordination.